RNA sequencing demonstrates large-scale temporal dysregulation of gene expression in stimulated macrophages derived from MHC-defined chicken haplotypes
- PMID: 28846708
- PMCID: PMC5573159
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179391
RNA sequencing demonstrates large-scale temporal dysregulation of gene expression in stimulated macrophages derived from MHC-defined chicken haplotypes
Abstract
Discovering genetic biomarkers associated with disease resistance and enhanced immunity is critical to developing advanced strategies for controlling viral and bacterial infections in different species. Macrophages, important cells of innate immunity, are directly involved in cellular interactions with pathogens, the release of cytokines activating other immune cells and antigen presentation to cells of the adaptive immune response. IFNγ is a potent activator of macrophages and increased production has been associated with disease resistance in several species. This study characterizes the molecular basis for dramatically different nitric oxide production and immune function between the B2 and the B19 haplotype chicken macrophages.A large-scale RNA sequencing approach was employed to sequence the RNA of purified macrophages from each haplotype group (B2 vs. B19) during differentiation and after stimulation. Our results demonstrate that a large number of genes exhibit divergent expression between B2 and B19 haplotype cells both prior and after stimulation. These differences in gene expression appear to be regulated by complex epigenetic mechanisms that need further investigation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
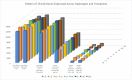

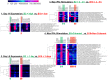
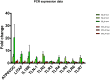
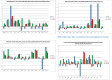

Similar articles
-
Dramatic differences in the response of macrophages from B2 and B19 MHC-defined haplotypes to interferon gamma and polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid stimulation.Poult Sci. 2014 Apr;93(4):830-8. doi: 10.3382/ps.2013-03511. Poult Sci. 2014. PMID: 24706959 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophages from disease resistant B2 haplotype chickens activate T lymphocytes more effectively than macrophages from disease susceptible B19 birds.Dev Comp Immunol. 2017 Feb;67:249-256. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2016.09.013. Epub 2016 Oct 14. Dev Comp Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27746172 Free PMC article.
-
Role of chicken melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 in induction and activation of innate and adaptive immune responses to infectious bursal disease virus in cultured macrophages.Arch Virol. 2015 Dec;160(12):3021-35. doi: 10.1007/s00705-015-2612-y. Epub 2015 Sep 21. Arch Virol. 2015. PMID: 26392283
-
The chicken TH1 response: potential therapeutic applications of ChIFN-γ.Dev Comp Immunol. 2013 Nov;41(3):389-96. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2013.05.009. Epub 2013 May 21. Dev Comp Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23707786 Review.
-
Immune responses against Marek's disease virus.Anim Health Res Rev. 2010 Dec;11(2):123-34. doi: 10.1017/S1466252310000022. Anim Health Res Rev. 2010. PMID: 21087575 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic variation in chicken interferon signalling pathway genes in research lines showing differential viral resistance.Anim Genet. 2022 Oct;53(5):640-656. doi: 10.1111/age.13233. Epub 2022 Jun 23. Anim Genet. 2022. PMID: 35739459 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shi K.Q.; Cai X.H.; Xiao D.D.; Wu S.J.; Peng M.M.; Lin X.F.; Liu W.Y.; Fan Y.C.; Chen Y.P.; Zheng M.H. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha-857T allele reduces the risk of hepatitis B virus infection in an Asian population. Journal of viral hepatitis. 2012. February;19(2):e66–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2011.01540.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ferro P.J.; Swaggerty C.L.; Kaiser P.; Pevzner I.Y.; Kogut M.H. Heterophils isolated from chickens resistant to extra-intestinal Salmonella enteritidis infection express higher levels of pro-inflammatory cytokine mRNA following infection than heterophils from susceptible chickens. Epidemiol Infect. 2004. December;132(6):1029–1037. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Swaggerty C.L.; Pevzner I.Y.; Kaiser P.; Kogut M.H. Profiling pro-inflammatory cytokine and chemokine mRNA expression levels as a novel method for selection of increased innate immune responsiveness. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2008. November 15;126(1–2):35–42. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2008.06.005 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yoo B.H.; Sheldon B.L. Association of the major histocompatibility complex with avian leukosis virus infection in chickens. Br Poult Sci. 1992. July;33(3):613–620. doi: 10.1080/00071669208417500 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

