Pharmacokinetics and in vitro/in vivo antitumor efficacy of aptamer-targeted Ecoflex® nanoparticles for docetaxel delivery in ovarian cancer
- PMID: 29416331
- PMCID: PMC5789074
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S152474
Pharmacokinetics and in vitro/in vivo antitumor efficacy of aptamer-targeted Ecoflex® nanoparticles for docetaxel delivery in ovarian cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Epithelixal ovarian cancer is the fourth cause of cancer death in developed countries with 77% of ovarian cancer cases diagnosed with regional or distant metastasis, with poor survival rates. Docetaxel (DTX) is a well-known anticancer agent, with clinically proven efficacy in several malignancies, including ovarian cancer. However, the adverse effects caused by the active ingredient or currently marketed formulations could even deprive the patient of the advantages of treatment. Therefore, in the current study, polymeric nanoparticles (NPs) equipped with aptamer molecules as targeting agents were proposed to minimize the adverse effects and enhance the antitumor efficacy through directing the drug cargo toward its site of action.
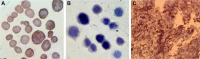
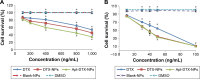
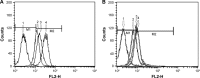
Materials and methods: Electrospraying technique was implemented to fabricate poly (butylene adipate-co-butylene terephthalate) (Ecoflex®) NPs loaded with DTX (DTX-NPs). Afterward, aptamer molecules were added to the DTX-NPs, which bound via covalent bonds (Apt-DTX-NPs). The particle size, size distribution, zeta potential, entrapment efficiency, and release profile of the NPs were characterized. Using MTT assay and flow-cytometry analysis, the in vitro cytotoxicity and cellular uptake of the NPs were compared to those of the free drug. Following intravenous administration of Taxotere®, DTX-NPs, and Apt-DTX-NPs (at an equivalent dose of 5 mg/kg of DTX), pharmacokinetic parameters and antitumor efficacy were compared in female Balb/c and HER-2-overexpressing tumor-bearing B6 athymic mice, respectively.
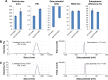
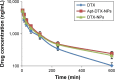
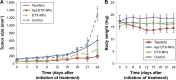
Results: The obtained results demonstrated significantly enhanced in vitro cytotoxicity and cellular uptake of Apt-DTX-NPs in a HER-2-overexpressing cell line, comparing to DTX-NPs and the free drug. The results of in vivo studies indicated significant increment in pharmacokinetic parameters including the area under the plasma concentration-time curve, mean residence time, and elimination half-life. Significant increment in antitumor efficacy was also observed, probably due to the targeted delivery of DTX to the tumor site and enhanced cellular uptake as evaluated in the aforementioned tests.
Conclusion: Hence, the proposed drug delivery system could be considered as an appropriate potential substitute for currently marketed DTX formulations.
Keywords: Ecoflex; aptamer; docetaxel; electrospraying; nanoparticles; ovarian cancer; pharmacokinetic.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Poly (butylene adipate-co-butylene terephthalate) nanoparticles prepared by electrospraying technique for docetaxel delivery in ovarian cancer induced mice.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2018 Jun;44(6):1012-1022. doi: 10.1080/03639045.2018.1430819. Epub 2018 Feb 2. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2018. PMID: 29347846
-
Aptamer-mediated delivery of docetaxel to prostate cancer through polymeric nanoparticles for enhancement of antitumor efficacy.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2016 Oct;107:130-41. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2016.07.007. Epub 2016 Jul 5. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2016. PMID: 27393562
-
Biodistribution, Safety and Organ Toxicity of Docetaxel-Loaded in HER-2 Aptamer Conjugated Ecoflex® Nanoparticles in a Mouse Xenograft Model of Ovarian Cancer.Recent Pat Nanotechnol. 2019;13(1):49-58. doi: 10.2174/1872210513666181128162403. Recent Pat Nanotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30488805
-
Advancements in the oral delivery of Docetaxel: challenges, current state-of-the-art and future trends.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Jun 8;13:3145-3161. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S164518. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 29922053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Local administration of large surface area microparticle docetaxel to solid carcinomas induces direct cytotoxicity and immune-mediated tumoricidal effects: preclinical and clinical studies.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2023 Feb;13(2):503-519. doi: 10.1007/s13346-022-01226-2. Epub 2022 Sep 4. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 36058988 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Aptamer-Enabled Nanomaterials for Therapeutics, Drug Targeting and Imaging.Cells. 2022 Jan 4;11(1):159. doi: 10.3390/cells11010159. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35011722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HER-2 aptamer-targeted Ecoflex® nanoparticles loaded with docetaxel promote breast cancer cells apoptosis and anti-metastatic effect.IET Nanobiotechnol. 2019 Jun;13(4):428-434. doi: 10.1049/iet-nbt.2018.5047. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31171748 Free PMC article.
-
Electrospraying: Possibilities and Challenges of Engineering Carriers for Biomedical Applications-A Mini Review.Front Chem. 2019 Apr 25;7:258. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00258. eCollection 2019. Front Chem. 2019. PMID: 31106194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aptamer Nanomaterials for Ovarian Cancer Target Theranostics.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Mar 28;10:884405. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.884405. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35419352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aptamers for the Delivery of Plant-Based Compounds: A Review.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Apr 14;16(4):541. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16040541. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38675202 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jayson GC, Kohn EC, Kitchener HC, Ledermann JA. Ovarian cancer. Lancet. 2014;384:1376–1388. - PubMed
-
- Kornblith AB, Thaler HT, Wong G, et al. Quality of life of women with ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 1995;59:231–242. - PubMed
-
- Bodurka-Bevers D, Basen-Engquist K, Carmack CL, et al. Depression, anxiety, and quality of life in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2000;78:302–308. - PubMed
-
- Wang L, Liu Z, Liu D, Liu C, Juan Z, Zhang N. Docetaxel-loaded-lipid-based-nanosuspensions (DTX-LNS): preparation, pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution and antitumor activity. Int J Pharm. 2011;413:194–201. - PubMed
-
- Naik S, Patel D, Surti N, Misra A. Preparation of PEGylated liposomes of docetaxel using supercritical fluid technology. J Supercrit Fluids. 2010;54:110–119.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

