Axatilimab for Chronic Graft-Versus-Host Disease After Failure of at Least Two Prior Systemic Therapies: Results of a Phase I/II Study
- PMID: 36459673
- PMCID: PMC10082302
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.22.00958
Axatilimab for Chronic Graft-Versus-Host Disease After Failure of at Least Two Prior Systemic Therapies: Results of a Phase I/II Study
Abstract
Purpose: Chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD) remains the major cause of late morbidity after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF-1R)-dependent macrophages promote cGVHD fibrosis, and their elimination in preclinical studies ameliorated cGVHD. Axatilimab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that inhibits CSF-1R signaling and restrains macrophage development.
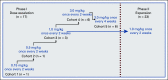
Patients and methods: This phase I (phI)/phase II (phII) open-label study (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03604692) evaluated safety, tolerability, and efficacy of axatilimab in patients age ≥ 6 years with active cGVHD after ≥ 2 prior systemic therapy lines. Primary objectives in phI were to identify the optimal biologic and recommended phII dose and in phII to evaluate the overall (complete and partial) response rate (ORR) at the start of treatment cycle 7.
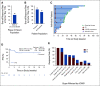
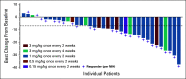
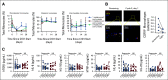
Results: Forty enrolled patients (17 phI; 23 phII) received at least one axatilimab dose. In phI, a dose of 3 mg/kg given once every 4 weeks met the optimal biologic dose definition. Two dose-limiting toxicities occurred at the 3 mg/kg dose given once every 2 weeks. At least one treatment-related adverse event (TRAE) was observed in 30 patients with grade ≥ 3 TRAEs in eight patients, the majority known on-target effects of CSF-1R inhibition. No cytomegalovirus reactivations occurred. With the 50% ORR at cycle 7 day 1, the phII cohort met the primary efficacy end point. Furthermore, the ORR in the first six cycles, an end point supporting regulatory approvals, was 82%. Responses were seen in all affected organs regardless of prior therapy. Fifty-eight percent of patients reported significant improvement in cGVHD-related symptoms using the Lee Symptom Scale. On-target activity of axatilimab was suggested by the decrease in skin CSF-1R-expressing macrophages.
Conclusion: Targeting profibrotic macrophages with axatilimab is a therapeutically promising novel strategy with a favorable safety profile for refractory cGVHD.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Axatilimab in Recurrent or Refractory Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease.N Engl J Med. 2024 Sep 19;391(11):1002-1014. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2401537. N Engl J Med. 2024. PMID: 39292927 Clinical Trial.
-
A phase II study of belumosudil for chronic graft-versus-host disease in patients who failed at least one line of systemic therapy in China.BMC Med. 2024 Mar 26;22(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s12916-024-03348-5. BMC Med. 2024. PMID: 38532458 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
IL6-receptor antibody tocilizumab as salvage therapy in severe chronic graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a retrospective analysis.Ann Hematol. 2020 Apr;99(4):847-853. doi: 10.1007/s00277-020-03968-w. Epub 2020 Feb 21. Ann Hematol. 2020. PMID: 32086584 Free PMC article.
-
A critical review of belumosudil in adult and pediatric patients with chronic graft-versus-host disease.Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2023 Mar;19(3):241-251. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2023.2152330. Epub 2022 Nov 30. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36440483 Review.
-
Perspectives on oral chronic graft-versus-host disease from immunobiology to morbid diagnoses.Front Immunol. 2023 Jun 28;14:1151493. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1151493. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37449200 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological treatment in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: current issues and future perspectives.Multidiscip Respir Med. 2024 Jun 13;19(1):982. doi: 10.5826/mrm.2024.982. Multidiscip Respir Med. 2024. PMID: 38869027 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the CSF1/CSF1R signaling pathway: an innovative strategy for ultrasound combined with macrophage exhaustion in pancreatic cancer therapy.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 2;15:1481247. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1481247. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39416792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pulmonary GvHD: is it time to change the NIH diagnostic criteria?Clin Hematol Int. 2024 Oct 19;6(4):69-73. doi: 10.46989/001c.124551. eCollection 2024. Clin Hematol Int. 2024. PMID: 39440225 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Chronic graft-versus-host disease: unresolved complication or ancient history?Blood. 2024 Sep 26;144(13):1363-1373. doi: 10.1182/blood.2023022735. Blood. 2024. PMID: 39008818 Review.
-
Separation of GVL from GVHD -location, location, location.Front Immunol. 2023 Dec 5;14:1296663. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1296663. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38116007 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

