Whole-Exome Sequencing Identifies a de novo AHDC1 Mutation in a Colombian Patient with Xia-Gibbs Syndrome
- PMID: 29230160
- PMCID: PMC5701272
- DOI: 10.1159/000479357
Whole-Exome Sequencing Identifies a de novo AHDC1 Mutation in a Colombian Patient with Xia-Gibbs Syndrome
Abstract
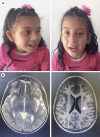
Xia-Gibbs syndrome is an autosomal dominant multisystem developmental disorder characterized by global developmental delay, hypotonia, obstructive sleep apnea, seizures, retrocerebellar cysts, delayed myelination, micrognathia, and mild dysmorphic features. Using whole-exome sequencing, we identified a de novo AHDC1 frameshift mutation c.2030_2030delG (p.G677Afs*52) in a Colombian patient, which was absent in both parents. Furthermore, we summarized the phenotypes of patients reported in the literature.
Keywords: AHDC1 mutation; Whole-exome sequencing; Xia-Gibbs syndrome.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Syndromic Intellectual Disability Caused by a Novel Truncating Variant in AHDC1: A Case Report.Iran J Med Sci. 2019 May;44(3):257-261. Iran J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31182893 Free PMC article.
-
Xia-Gibbs Syndrome: A Review of Literature.Cureus. 2020 Dec 29;12(12):e12352. doi: 10.7759/cureus.12352. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 33520547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two Chinese Xia-Gibbs syndrome patients with partial growth hormone deficiency.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019 Apr;7(4):e00596. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.596. Epub 2019 Feb 6. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019. PMID: 30729726 Free PMC article.
-
Microdeletion and microduplication of 1p36.11p35.3 involving AHDC1 contribute to neurodevelopmental disorder.Eur J Med Genet. 2020 Jan;63(1):103611. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2019.01.001. Epub 2019 Jan 4. Eur J Med Genet. 2020. PMID: 30615951
-
Genotype-phenotype spectrum and correlations in Xia-Gibbs syndrome: Report of five novel cases and literature review.Birth Defects Res. 2022 Aug 1;114(13):759-767. doi: 10.1002/bdr2.2058. Epub 2022 Jun 18. Birth Defects Res. 2022. PMID: 35716097 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Syndromic Intellectual Disability Caused by a Novel Truncating Variant in AHDC1: A Case Report.Iran J Med Sci. 2019 May;44(3):257-261. Iran J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31182893 Free PMC article.
-
AT-hook DNA-binding motif-containing protein one knockdown downregulates EWS-FLI1 transcriptional activity in Ewing's sarcoma cells.PLoS One. 2022 Oct 4;17(10):e0269077. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0269077. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36194562 Free PMC article.
-
Gibbin mesodermal regulation patterns epithelial development.Nature. 2022 Jun;606(7912):188-196. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04727-9. Epub 2022 May 18. Nature. 2022. PMID: 35585237 Free PMC article.
-
Xia-Gibbs Syndrome: A Review of Literature.Cureus. 2020 Dec 29;12(12):e12352. doi: 10.7759/cureus.12352. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 33520547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long read sequencing and expression studies of AHDC1 deletions in Xia-Gibbs syndrome reveal a novel genetic regulatory mechanism.Hum Mutat. 2022 Dec;43(12):2033-2053. doi: 10.1002/humu.24461. Epub 2022 Sep 24. Hum Mutat. 2022. PMID: 36054313 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ACMG Board of Directors Points to consider in the clinical application of genomic sequencing. Genet Med. 2012;14:759–761. - PubMed
-
- Calabrese R, Capriotti E, Fariselli P, Martelli P, Casadio R. Functional annotations improve the predictive score of human disease-related mutations in proteins. Hum Mutat. 2009;30:1237–1244. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

