Two distinct heterotypic channels mediate gap junction coupling between astrocyte and oligodendrocyte connexins
- PMID: 18094232
- PMCID: PMC6673504
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3395-07.2007
Two distinct heterotypic channels mediate gap junction coupling between astrocyte and oligodendrocyte connexins
Abstract
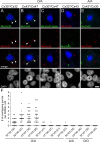
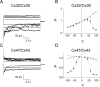
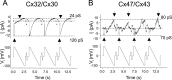
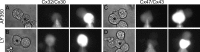
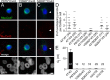
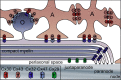
Genetic diseases demonstrate that the normal function of CNS myelin depends on connexin32 (Cx32) and Cx47, gap junction (GJ) proteins expressed by oligodendrocytes. GJs couple oligodendrocytes and astrocytes (O/A channels) as well as astrocytes themselves (A/A channels). Because astrocytes express different connexins (Cx30 and Cx43), O/A channels must be heterotypic, whereas A/A channels may be homotypic or heterotypic. Using electrophysiological and immunocytochemical approaches, we found that Cx47/Cx43 and Cx32/Cx30 efficiently formed functional channels, but other potential heterotypic O/A and A/A pairs did not. These results suggest that Cx30/Cx30 and Cx43/Cx43 channels mediate A/A coupling, and Cx47/Cx43 and Cx32/Cx30 channels mediate O/A coupling. Furthermore, Cx47/Cx43 and Cx32/Cx30 channels have distinct macroscopic and single-channel properties and different dye permeabilities. Finally, Cx47 mutants that cause Pelizaeus-Merzbacher-like disease do not efficiently form functional channels with Cx43, indicating that disrupted Cx47/Cx43 channels cause this disease.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Coupling of astrocyte connexins Cx26, Cx30, Cx43 to oligodendrocyte Cx29, Cx32, Cx47: Implications from normal and connexin32 knockout mice.Glia. 2003 Dec;44(3):205-18. doi: 10.1002/glia.10278. Glia. 2003. PMID: 14603462 Free PMC article.
-
The distribution and functional properties of Pelizaeus-Merzbacher-like disease-linked Cx47 mutations on Cx47/Cx47 homotypic and Cx47/Cx43 heterotypic gap junctions.Biochem J. 2013 Jun 1;452(2):249-58. doi: 10.1042/BJ20121821. Biochem J. 2013. PMID: 23544880
-
Ablation of Cx47 in transgenic mice leads to the loss of MUPP1, ZONAB and multiple connexins at oligodendrocyte-astrocyte gap junctions.Eur J Neurosci. 2008 Oct;28(8):1503-17. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06431.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18973575 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Diseases Associated with Mutation in GJC2/Connexin 47.Biomolecules. 2023 Apr 21;13(4):712. doi: 10.3390/biom13040712. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37189458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early disruption of glial communication via connexin gap junction in multiple sclerosis, Baló's disease and neuromyelitis optica.Neuropathology. 2015 Oct;35(5):469-80. doi: 10.1111/neup.12211. Epub 2015 May 28. Neuropathology. 2015. PMID: 26016402 Review.
Cited by
-
Pelizaeus-Merzbacher-like disease is caused not only by a loss of connexin47 function but also by a hemichannel dysfunction.Eur J Hum Genet. 2010 Sep;18(9):985-92. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2010.61. Epub 2010 May 5. Eur J Hum Genet. 2010. PMID: 20442743 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocytes: The Housekeepers and Guardians of the CNS.Adv Neurobiol. 2021;26:21-53. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-77375-5_2. Adv Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 34888829 Free PMC article.
-
Cx50 requires an intact PDZ-binding motif and ZO-1 for the formation of functional intercellular channels.Mol Biol Cell. 2011 Dec;22(23):4503-12. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-05-0438. Epub 2011 Sep 30. Mol Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21965293 Free PMC article.
-
The Multifaceted Role of Astrocyte Connexin 43 in Ischemic Stroke Through Forming Hemichannels and Gap Junctions.Front Neurol. 2020 Jul 31;11:703. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00703. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32849190 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Loss of astrocyte connexins 43 and 30 does not significantly alter susceptibility or severity of acute experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice.J Neuroimmunol. 2012 Apr;245(1-2):8-14. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2012.01.007. Epub 2012 Feb 18. J Neuroimmunol. 2012. PMID: 22342190 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS050705-03/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS055284/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K02 NS050345-03/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS054363/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS043560/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS50345/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K02 NS050345-02/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS55284/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS050705-02/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F30 NS054363/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS050705/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K02 NS050345/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS043560/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS050705/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
