Prognostic value of FGFR1 expression and amplification in patients with HNSCC: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 33989301
- PMCID: PMC8121309
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0251202
Prognostic value of FGFR1 expression and amplification in patients with HNSCC: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
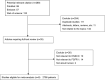
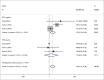
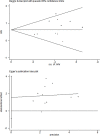
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1) has recently been identified as a promising novel therapeutic target and prognostic marker in different types of cancer. In the present study, a meta-analysis was performed to clarify the correlation between FGFR1 and the survival outcomes of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) patients. PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science were systematically searched for relevant studies in order to explore the prognostic significance of FGFR1 in HNSCC. Hazards ratios (HR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were collected to estimate the correlation between overexpression and amplification of FGFR1 and survival outcomes of HNSCC patients. Nine studies including 2708 patients with HNSCC were finally selected for the meta-analysis. The results indicated that FGFR1 predicted poor overall survival (OS) (HR, 1.97; 95% CI, 1.49-2.61, P<0.001) in HNSCC patients. Futhermore, FGFR1 was related to poor OS in human papillomavirus (HPV) negative HNSCC not in HPV positive HNSCC patients. Subgroup analysis stratified by molecular abnormalities, such as overexpression or amplification showed the similar results. The present study demonstrated that HNSCC patients with FGFR1 overexpression and amplification were more likely to exhibit poorer survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
FGFR1 Is a Potential Prognostic Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Aug 1;22(15):3884-93. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-1874. Epub 2016 Mar 2. Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26936917
-
Comprehensive genomic profiling of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma reveals FGFR1 amplifications and tumour genomic alterations burden as prognostic biomarkers of survival.Eur J Cancer. 2018 Mar;91:47-55. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2017.12.016. Epub 2018 Jan 11. Eur J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29331751
-
Prognostic implications of Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1) gene amplification and protein overexpression in hypopharyngeal and laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2020 Apr 18;20(1):348. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-06792-7. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32326908 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Family Members as Prognostic Biomarkers in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review.Target Oncol. 2016 Feb;11(1):17-27. doi: 10.1007/s11523-015-0374-9. Target Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26115874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic value of epithelial-mesenchymal transition-inducing transcription factors in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A meta-analysis.Head Neck. 2020 May;42(5):1067-1076. doi: 10.1002/hed.26104. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Head Neck. 2020. PMID: 32048783 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression and clinical significance of FGFR1 and FGFR2 in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma.Transl Cancer Res. 2022 Sep;11(9):3222-3234. doi: 10.21037/tcr-22-1936. Transl Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36237262 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of chromosome 8p11.2 translocations and correlation with myeloid and lymphoid neoplasms associated with FGFR1 abnormalities in a consecutive cohort from nine institutions in Japan.Int J Hematol. 2024 Jun;119(6):722-727. doi: 10.1007/s12185-024-03740-0. Epub 2024 Mar 8. Int J Hematol. 2024. PMID: 38457113 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol and Head and Neck Cancer: Updates on the Role of Oxidative Stress, Genetic, Epigenetics, Oral Microbiota, Antioxidants, and Alkylating Agents.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jan 11;11(1):145. doi: 10.3390/antiox11010145. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35052649 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomarkers in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: unraveling the path to precision immunotherapy.Front Oncol. 2024 Oct 8;14:1473706. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1473706. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39439946 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

