Practical Considerations for Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory FLT3-ITD Acute Myeloid Leukaemia with Quizartinib: Illustrative Case Reports
- PMID: 31912423
- PMCID: PMC7035240
- DOI: 10.1007/s40261-019-00881-7
Practical Considerations for Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory FLT3-ITD Acute Myeloid Leukaemia with Quizartinib: Illustrative Case Reports
Abstract
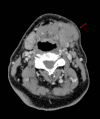
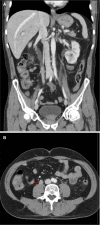
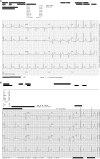
Quizartinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor selectively targeting the FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3) receptor that has been developed for the treatment of acute myeloid leukaemia (AML). The Phase 3 QuANTUM-R study investigated the efficacy of quizartinib monotherapy in patients with relapsed/refractory FLT3-ITD mutation-positive AML. The clinical course of four QuANTUM-R participants exemplifies issues specific to quizartinib treatment and is described here. Patient 1 was FLT3-ITD mutation-negative at AML diagnosis, but became FLT3-ITD mutation-positive during treatment that included several lines of chemotherapy and was therefore a suitable candidate for quizartinib. Because of the clonal shifts of AML during treatment, retesting genetic alterations at each relapse or resistance may help to identify candidates for targeted treatment options. Patient 2 developed QTc prolongation during quizartinib treatment, but the QTc interval normalised after dose reduction, allowing the patient to continue treatment and eventually resume the recommended dose. Patient 3 responded to quizartinib and was scheduled for haematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT), but developed febrile neutropenia and invasive aspergillosis during conditioning and subsequently died (to avoid drug-drug interactions, no azole antifungal was administered concomitantly). Care is required when selecting concomitant medications, and if there is potential for interactions (e.g. if prophylactic azole antifungals are required) the quizartinib dose should be reduced to minimise the risk of QTc prolongation. Patient 4 was able to undergo HSCT after responding to quizartinib and experienced a durable response after HSCT while on quizartinib maintenance therapy. Together, these cases illustrate the main issues to be addressed when managing patients under quizartinib, allowing for adequate scheduling and tolerability, bridging to HSCT, and durable remission on maintenance therapy in some patients.
Conflict of interest statement
David Martínez-Cuadrón has acted in an advisory role for JazzPharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Teva and Daiichi Sankyo; has served on the Speakers’ Bureau of Pfizer, Janssen, Amgen and Gilead; and has received travel grants from JazzPharma, Novartis, Pfizer and Amgen. Pau Montesinos has provided consultations or acted in an advisory role for JazzPharma, Novartis, AbbVie, Celgene, Shire, Takeda, Daiichi Sankyo, Pfizer, Tolero and Agios; has served on the Speakers’ Bureau of Otsuka, Novartis, AbbVie, Celgene, Incyte, Daiichi Sankyo and Pfizer; has received research funding from Novartis, Janssen, Celgene, Daiichi Sankyo, Pfizer and Teva; and has received travel grants from Teva, Novartis, Celgene, Daiichi Sankyo and Amgen. Rebeca Rodríguez-Veiga has served on the Speakers’ Bureau of Teva, Pfizer, Janssen and Novartis; and has received travel grants from Sanofi and Daiichi Sankyo. All other co-authors: nothing to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quizartinib, an FLT3 inhibitor, as monotherapy in patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukaemia: an open-label, multicentre, single-arm, phase 2 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2018 Jul;19(7):889-903. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30240-7. Epub 2018 May 31. Lancet Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29859851 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Quizartinib versus salvage chemotherapy in relapsed or refractory FLT3-ITD acute myeloid leukaemia (QuANTUM-R): a multicentre, randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jul;20(7):984-997. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30150-0. Epub 2019 Jun 4. Lancet Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31175001 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical Outcomes in Patients with FLT3-ITD-Mutated Relapsed/Refractory Acute Myelogenous Leukemia Undergoing Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation after Quizartinib or Salvage Chemotherapy in the QuANTUM-R Trial.Transplant Cell Ther. 2021 Feb;27(2):153-162. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2020.09.036. Epub 2020 Oct 2. Transplant Cell Ther. 2021. PMID: 33017662
-
Quizartinib (AC220): a promising option for acute myeloid leukemia.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019 Apr 8;13:1117-1125. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S198950. eCollection 2019. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019. PMID: 31114157 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quizartinib for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020 Dec;21(17):2077-2090. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2020.1801637. Epub 2020 Aug 9. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32772726 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in targeted therapy for acute myeloid leukemia.Biomark Res. 2020 May 20;8:17. doi: 10.1186/s40364-020-00196-2. eCollection 2020. Biomark Res. 2020. PMID: 32477567 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mrozek K, Marcucci G, Paschka P, et al. Clinical relevance of mutations and gene-expression changes in adult acute myeloid leukemia with normal cytogenetics: are we ready for a prognostically prioritized molecular classification? Blood. 2007;109(2):431–448. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-06-001149. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

