Ribosome collisions induce mRNA cleavage and ribosome rescue in bacteria
- PMID: 35264790
- PMCID: PMC8934283
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-04416-7
Ribosome collisions induce mRNA cleavage and ribosome rescue in bacteria
Abstract
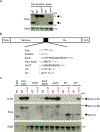
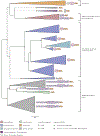
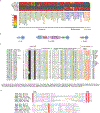
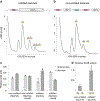
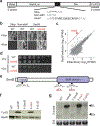
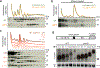
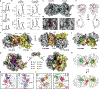
Ribosome rescue pathways recycle stalled ribosomes and target problematic mRNAs and aborted proteins for degradation1,2. In bacteria, it remains unclear how rescue pathways distinguish ribosomes stalled in the middle of a transcript from actively translating ribosomes3-6. Here, using a genetic screen in Escherichia coli, we discovered a new rescue factor that has endonuclease activity. SmrB cleaves mRNAs upstream of stalled ribosomes, allowing the ribosome rescue factor tmRNA (which acts on truncated mRNAs3) to rescue upstream ribosomes. SmrB is recruited to ribosomes and is activated by collisions. Cryo-electron microscopy structures of collided disomes from E. coli and Bacillus subtilis show distinct and conserved arrangements of individual ribosomes and the composite SmrB-binding site. These findings reveal the underlying mechanisms by which ribosome collisions trigger ribosome rescue in bacteria.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures








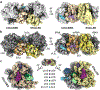
Comment in
-
Ribosome collisions: New ways to initiate ribosome rescue.Curr Biol. 2022 May 23;32(10):R469-R472. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2022.04.038. Curr Biol. 2022. PMID: 35609545 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
B. subtilis MutS2 splits stalled ribosomes into subunits without mRNA cleavage.EMBO J. 2024 Feb;43(4):484-506. doi: 10.1038/s44318-023-00010-3. Epub 2023 Dec 14. EMBO J. 2024. PMID: 38177497 Free PMC article.
-
B. subtilis MutS2 splits stalled ribosomes into subunits without mRNA cleavage.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 May 6:2023.05.05.539626. doi: 10.1101/2023.05.05.539626. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: EMBO J. 2024 Feb;43(4):484-506. doi: 10.1038/s44318-023-00010-3. PMID: 37205477 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
tmRNA regulates synthesis of the ArfA ribosome rescue factor.Mol Microbiol. 2011 Jun;80(5):1204-19. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07638.x. Epub 2011 Mar 30. Mol Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21435036 Free PMC article.
-
Dial tm for rescue: tmRNA engages ribosomes stalled on defective mRNAs.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2004 Feb;14(1):58-65. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2004.01.010. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2004. PMID: 15102450 Review.
-
Emerging views on tmRNA-mediated protein tagging and ribosome rescue.Mol Microbiol. 2001 Nov;42(4):879-85. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02701.x. Mol Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11737633 Review.
Cited by
-
Expansion of the MutS Gene Family in Plants.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 20:2024.07.17.603841. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.17.603841. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Plant Cell. 2024 Dec 18:koae277. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koae277. PMID: 39071318 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Gut colonization by Bacteroides requires translation by an EF-G paralog lacking GTPase activity.EMBO J. 2023 Jan 16;42(2):e112372. doi: 10.15252/embj.2022112372. Epub 2022 Dec 6. EMBO J. 2023. PMID: 36472247 Free PMC article.
-
Posttranscriptional Regulation by Copper with a New Upstream Open Reading Frame.mBio. 2022 Aug 30;13(4):e0091222. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00912-22. Epub 2022 Jul 13. mBio. 2022. PMID: 35862763 Free PMC article.
-
Recognition of an Ala-rich C-degron by the E3 ligase Pirh2.Nat Commun. 2023 Apr 29;14(1):2474. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-38173-6. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37120596 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosome profiling reveals downregulation of UMP biosynthesis as the major early response to phage infection.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Apr 2;12(4):e0398923. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03989-23. Epub 2024 Mar 7. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38451091 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Keiler KC, Waller PR & Sauer RT Role of a peptide tagging system in degradation of proteins synthesized from damaged messenger RNA. Science 271, 990–993 (1996). - PubMed
-
- Ivanova N, Pavlov MY, Felden B & Ehrenberg M Ribosome rescue by tmRNA requires truncated mRNAs. J. Mol. Biol. 338, 33–41 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Hayes CS & Sauer RT Cleavage of the A site mRNA codon during ribosome pausing provides a mechanism for translational quality control. Mol. Cell 12, 903–911 (2003). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

