Selective deficits in verbal working memory associated with a known genetic etiology: the neuropsychological profile of duchenne muscular dystrophy
- PMID: 11253841
- PMCID: PMC1931425
- DOI: 10.1017/s1355617701711058
Selective deficits in verbal working memory associated with a known genetic etiology: the neuropsychological profile of duchenne muscular dystrophy
Abstract
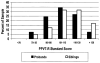
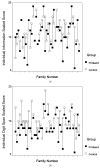
Forty-one boys diagnosed with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) were each compared to an unaffected sibling on a battery of neuropsychological tests. Verbal. visuospatial, attention/memory, abstract thinking, and academic achievement skills were tested. Results indicated the boys with DMD performed similarly to their siblings on the majority of measures, indicating intact verbal, visuospatial, long-term memory, and abstract skills. However, the DMD group did significantly more poorly than their siblings on specific measures of story recall, digit span, and auditory comprehension, as well as in all areas of academic achievement (reading, writing, and math). This profile indicates that verbal working memory skills are selectively impaired in DMD, and that that likely contributes to limited academic achievement. The association between the known impact of the genetic mutation on the development of the central nervous system and boys' cognitive profile is discussed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Poor verbal working memory across intellectual level in boys with Duchenne dystrophy.Neurology. 2000 Jun 13;54(11):2127-32. doi: 10.1212/wnl.54.11.2127. Neurology. 2000. PMID: 10851376 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropsychological profile of duchenne muscular dystrophy.Appl Neuropsychol Child. 2015;4(1):49-57. doi: 10.1080/21622965.2013.802649. Epub 2013 Nov 26. Appl Neuropsychol Child. 2015. PMID: 24279481
-
Verbal and memory skills in males with Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Dev Med Child Neurol. 2007 Feb;49(2):123-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.2007.00123.x. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2007. PMID: 17254000 Free PMC article.
-
Duchenne muscular dystrophy: a cerebellar disorder?Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2008;32(3):486-96. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2007.09.001. Epub 2007 Oct 4. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2008. PMID: 18022230 Review.
-
The neurobiology of duchenne muscular dystrophy: learning lessons from muscle?Trends Neurosci. 2000 Mar;23(3):92-9. doi: 10.1016/s0166-2236(99)01510-6. Trends Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 10675908 Review.
Cited by
-
Poor verbal working memory across intellectual level in boys with Duchenne dystrophy.Neurology. 2000 Jun 13;54(11):2127-32. doi: 10.1212/wnl.54.11.2127. Neurology. 2000. PMID: 10851376 Free PMC article.
-
Descriptive Phenotype of Obsessive Compulsive Symptoms in Males With Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy.J Child Neurol. 2018 Aug;33(9):572-579. doi: 10.1177/0883073818774439. Epub 2018 May 20. J Child Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29779439 Free PMC article.
-
Dystrophins, utrophins, and associated scaffolding complexes: role in mammalian brain and implications for therapeutic strategies.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010;2010:849426. doi: 10.1155/2010/849426. Epub 2010 Jun 17. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20625423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Age-associated sleep spindle characteristics in Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Sleep Adv. 2024 Mar 14;5(1):zpae015. doi: 10.1093/sleepadvances/zpae015. eCollection 2024. Sleep Adv. 2024. PMID: 38525359 Free PMC article.
-
Computational cognitive modeling and validation of Dp140 induced alteration of working memory in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 20;10(1):11989. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-68381-9. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32686699 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Achenbach TM. Manual for the Child Behavior Checklist/4-18 and 1991 Profile. Burlington, Vermont: University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry; 1991.
-
- Anderson SW, Routh DK, Ionasescu VV. Serial position memory of boys with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology. 1988;30:328–333. - PubMed
-
- Appleton RE, Bushby K, Gardner-Medwin D, Welch J, Kelly PJ. Head circumference and intellectual performance of patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology. 1991;33:884–890. - PubMed
-
- Baddeley AD. Working memory. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1986.
-
- Baddeley A, Gathercole S, Papagno C. The phonological loop as a language learning device. Psychological Review. 1998;105:158–173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
