Trichoderma virens Gl006 and Bacillus velezensis Bs006: a compatible interaction controlling Fusarium wilt of cape gooseberry
- PMID: 32321998
- PMCID: PMC7176702
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-63689-y
Trichoderma virens Gl006 and Bacillus velezensis Bs006: a compatible interaction controlling Fusarium wilt of cape gooseberry
Abstract
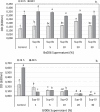
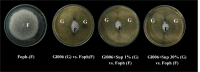
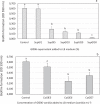
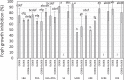
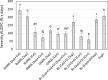
The combination of Trichoderma virens Gl006 and B. velezensis Bs006 as a consortium has high potential to control Fusarium wilt (FW) of cape gooseberry (Physalis peruviana) caused by Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. physali (Foph). However, the interactions between these two microorganisms that influence the biocontrol activity as a consortium have not been studied. Here, we studied the interactions between Gl006 and Bs006 that keep their compatibility under in vitro and greenhouse conditions. Antagonism tests between Gl006 and Bs006 inoculated both individually and in consortium against Foph strain Map5 was carried out on several solid media. The effect of supernatant of each selected microorganism on growth, conidia germination, biofilm formation and antagonistic activity on its partner was also studied. Biocontrol activity by different combinations of cells and supernatants from both microorganisms against Fusarium wilt was evaluated under greenhouse conditions. In vitro antagonism of the consortium against Foph showed a differential response among culture media and showed compatibility among BCA under nutritional conditions close to those of the rhizosphere. The supernatant of Bs006 did not affect the antagonistic activity of Gl006 and vice versa. However, the supernatant of Bs006 promoted the biocontrol activity of Gl006 in a synergistic way under greenhouse, reducing the disease severity by 71%. These results prove the compatibility between T. virens Gl006 and B. velezensis Bs006 as a potential tool to control Fusarium wilt of cape gooseberry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of Fengycins and Iturins on Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. physali and Root Colonization by Bacillus velezensis Bs006 Protect Golden Berry Against Vascular Wilt.Phytopathology. 2021 Dec;111(12):2227-2237. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-01-21-0001-R. Epub 2021 Nov 29. Phytopathology. 2021. PMID: 34032523
-
Controlling Fusarium wilt of cape gooseberry by microbial consortia.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2023 Jul 3;76(7):ovad072. doi: 10.1093/lambio/ovad072. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37348479
-
Physiological Response of Cape Gooseberry Seedlings to Three Biological Control Agents Under Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. physali Infection.Plant Dis. 2020 Feb;104(2):388-397. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-03-19-0466-RE. Epub 2019 Dec 6. Plant Dis. 2020. PMID: 31809256
-
Biosynthesis of Cyclic Lipopeptides by Bacillus velezensis Bs006 and its Antagonistic Activity are Modulated by the Temperature and Culture Media Conditions.Curr Microbiol. 2021 Sep;78(9):3505-3515. doi: 10.1007/s00284-021-02612-8. Epub 2021 Jul 22. Curr Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34292378
-
Combating Fusarium Infection Using Bacillus-Based Antimicrobials.Microorganisms. 2017 Nov 22;5(4):75. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms5040075. Microorganisms. 2017. PMID: 29165349 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Trichoderma Species: Our Best Fungal Allies in the Biocontrol of Plant Diseases-A Review.Plants (Basel). 2023 Jan 17;12(3):432. doi: 10.3390/plants12030432. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36771517 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coculture of Trichoderma harzianum and Bacillus velezensis Based on Metabolic Cross-Feeding Modulates Lipopeptide Production.Microorganisms. 2022 May 20;10(5):1059. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10051059. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35630500 Free PMC article.
-
The fungal root endophyte Serendipita vermifera displays inter-kingdom synergistic beneficial effects with the microbiota in Arabidopsis thaliana and barley.ISME J. 2022 Mar;16(3):876-889. doi: 10.1038/s41396-021-01138-y. Epub 2021 Oct 22. ISME J. 2022. PMID: 34686763 Free PMC article.
-
Shifting Perspectives of Translational Research in Bio-Bactericides: Reviewing the Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Paradigm.Biology (Basel). 2021 Nov 18;10(11):1202. doi: 10.3390/biology10111202. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34827195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacterial-fungal interactions under agricultural settings: from physical to chemical interactions.Stress Biol. 2022 Jun 1;2(1):22. doi: 10.1007/s44154-022-00046-1. Stress Biol. 2022. PMID: 37676347 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Moreno-Velandia CM, Izquierdo-García. LF, Ongena M, Kloepper JW, Cotes AM. Soil sterilization, pathogen and antagonist concentration affect biological control of Fusarium wilt of cape gooseberry by Bacillus velezensis Bs006. Plant Soil. 2019;435:39–55. doi: 10.1007/s11104-018-3866-4. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

