Novel GNB1 missense mutation in a patient with generalized dystonia, hypotonia, and intellectual disability
- PMID: 27668284
- PMCID: PMC5022844
- DOI: 10.1212/NXG.0000000000000106
Novel GNB1 missense mutation in a patient with generalized dystonia, hypotonia, and intellectual disability
Abstract
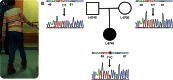
Recently, exome sequencing has extended our knowledge of genetic causes of developmental delay through identification of de novo, germline mutations in the guanine nucleotide-binding protein, beta 1 (GNB1) in 13 patients with neurodevelopmental disability and a wide range of additional symptoms and signs including hypotonia in 11 and seizures in 10 of the patients. Limb/arm dystonia was found in 2 patients.(1).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel GNB1 mutations disrupt assembly and function of G protein heterotrimers and cause global developmental delay in humans.Hum Mol Genet. 2017 Mar 15;26(6):1078-1086. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddx018. Hum Mol Genet. 2017. PMID: 28087732 Free PMC article.
-
Germline De Novo Mutations in GNB1 Cause Severe Neurodevelopmental Disability, Hypotonia, and Seizures.Am J Hum Genet. 2016 May 5;98(5):1001-1010. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.03.011. Epub 2016 Apr 21. Am J Hum Genet. 2016. PMID: 27108799 Free PMC article.
-
Novel GNB1 de novo mutation in a patient with neurodevelopmental disorder and cutaneous mastocytosis: Clinical report and literature review.Eur J Med Genet. 2018 Mar;61(3):157-160. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2017.11.010. Epub 2017 Nov 23. Eur J Med Genet. 2018. PMID: 29174093 Review.
-
Refining the phenotype associated with GNB1 mutations: Clinical data on 18 newly identified patients and review of the literature.Am J Med Genet A. 2018 Nov;176(11):2259-2275. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.40472. Epub 2018 Sep 8. Am J Med Genet A. 2018. PMID: 30194818 Review.
-
Exome sequencing identifies a de novo SCN2A mutation in a patient with intractable seizures, severe intellectual disability, optic atrophy, muscular hypotonia, and brain abnormalities.Epilepsia. 2014 Apr;55(4):e25-9. doi: 10.1111/epi.12554. Epub 2014 Mar 1. Epilepsia. 2014. PMID: 24579881 Review.
Cited by
-
Biallelic SHQ1 variants in early infantile hypotonia and paroxysmal dystonia as the leading manifestation.Hum Genet. 2023 Aug;142(8):1029-1041. doi: 10.1007/s00439-023-02533-5. Epub 2023 Feb 27. Hum Genet. 2023. PMID: 36847845
-
Three Blind Moles: Molecular Evolutionary Insights on the Tempo and Mode of Convergent Eye Degeneration in Notoryctes typhlops (Southern Marsupial Mole) and Two Chrysochlorids (Golden Moles).Genes (Basel). 2023 Oct 28;14(11):2018. doi: 10.3390/genes14112018. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38002961 Free PMC article.
-
Members of the KCTD family are major regulators of cAMP signaling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Jan 4;119(1):e2119237119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2119237119. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 34934014 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging and converging molecular mechanisms in dystonia.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2021 Apr;128(4):483-498. doi: 10.1007/s00702-020-02290-z. Epub 2021 Jan 1. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2021. PMID: 33386558 Review.
-
Novel GNB1 mutations disrupt assembly and function of G protein heterotrimers and cause global developmental delay in humans.Hum Mol Genet. 2017 Mar 15;26(6):1078-1086. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddx018. Hum Mol Genet. 2017. PMID: 28087732 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Domingo A, Erro R, Lohmann K. Novel dystonia genes: clues on disease mechanisms and the complexities of high-throughput sequencing. Mov Disord 2016;31:471–477. - PubMed
-
- Vissers LE, Gilissen C, Veltman JA. Genetic studies in intellectual disability and related disorders. Nat Rev Genet 2016;17:9–18. - PubMed
-
- Lambright DG, Sondek J, Bohm A, Skiba NP, Hamm HE, Sigler PB. The 2.0 A crystal structure of a heterotrimeric G protein. Nature 1996;379:311–319. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
