Haploinsufficiency of A20 caused by a novel nonsense variant or entire deletion of TNFAIP3 is clinically distinct from Behçet's disease
- PMID: 31164164
- PMCID: PMC6549368
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-019-1928-5
Haploinsufficiency of A20 caused by a novel nonsense variant or entire deletion of TNFAIP3 is clinically distinct from Behçet's disease
Abstract
Background: Haploinsufficiency of A20 (HA20) is caused by loss-of-function TNFAIP3 variants. Phenotypic and genetic features of HA20 remain uncertain; therefore, the clinical distinction between HA20 and Behçet's disease (BD) requires clarification.
Methods: We have collected 12 Japanese BD-like families. Probands of these families were analyzed by whole exome sequencing (WES) and subsequent Sanger sequencing. Clinical features were compared between 54 HA20 patients (including previously reported and new cases) and 520 Japanese BD patients.
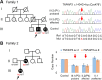
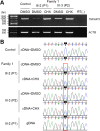
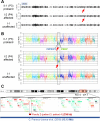
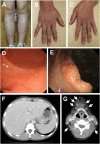
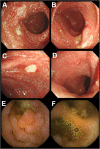
Results: We identified c.1434C>A:p.(Cys478*) in one family and a 236 kb deletion at 6q23.3 containing TNFAIP3 in another family. Four HA20 patients in the two families presented with childhood-onset recurrent oral and genital ulcers and were initially diagnosed and treated as BD. Consistent with the clinical features of HA20, recurrent, refractory fever attacks (three of four patients), and digestive ulcers (two of the four patients) were observed. A comparison of clinical features between HA20 patients and cohorts of BD patients revealed several critical features specific to HA20. These were early-onset, familial occurrence, recurrent fever attacks, gastrointestinal involvement, and infrequent ocular involvement.
Conclusions: We identified a novel nonsense variant and deletion of the entire TNFAIP3 gene in two unrelated Japanese HA20 families. Genetic screening of TNFAIP3 should be considered for familial BD-like patients with early-onset recurrent fevers.
Keywords: Autoinflammatory; Behçet’s disease; Haploinsufficiency of A20; TNFAIP3; Whole exome sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A20 Haploinsufficiency in a Chinese Patient With Intestinal Behcet's Disease-Like Symptoms: A Case Report.Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 3;11:1414. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01414. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32719680 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Clinical Phenotypes in Haploinsufficiency A20 (HA20) With Disrupted Domains of A20.Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 23;11:574992. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.574992. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33101300 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autosomic dominant familial Behçet disease and haploinsufficiency A20: A review of the literature.Autoimmun Rev. 2018 Aug;17(8):809-815. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2018.02.012. Epub 2018 Jun 8. Autoimmun Rev. 2018. PMID: 29890348 Review.
-
Mutation analysis of the TNFAIP3 in A20 haploinsufficiency: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 May 21;100(20):e25954. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000025954. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 34011076 Free PMC article.
-
Case Report: A novel mutation in TNFAIP3 in a patient with type 1 diabetes mellitus and haploinsufficiency of A20.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 May 31;14:1131437. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1131437. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37324276 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pathogenesis of Behçet's Syndrome: Genetic, Environmental and Immunological Factors.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Oct 8;8:713052. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.713052. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34692721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel TNFAIP3 microdeletion in a girl with infantile-onset inflammatory bowel disease complicated by a severe perianal lesion.Hum Genome Var. 2021 Jan 14;8(1):1. doi: 10.1038/s41439-020-00128-4. Hum Genome Var. 2021. PMID: 33446651 Free PMC article.
-
Haploinsufficiency of A20 in a Chinese child caused by loss-of-function mutations in TNFAIP3: A case report and review of the literature.Front Pediatr. 2023 Jan 11;10:990008. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.990008. eCollection 2022. Front Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 36727002 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical characteristics and genetic analysis of A20 haploinsufficiency.Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2021 May 24;19(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s12969-021-00558-6. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2021. PMID: 34030699 Free PMC article.
-
Update on ocular manifestations of the main monogenic and polygenic autoinflammatory diseases.Front Ophthalmol (Lausanne). 2024 Feb 22;4:1337329. doi: 10.3389/fopht.2024.1337329. eCollection 2024. Front Ophthalmol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38984133 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- International Study Group for Behcet's Disease Criteria for diagnosis of Behcet’s disease. Lancet. 1990;335(8697):1078–1080. - PubMed
-
- Kirino Y, Bertsias G, Ishigatsubo Y, Mizuki N, Tugal-Tutkun I, Seyahi E, Ozyazgan Y, Sacli FS, Erer B, Inoko H, et al. Genome-wide association analysis identifies new susceptibility loci for Behcet’s disease and epistasis between HLA-B*51 and ERAP1. Nat Genet. 2013;45(2):202–207. doi: 10.1038/ng.2520. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- JP26713036/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science/International
- JP17H01539/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science/International
- JP16H05357/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science/International
- JP16H06254/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science/International
- JP17K10080/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

