The effect of librarian involvement on the quality of systematic reviews in dental medicine
- PMID: 34469487
- PMCID: PMC8409615
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0256833
The effect of librarian involvement on the quality of systematic reviews in dental medicine
Abstract
Objectives: To determine whether librarian or information specialist authorship is associated with better reproducibility of the search, at least three databases searched, and better reporting quality in dental systematic reviews (SRs).
Methods: SRs from the top ten dental research journals (as determined by Journal Citation Reports and Scimago) were reviewed for search quality and reproducibility by independent reviewers using two Qualtrics survey instruments. Data was reviewed for all SRs based on reproducibility and librarian participation and further reviewed for search quality of reproducible searches.
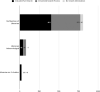
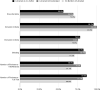
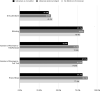
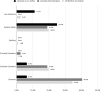
Results: Librarians were co-authors in only 2.5% of the 913 included SRs and librarians were mentioned or acknowledged in only 9% of included SRs. Librarian coauthors were associated with more reproducible searches, higher search quality, and at least three databases searched. Although the results indicate librarians are associated with improved SR quality, due to the small number of SRs that included a librarian, results were not statistically significant.
Conclusion: Despite guidance from organizations that produce SR guidelines recommending the inclusion of a librarian or information specialist on the review team, and despite evidence showing that librarians improve the reproducibility of searches and the reporting of methodology in SRs, librarians are not being included in SRs in the field of dental medicine. The authors of this review recommend the inclusion of a librarian on SR teams in dental medicine and other fields.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Librarian co-authors correlated with higher quality reported search strategies in general internal medicine systematic reviews.J Clin Epidemiol. 2015 Jun;68(6):617-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2014.11.025. Epub 2015 Feb 7. J Clin Epidemiol. 2015. PMID: 25766056
-
Librarian involvement in systematic reviews was associated with higher quality of reported search methods: a cross-sectional survey.J Clin Epidemiol. 2024 Feb;166:111237. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2023.111237. Epub 2023 Dec 8. J Clin Epidemiol. 2024. PMID: 38072177
-
Effect of librarian collaboration on otolaryngology systematic review and meta-analysis quality.J Med Libr Assoc. 2024 Jul 1;112(3):261-274. doi: 10.5195/jmla.2024.1774. Epub 2024 Jul 29. J Med Libr Assoc. 2024. PMID: 39308914 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating clinical librarian services: a systematic review.Health Info Libr J. 2011 Mar;28(1):3-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-1842.2010.00925.x. Epub 2010 Dec 27. Health Info Libr J. 2011. PMID: 21314890 Review.
-
New activities and changing roles of health sciences librarians: a systematic review, 1990-2012.J Med Libr Assoc. 2013 Oct;101(4):268-77. doi: 10.3163/1536-5050.101.4.008. J Med Libr Assoc. 2013. PMID: 24163598 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inclusion of librarians and information professionals in Canadian knowledge synthesis grant funding.J Can Health Libr Assoc. 2024 Apr 1;45(1):3-15. doi: 10.29173/jchla29701. eCollection 2024 Apr. J Can Health Libr Assoc. 2024. PMID: 38737780 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid evidence synthesis to enable innovation and adoption in health and social care.Syst Rev. 2022 Nov 23;11(1):250. doi: 10.1186/s13643-022-02106-z. Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36419199 Free PMC article.
-
Critical appraisal of systematic reviews of intervention studies in periodontology using AMSTAR 2 and ROBIS tools.J Clin Exp Dent. 2023 Aug 1;15(8):e678-e694. doi: 10.4317/jced.60197. eCollection 2023 Aug. J Clin Exp Dent. 2023. PMID: 37674600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Designing a framework for curriculum building in systematic review competencies for librarians: a case report.J Med Libr Assoc. 2024 Oct 1;112(4):357-363. doi: 10.5195/jmla.2024.1930. Epub 2024 Oct 7. J Med Libr Assoc. 2024. PMID: 39429500 Free PMC article.
-
Large-scale systematic review support for guideline development in diabetes precision medicine.J Med Libr Assoc. 2024 Jul 1;112(3):275-280. doi: 10.5195/jmla.2024.1863. Epub 2024 Jul 29. J Med Libr Assoc. 2024. PMID: 39308915 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Faggion CM Jr, Huivin R, Aranda L, Pandis N, Alarcon M. The search and selection for primary studies in systematic reviews published in dental journals indexed in MEDLINE was not fully reproducible. Journal of clinical epidemiology. 2018Jun1;98:53–61. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2018.02.011 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

