PNPLA1-Mediated Acylceramide Biosynthesis and Autosomal Recessive Congenital Ichthyosis
- PMID: 35893253
- PMCID: PMC9332298
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo12080685
PNPLA1-Mediated Acylceramide Biosynthesis and Autosomal Recessive Congenital Ichthyosis
Abstract
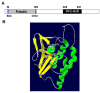
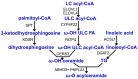
The stratum corneum of the epidermis acts as a life-sustaining permeability barrier. Unique heterogeneous ceramides, especially ω-O-acylceramides, are key components for the formation of stable lamellar membrane structures in the stratum corneum and are essential for a vital epidermal permeability barrier. Several enzymes involved in acylceramide synthesis have been demonstrated to be associated with ichthyosis. The function of patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 1 (PNPLA1) was a mystery until the finding that PNPLA1 gene mutations were involved in autosomal-recessive congenital ichthyosis (ARCI) patients, both humans and dogs. PNPLA1 plays an essential role in the biosynthesis of acylceramide as a CoA-independent transacylase. PNPLA1 gene mutations cause decreased acylceramide levels and impaired skin barrier function. More and more mutations in PNPLA1 genes have been identified in recent years. Herein, we describe the structural and functional specificity of PNPLA1, highlight its critical roles in acylceramide synthesis and skin barrier maintenance, and summarize the PNPLA1 mutations currently identified in ARCI patients.
Keywords: ARCI; PNPLA1; acylceramide; gene mutation; skin barrier.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of PNPLA1 in ω-O-acylceramide synthesis and skin barrier function.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2019 Jun;1864(6):869-879. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2018.09.010. Epub 2018 Oct 2. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2019. PMID: 30290227 Review.
-
PNPLA1 defects in patients with autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis and KO mice sustain PNPLA1 irreplaceable function in epidermal omega-O-acylceramide synthesis and skin permeability barrier.Hum Mol Genet. 2017 May 15;26(10):1787-1800. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddx079. Hum Mol Genet. 2017. PMID: 28369476
-
PNPLA1 has a crucial role in skin barrier function by directing acylceramide biosynthesis.Nat Commun. 2017 Mar 1;8:14609. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14609. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28248300 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired production of skin barrier lipid acylceramides and abnormal localization of PNPLA1 due to ichthyosis-causing mutations in PNPLA1.J Dermatol Sci. 2022 Aug;107(2):89-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2022.07.008. Epub 2022 Aug 4. J Dermatol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35970721
-
[Elucidation of the Synthetic Mechanism of Acylceramide, an Essential Lipid for Skin Barrier Function].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2017;137(10):1201-1208. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.17-00126. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2017. PMID: 28966260 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
ABHD5-A Regulator of Lipid Metabolism Essential for Diverse Cellular Functions.Metabolites. 2022 Oct 24;12(11):1015. doi: 10.3390/metabo12111015. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 36355098 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zimmer A.D., Kim G.J., Hotz A., Bourrat E., Hausser I., Has C., Oji V., Stieler K., Vahlquist A., Kunde V., et al. Sixteen novel mutations in PNPLA1 in patients with autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis reveal the importance of an extended patatin domain in PNPLA1 that is essential for proper human skin barrier function. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017;177:445–455. doi: 10.1111/bjd.15308. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

