Symmetric polymicrogyria and pachygyria associated with TUBB2B gene mutations
- PMID: 22333901
- PMCID: PMC3421113
- DOI: 10.1038/ejhg.2012.21
Symmetric polymicrogyria and pachygyria associated with TUBB2B gene mutations
Abstract
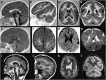
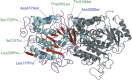
The purpose of the study is to explore the causative role of TUBB2B gene mutations in patients with different malformations of cortical development. We collected and evaluated clinical and MRI data of a cohort of 128 consecutive patients (61 females and 67 males) in whom brain MRI had detected a spectrum of malformations of cortical development including polymicrogyria or pachygyria, who were mutation-negative to other possible causative genes. Mutation analysis of the TUBB2B gene was performed. We identified three new TUBB2B mutations in three unrelated patients (3 out of 128; 2.3%) with a diffuse and rather symmetrical cortical abnormality, including diffuse polymicrogyria in two and bilateral regional pachygyria in one. One patient harbored a p.Asp417Asn amino-acid substitution in the C-terminal domain of the protein; one patient a p.Asn256Ser amino-acid substitution in the intermediate domain and one patient a p.Leu117Pro amino-acid substitution in the N-terminal domain. The localization of each mutation within the secondary structure of the β2-tubulin polypeptide suggests that these mutations might alter the proper functions of microtubules. The phenotypic spectrum associated with TUBB2B mutations is wider than previously reported and includes diffuse, symmetric malformations of cortical development.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An inherited TUBB2B mutation alters a kinesin-binding site and causes polymicrogyria, CFEOM and axon dysinnervation.Hum Mol Genet. 2012 Dec 15;21(26):5484-99. doi: 10.1093/hmg/dds393. Epub 2012 Sep 21. Hum Mol Genet. 2012. PMID: 23001566 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in the beta-tubulin gene TUBB2B result in asymmetrical polymicrogyria.Nat Genet. 2009 Jun;41(6):746-52. doi: 10.1038/ng.380. Epub 2009 May 24. Nat Genet. 2009. PMID: 19465910 Free PMC article.
-
Overlapping cortical malformations and mutations in TUBB2B and TUBA1A.Brain. 2013 Feb;136(Pt 2):536-48. doi: 10.1093/brain/aws338. Epub 2013 Jan 29. Brain. 2013. PMID: 23361065
-
[Epileptogenic brain malformations: radiological and clinical presentation and indications for genetic testing].Rev Neurol (Paris). 2008 Dec;164(12):995-1009. doi: 10.1016/j.neurol.2008.04.006. Epub 2008 Jun 9. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2008. PMID: 18808783 Review. French.
-
Tubulin genes and malformations of cortical development.Eur J Med Genet. 2018 Dec;61(12):744-754. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2018.07.012. Epub 2018 Jul 17. Eur J Med Genet. 2018. PMID: 30016746 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic Basis of Brain Malformations.Mol Syndromol. 2016 Sep;7(4):220-233. doi: 10.1159/000448639. Epub 2016 Aug 27. Mol Syndromol. 2016. PMID: 27781032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disorders of neurogenesis and cortical development.Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2018 Dec;20(4):255-266. doi: 10.31887/DCNS.2018.20.4/ccardoso. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30936766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mutations in tubulin genes are frequent causes of various foetal malformations of cortical development including microlissencephaly.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2014 Jul 25;2:69. doi: 10.1186/2051-5960-2-69. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2014. PMID: 25059107 Free PMC article.
-
Novel maternal duplication of 6p22.3-p25.3 with subtelomeric 6p25.3 deletion: new clinical findings and genotype-phenotype correlations.Mol Cytogenet. 2023 Jun 11;16(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s13039-023-00640-6. Mol Cytogenet. 2023. PMID: 37303060 Free PMC article.
-
An inherited TUBB2B mutation alters a kinesin-binding site and causes polymicrogyria, CFEOM and axon dysinnervation.Hum Mol Genet. 2012 Dec 15;21(26):5484-99. doi: 10.1093/hmg/dds393. Epub 2012 Sep 21. Hum Mol Genet. 2012. PMID: 23001566 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barkovich AJ, Kuzniecky RI, Jackson GD, Guerrini R, Dobyns WB. A developmental and genetic classification for malformations of cortical development. Neurology. 2005;65:1873–1887. - PubMed
-
- Guerrini R, Dobyns WB, Barkovich AJ. Abnormal development of the human cerebral cortex: genetics, functional consequences and treatment options. TrendsNeurosci. 2008;31:154–162. - PubMed
-
- Piao X, Hill RS, Bodell A, et al. G protein-coupled receptor-dependent development of human frontal cortex. Science. 2004;303:2033–2036. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

