Drug-Induced Liver Injury From Sacubitril-Valsartan Versus a Single Dose of Acarbose
- PMID: 35989811
- PMCID: PMC9386752
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.27005
Drug-Induced Liver Injury From Sacubitril-Valsartan Versus a Single Dose of Acarbose
Abstract
Numerous known medications can induce liver injury. Sacubitril-valsartan was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2015 for use in patients with chronic heart failure to reduce the rate of cardiovascular death and hospitalizations related to heart failure. There are yet to be any reported cases of drug-induced liver injury secondary to sacubitril-valsartan use. Acarbose is well known to be associated with liver failure, but typically liver injury occurs months after initiation of therapy. Here, we report the case of a 76-year-old woman who developed acute liver failure after one month of sacubitril-valsartan use and one day after being prescribed acarbose.
Keywords: acarbose; acute liver failure (alf); drug-induced acute liver failure; drug-induced liver injury (dili); entrestro; sacubitril-valsartan.
Copyright © 2022, Achuthanandan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
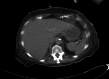
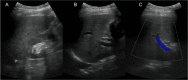
Similar articles
-
Approaches to management of rhabdomyolysis as the adverse effect of drug interaction between atorvastatin and sacubitril/valsartan: a case report.Eur Heart J Case Rep. 2022 Feb 22;6(3):ytac091. doi: 10.1093/ehjcr/ytac091. eCollection 2022 Mar. Eur Heart J Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35261962 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin-Neprilysin Inhibition in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction.N Engl J Med. 2019 Oct 24;381(17):1609-1620. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1908655. Epub 2019 Sep 1. N Engl J Med. 2019. PMID: 31475794 Clinical Trial.
-
Sacubitril/Valsartan Initiation Among Veterans Who Are Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Inhibitor Naïve With Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction.J Am Heart Assoc. 2021 Oct 19;10(20):e020474. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.020474. Epub 2021 Oct 6. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021. PMID: 34612065 Free PMC article.
-
The safety of sacubitril-valsartan for the treatment of chronic heart failure.Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2017 Feb;16(2):257-263. doi: 10.1080/14740338.2017.1279144. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2017. PMID: 28060547 Review.
-
Neprilysin inhibition with sacubitril/valsartan in the treatment of heart failure: mortality bang for your buck.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2016 Apr;41(2):119-27. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.12363. Epub 2016 Mar 18. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2016. PMID: 26992459 Review.
References
-
- Drug-induced liver disease. Zimmerman HJ. Clin Liver Dis. 2000;4:73-96, vi. - PubMed
-
- Hepatotoxicity of commonly used drugs: nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antihypertensives, antidiabetic agents, anticonvulsants, lipid-lowering agents, psychotropic drugs. Chitturi S, George J. Semin Liver Dis. 2002;22:169–183. - PubMed
-
- [Acute hepatitis induced by valsartan] Reñé JM, Buenestado J, Sesé E, Miñana JM. Med Clin (Barc) 2001;117:637–638. - PubMed
-
- Review article: drug hepatotoxicity. Chang CY, Schiano TD. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2007;25:1135–1151. - PubMed
-
- Acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure: results of a United States multicenter, prospective study. Larson AM, Polson J, Fontana RJ, et al. Hepatology. 2005;42:1364–1372. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
