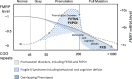
Fragile X spectrum disorders
- PMID: 25606363
- PMCID: PMC4298643
- DOI: 10.5582/irdr.2014.01022
Fragile X spectrum disorders
Abstract
The fragile X mental retardation 1 gene (FMR1), which codes for the fragile X mental retardation 1 protein (FMRP), is located at Xp27.3. The normal allele of the FMR1 gene typically has 5 to 40 CGG repeats in the 5' untranslated region; abnormal alleles of dynamic mutations include the full mutation (> 200 CGG repeats), premutation (55-200 CGG repeats) and the gray zone mutation (45-54 CGG repeats). Premutation carriers are common in the general population with approximately 1 in 130-250 females and 1 in 250-810 males, whereas the full mutation and Fragile X syndrome (FXS) occur in approximately 1 in 4000 to 1 in 7000. FMR1 mutations account for a variety of phenotypes including the most common monogenetic cause of inherited intellectual disability (ID) and autism (FXS), the most common genetic form of ovarian failure, the fragile X-associated primary ovarian insufficiency (FXPOI, premutation); and fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome (FXTAS, premutation). The premutation can also cause developmental problems including ASD and ADHD especially in boys and psychopathology including anxiety and depression in children and adults. Some premutation carriers can have a deficit of FMRP and some unmethylated full mutation individuals can have elevated FMR1 mRNA that is considered a premutation problem. Therefore the term "Fragile X Spectrum Disorder" (FXSD) should be used to include the wide range of overlapping phenotypes observed in affected individuals with FMR1 mutations. In this review we focus on the phenotypes and genotypes of children with FXSD.
Keywords: Fragile X syndrome; autism spectrum disorder; developmental delay; intellectual disability; premutation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Unstable mutations in the FMR1 gene and the phenotypes.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;769:78-114. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-5434-2_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 23560306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fragile X-Associated Neuropsychiatric Disorders (FXAND).Front Psychiatry. 2018 Nov 13;9:564. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00564. eCollection 2018. Front Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 30483160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fragile X syndrome and fragile X-associated tremor ataxia syndrome.Handb Clin Neurol. 2018;147:377-391. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-63233-3.00025-7. Handb Clin Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29325626 Review.
-
[FMR1 PREMUTATION CARRIERS - ARE THEY REALLY ASYMPTOMATIC?].Harefuah. 2018 Apr;157(4):241-244. Harefuah. 2018. PMID: 29688643 Review. Hebrew.
-
High functioning male with fragile X syndrome and fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome.Am J Med Genet A. 2015 Sep;167A(9):2154-61. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.37125. Epub 2015 Apr 29. Am J Med Genet A. 2015. PMID: 25920745
Cited by
-
The intersection of sleep and synaptic translation in synaptic plasticity deficits in neurodevelopmental disorders.J Comp Physiol B. 2024 Jun;194(3):253-263. doi: 10.1007/s00360-023-01531-3. Epub 2024 Feb 24. J Comp Physiol B. 2024. PMID: 38396062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Asparaginase treatment side-effects may be due to genes with homopolymeric Asn codons (Review-Hypothesis).Int J Mol Med. 2015 Sep;36(3):607-26. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2015.2285. Epub 2015 Jul 15. Int J Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 26178806 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lovastatin, not Simvastatin, Corrects Core Phenotypes in the Fragile X Mouse Model.eNeuro. 2019 Jun 12;6(3):ENEURO.0097-19.2019. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0097-19.2019. Print 2019 May/Jun. eNeuro. 2019. PMID: 31147392 Free PMC article.
-
Reducing histone acetylation rescues cognitive deficits in a mouse model of Fragile X syndrome.Nat Commun. 2018 Jun 27;9(1):2494. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04869-3. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29950602 Free PMC article.
-
Association between mutations in the FMR1 gene and ovarian dysfunction in Brazilian patients.JBRA Assist Reprod. 2022 Apr 17;26(2):237-240. doi: 10.5935/1518-0557.20210063. JBRA Assist Reprod. 2022. PMID: 34542254 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yrigollen CM, Martorell L, Durbin-Johnson B, Naudo M, Genoves J, Murgia A, Polli R, Zhou L, Barbouth D, Rupchock A, Finucane B, Latham GJ, Hadd A, Berry-Kravis E, Tassone F. AGG interruptions and maternal age affect FMR1 CGG repeat allele stability during transmission. J Neurodev Disord. 2014; 6:24. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Verkerk AJ, Pieretti M, Sutcliffe JS, et al. Identification of a gene (FMR-1) containing a CGG repeat coincident with a breakpoint cluster region exhibiting length variation in fragile X syndrome. Cell. 1991; 65:905-914. - PubMed
-
- Oberle I, Rousseau F, Heitz D, Kretz C, Devys D, Hanauer A, Boue J, Bertheas MF, Mandel JL. Instability of a 550-base pair DNA segment and abnormal methylation in fragile X syndrome. Science. 1991; 252:1097-1102. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources