Combinatorial regulation by MrpC2 and FruA involves three sites in the fmgE promoter region during Myxococcus xanthus development
- PMID: 21441502
- PMCID: PMC3133106
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00205-11
Combinatorial regulation by MrpC2 and FruA involves three sites in the fmgE promoter region during Myxococcus xanthus development
Abstract
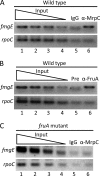
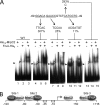
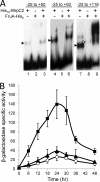
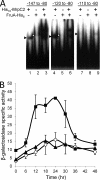
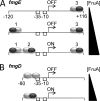
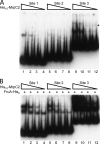
Starvation causes cells in a dense population of Myxococcus xanthus to change their gliding movements and construct mounds. Short-range C-signaling between rod-shaped cells within mounds induces gene expression that promotes differentiation into spherical spores. Several C-signal-dependent genes have been shown to be regulated by cooperative binding of two transcription factors to the promoter region. These FruA- and MrpC2-regulated genes (designated fmg) each exhibit a different arrangement of binding sites. Here, we describe fmgE, which appears to be regulated by three sites for cooperative binding of FruA and MrpC2. Chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis showed that association of MrpC2 and/or its longer form, MrpC with the fmgE promoter region, depends on FruA, consistent with cooperative binding of the two proteins in vivo. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays with purified His(10)-MrpC2 and FruA-His(6) indicated cooperative binding in vitro to three sites in the fmgE promoter region. The effects of mutations on binding in vitro and on expression of fmgE-lacZ fusions correlated site 1 (at about position -100 relative to the transcriptional start site) with negative regulation and site 2 (just upstream of the promoter) and site 3 (at about position +100) with positive regulation. Site 3 was bound by His(10)-MrpC2 alone, or the combination of His(10)-MrpC2 and FruA-His(6), with the highest affinity, followed by site 1 and then site 2, supporting a model in which site 3 recruits MrpC2 and FruA to the fmgE promoter region, site 1 competes with site 2 for transcription factor binding, and site 2 occupancy is required to activate the promoter but only occurs when C-signaling produces a high concentration of active FruA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combinatorial regulation of the dev operon by MrpC2 and FruA during Myxococcus xanthus development.J Bacteriol. 2015 Jan;197(2):240-51. doi: 10.1128/JB.02310-14. Epub 2014 Oct 27. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 25349159 Free PMC article.
-
Combinatorial regulation by a novel arrangement of FruA and MrpC2 transcription factors during Myxococcus xanthus development.J Bacteriol. 2009 Apr;191(8):2753-63. doi: 10.1128/JB.01818-08. Epub 2009 Feb 6. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19201804 Free PMC article.
-
Combinatorial regulation of fmgD by MrpC2 and FruA during Myxococcus xanthus development.J Bacteriol. 2011 Apr;193(7):1681-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.01541-10. Epub 2011 Jan 21. J Bacteriol. 2011. PMID: 21257775 Free PMC article.
-
Dual regulation with Ser/Thr kinase cascade and a His/Asp TCS in Myxococcus xanthus.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;631:111-21. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-78885-2_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008. PMID: 18792684 Review.
-
Two-Component Signal Transduction Systems That Regulate the Temporal and Spatial Expression of Myxococcus xanthus Sporulation Genes.J Bacteriol. 2015 Sep 14;198(3):377-85. doi: 10.1128/JB.00474-15. Print 2016 Feb 1. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 26369581 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Expanding the direct HetR regulon in Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120.J Bacteriol. 2014 Mar;196(5):1113-21. doi: 10.1128/JB.01372-13. Epub 2013 Dec 27. J Bacteriol. 2014. PMID: 24375104 Free PMC article.
-
Combinatorial regulation of the dev operon by MrpC2 and FruA during Myxococcus xanthus development.J Bacteriol. 2015 Jan;197(2):240-51. doi: 10.1128/JB.02310-14. Epub 2014 Oct 27. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 25349159 Free PMC article.
-
The dev Operon Regulates the Timing of Sporulation during Myxococcus xanthus Development.J Bacteriol. 2017 Apr 25;199(10):e00788-16. doi: 10.1128/JB.00788-16. Print 2017 May 15. J Bacteriol. 2017. PMID: 28264995 Free PMC article.
-
An ambruticin-sensing complex modulates Myxococcus xanthus development and mediates myxobacterial interspecies communication.Nat Commun. 2020 Nov 4;11(1):5563. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19384-7. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 33149152 Free PMC article.
-
devI is an evolutionarily young negative regulator of Myxococcus xanthus development.J Bacteriol. 2015 Apr;197(7):1249-62. doi: 10.1128/JB.02542-14. Epub 2015 Feb 2. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 25645563 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

