Purified Wnt5a protein activates or inhibits beta-catenin-TCF signaling depending on receptor context
- PMID: 16602827
- PMCID: PMC1420652
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040115
Purified Wnt5a protein activates or inhibits beta-catenin-TCF signaling depending on receptor context
Abstract
The Wnts comprise a large class of secreted proteins that control essential developmental processes such as embryonic patterning, cell growth, migration, and differentiation. In the most well-understood "canonical" Wnt signaling pathway, Wnt binding to Frizzled receptors induces beta-catenin protein stabilization and entry into the nucleus, where it complexes with T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor transcription factors to affect the transcription of target genes. In addition to the canonical pathway, evidence for several other Wnt signaling pathways has accumulated, in particular for Wnt5a, which has therefore been classified as a noncanonical Wnt family member. To study the alternative mechanisms by which Wnt proteins signal, we purified the Wnt5a protein to homogeneity. We find that purified Wnt5a inhibits Wnt3a protein-induced canonical Wnt signaling in a dose-dependent manner, not by influencing beta-catenin levels but by downregulating beta-catenin-induced reporter gene expression. The Wnt5a signal is mediated by the orphan tyrosine kinase Ror2, is pertussis toxin insensitive, and does not influence cellular calcium levels. We show that in addition to its inhibitory function, Wnt5a can also activate beta-catenin signaling in the presence of the appropriate Frizzled receptor, Frizzled 4. Thus, this study shows for the first time that a single Wnt ligand can initiate discrete signaling pathways through the activation of two distinct receptors. Based on these and additional observations, we propose a model wherein receptor context dictates Wnt signaling output. In this model, signaling by different Wnt family members is not intrinsically regulated by the Wnt proteins themselves but by receptor availability.
Figures
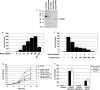
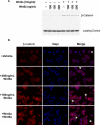

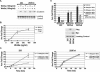
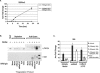

Comment in
-
One signal, multiple pathways: diversity comes from the receptor.PLoS Biol. 2006 Apr;4(4):e131. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040131. Epub 2006 Apr 4. PLoS Biol. 2006. PMID: 20076560 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
The Wnt5a/Ror2 noncanonical signaling pathway inhibits canonical Wnt signaling in K562 cells.Int J Mol Med. 2011 Jan;27(1):63-9. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2010.560. Epub 2010 Nov 10. Int J Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21069266
-
Wnt5a induces homodimerization and activation of Ror2 receptor tyrosine kinase.J Cell Biochem. 2008 Oct 1;105(2):497-502. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21848. J Cell Biochem. 2008. PMID: 18615587
-
Ror2 receptor requires tyrosine kinase activity to mediate Wnt5A signaling.J Biol Chem. 2009 Oct 30;284(44):30167-76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.041715. Epub 2009 Aug 31. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19720827 Free PMC article.
-
Hear the Wnt Ror: how melanoma cells adjust to changes in Wnt.Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2009 Dec;22(6):724-39. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-148X.2009.00627.x. Epub 2009 Aug 25. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2009. PMID: 19708915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ror-family receptor tyrosine kinases in noncanonical Wnt signaling: their implications in developmental morphogenesis and human diseases.Dev Dyn. 2010 Jan;239(1):1-15. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.21991. Dev Dyn. 2010. PMID: 19530173 Review.
Cited by
-
Wnt5a-Vangl1/2 signaling regulates the position and direction of lung branching through the cytoskeleton and focal adhesions.PLoS Biol. 2022 Aug 26;20(8):e3001759. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001759. eCollection 2022 Aug. PLoS Biol. 2022. PMID: 36026468 Free PMC article.
-
iPSC-derived mesenchymal cells that support alveolar organoid development.Cell Rep Methods. 2022 Sep 19;2(10):100314. doi: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2022.100314. eCollection 2022 Oct 24. Cell Rep Methods. 2022. PMID: 36313800 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Role of RNF43 in Canonical and Noncanonical Wnt Signaling.Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Jun 1;35(11):2007-23. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00159-15. Epub 2015 Mar 30. Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25825523 Free PMC article.
-
Hair Growth Activity of Three Plants of the Polynesian Cosmetopoeia and Their Regulatory Effect on Dermal Papilla Cells.Molecules. 2020 Sep 23;25(19):4360. doi: 10.3390/molecules25194360. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32977422 Free PMC article.
-
β-Catenin Signaling and Roles in Liver Homeostasis, Injury, and Tumorigenesis.Gastroenterology. 2015 Jun;148(7):1294-310. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.02.056. Epub 2015 Mar 5. Gastroenterology. 2015. PMID: 25747274 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Logan CY, Nusse R. The Wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2004;20:781–810. - PubMed
-
- Polakis P. Wnt signaling and cancer. Genes Dev. 2000;14:1837–1851. - PubMed
-
- Reya T, Clevers H. Wnt signalling in stem cells and cancer. Nature. 2005;434:843–850. - PubMed
-
- Shimizu H, Julius MA, Giarre M, Zheng Z, Brown AM, et al. Transformation by Wnt family proteins correlates with regulation of beta-catenin. Cell Growth Differ. 1997;8:1349–1358. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

