Function of YY1 in Long-Distance DNA Interactions
- PMID: 24575094
- PMCID: PMC3918653
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00045
Function of YY1 in Long-Distance DNA Interactions
Abstract
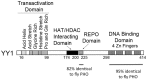
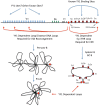
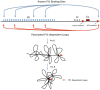
During B cell development, long-distance DNA interactions are needed for V(D)J somatic rearrangement of the immunoglobulin (Ig) loci to produce functional Ig genes, and for class switch recombination (CSR) needed for antibody maturation. The tissue-specificity and developmental timing of these mechanisms is a subject of active investigation. A small number of factors are implicated in controlling Ig locus long-distance interactions including Pax5, Yin Yang 1 (YY1), EZH2, IKAROS, CTCF, cohesin, and condensin proteins. Here we will focus on the role of YY1 in controlling these mechanisms. YY1 is a multifunctional transcription factor involved in transcriptional activation and repression, X chromosome inactivation, Polycomb Group (PcG) protein DNA recruitment, and recruitment of proteins required for epigenetic modifications (acetylation, deacetylation, methylation, ubiquitination, sumoylation, etc.). YY1 conditional knock-out indicated that YY1 is required for B cell development, at least in part, by controlling long-distance DNA interactions at the immunoglobulin heavy chain and Igκ loci. Our recent data show that YY1 is also required for CSR. The mechanisms implicated in YY1 control of long-distance DNA interactions include controlling non-coding antisense RNA transcripts, recruitment of PcG proteins to DNA, and interaction with complexes involved in long-distance DNA interactions including the cohesin and condensin complexes. Though common rearrangement mechanisms operate at all Ig loci, their distinct temporal activation along with the ubiquitous nature of YY1 poses challenges for determining the specific mechanisms of YY1 function in these processes, and their regulation at the tissue-specific and B cell stage-specific level. The large numbers of post-translational modifications that control YY1 functions are possible candidates for regulation.
Keywords: DNA loops; YY1; cohesin; condensin; immunoglobulin loci; polycomb.
Figures
Similar articles
-
YY1 controls Igκ repertoire and B-cell development, and localizes with condensin on the Igκ locus.EMBO J. 2013 Apr 17;32(8):1168-82. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2013.66. Epub 2013 Mar 26. EMBO J. 2013. PMID: 23531880 Free PMC article.
-
Polycomb Group Protein YY1 Is an Essential Regulator of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Quiescence.Cell Rep. 2018 Feb 6;22(6):1545-1559. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.01.026. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 29425509 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factor YY1 can control AID-mediated mutagenesis in mice.Eur J Immunol. 2018 Feb;48(2):273-282. doi: 10.1002/eji.201747065. Epub 2017 Nov 14. Eur J Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29080214 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic 3D Locus Organization and Its Drivers Underpin Immunoglobulin Recombination.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 18;11:633705. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.633705. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33679727 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spatial Regulation of V-(D)J Recombination at Antigen Receptor Loci.Adv Immunol. 2015;128:93-121. doi: 10.1016/bs.ai.2015.07.006. Epub 2015 Aug 13. Adv Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26477366 Review.
Cited by
-
Towards a predictive model of chromatin 3D organization.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2016 Sep;57:24-30. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2015.11.013. Epub 2015 Dec 3. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 26658098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IgH chain class switch recombination: mechanism and regulation.J Immunol. 2014 Dec 1;193(11):5370-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1401849. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25411432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Yin Yang 1 controls cerebellar astrocyte maturation.Glia. 2023 Oct;71(10):2437-2455. doi: 10.1002/glia.24434. Epub 2023 Jul 7. Glia. 2023. PMID: 37417428 Free PMC article.
-
YY1 binding association with sex-biased transcription revealed through X-linked transcript levels and allelic binding analyses.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 18;6:37324. doi: 10.1038/srep37324. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27857184 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental Switch in the Transcriptional Activity of a Long-Range Regulatory Element.Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Oct;35(19):3370-80. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00509-15. Epub 2015 Jul 20. Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26195822 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

