Do imaging findings modify the effect of non-surgical treatment in patients with knee and hip osteoarthritis? A systematic literature review
- PMID: 36927583
- PMCID: PMC10030490
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-065373
Do imaging findings modify the effect of non-surgical treatment in patients with knee and hip osteoarthritis? A systematic literature review
Abstract
Objectives: To review the available evidence on diagnostic imaging findings in knee and hip osteoarthritis (OA) as treatment effect modifiers in non-surgical OA interventions.
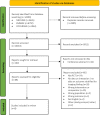
Methods: MEDLINE, Embase and The Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials were searched from the earliest records published to 22 March 2022. Studies in knee and hip OA reporting subgroup analyses in randomised controlled trials with imaging findings as potential treatment effect modifiers were included. Studies were critically appraised using the Cochrane risk of bias tool and a subgroup analysis quality assessment.
Results: Of 10 014 titles and abstracts screened, eight studies met the inclusion criteria, six on knee OA and two on hip OA. The studies investigated effect modifiers in exercise therapy, intra-articular injections and unloading shoes. Imaging findings assessed as potential treatment effect modifiers were radiographic OA severity, hip effusion (ultrasound), bone marrow lesions and meniscal pathology (MRI). Two studies fulfilled the methodological quality criteria for assessing effect modification. One reported that radiographic knee OA severity modified the effect of unloading shoes on walking pain. Those with more severe radiographic knee OA had a greater response to shoe inserts. One reported no interaction between radiographic OA severity or joint effusion and the effect of intraarticular injections of corticosteroid or hyaluronic acid in hip OA, indicating no difference in response in people with greater hip joint effusion or radiographic OA severity compared with those with less severe joint disease.
Conclusion: Overall, methodological limitations and very few studies do not permit conclusions on diagnostic imaging findings as effect modifiers in non-surgical interventions in knee and hip OA.Radiographic severity of knee OA potentially modifies the effect of unloading shoes.
Prospero registration number: CRD42020181934.
Keywords: diagnostic radiology; hip; knee; rheumatology.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intraarticular corticosteroid for treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006 Apr 19;(2):CD005328. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005328.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Oct 22;(10):CD005328. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005328.pub3. PMID: 16625636 Updated. Review.
-
Intra-articular viscosupplementation with hylan g-f 20 to treat osteoarthritis of the knee: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2005;5(10):1-66. Epub 2005 Jun 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2005. PMID: 23074461 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of placebo response to local (intra-articular) therapy in osteoarthritis: an individual patient data meta-analysis protocol.BMJ Open. 2019 May 24;9(5):e027372. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-027372. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 31129588 Free PMC article.
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise interventions and patient beliefs for people with hip, knee or hip and knee osteoarthritis: a mixed methods review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Apr 17;4(4):CD010842. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010842.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29664187 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous