Epimutations in Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes: a molecular study of 136 patients with an imprinting defect
- PMID: 12545427
- PMCID: PMC1180233
- DOI: 10.1086/367926
Epimutations in Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes: a molecular study of 136 patients with an imprinting defect
Abstract
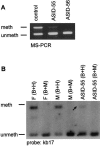
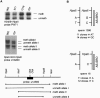
Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) and Angelman syndrome (AS) are neurogenetic disorders that are caused by the loss of function of imprinted genes in 15q11-q13. In a small group of patients, the disease is due to aberrant imprinting and gene silencing. Here, we describe the molecular analysis of 51 patients with PWS and 85 patients with AS who have such a defect. Seven patients with PWS (14%) and eight patients with AS (9%) were found to have an imprinting center (IC) deletion. Sequence analysis of 32 patients with PWS and no IC deletion and 66 patients with AS and no IC deletion did not reveal any point mutation in the critical IC elements. The presence of a faint methylated band in 27% of patients with AS and no IC deletion suggests that these patients are mosaic for an imprinting defect that occurred after fertilization. In patients with AS, the imprinting defect occurred on the chromosome that was inherited from either the maternal grandfather or grandmother; however, in all informative patients with PWS and no IC deletion, the imprinting defect occurred on the chromosome inherited from the paternal grandmother. These data suggest that this imprinting defect results from a failure to erase the maternal imprint during spermatogenesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sporadic imprinting defects in Prader-Willi syndrome and Angelman syndrome: implications for imprint-switch models, genetic counseling, and prenatal diagnosis.Am J Hum Genet. 1998 Jul;63(1):170-80. doi: 10.1086/301935. Am J Hum Genet. 1998. PMID: 9634532 Free PMC article.
-
Minimal definition of the imprinting center and fixation of chromosome 15q11-q13 epigenotype by imprinting mutations.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Jul 23;93(15):7811-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.15.7811. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996. PMID: 8755558 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of the Prader-Willi syndrome imprinting center on the DNA methylation landscape in the mouse brain.Epigenetics. 2014 Nov;9(11):1540-56. doi: 10.4161/15592294.2014.969667. Epigenetics. 2014. PMID: 25482058 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic imprinting: potential function and mechanisms revealed by the Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes.Mol Hum Reprod. 1997 Apr;3(4):321-32. doi: 10.1093/molehr/3.4.321. Mol Hum Reprod. 1997. PMID: 9237260 Review.
-
Mechanisms of imprinting of the Prader-Willi/Angelman region.Am J Med Genet A. 2008 Aug 15;146A(16):2041-52. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.32364. Am J Med Genet A. 2008. PMID: 18627066 Review.
Cited by
-
Methylation analysis and developmental profile of two individuals with Angelman syndrome due to mosaic imprinting defects.Eur J Med Genet. 2022 Apr;65(4):104456. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2022.104456. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Eur J Med Genet. 2022. PMID: 35218942 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant epigenetic regulation could explain the relationship of paternal age to schizophrenia.Schizophr Bull. 2007 Nov;33(6):1270-3. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbm093. Epub 2007 Aug 21. Schizophr Bull. 2007. PMID: 17712030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Growth Restriction and Genomic Imprinting-Overlapping Phenotypes Support the Concept of an Imprinting Network.Genes (Basel). 2021 Apr 17;12(4):585. doi: 10.3390/genes12040585. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33920525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prader-willi syndrome: clinical aspects.J Obes. 2012;2012:473941. doi: 10.1155/2012/473941. Epub 2012 Oct 23. J Obes. 2012. PMID: 23133744 Free PMC article.
-
Update of the EMQN/ACGS best practice guidelines for molecular analysis of Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes.Eur J Hum Genet. 2019 Sep;27(9):1326-1340. doi: 10.1038/s41431-019-0435-0. Epub 2019 Jun 24. Eur J Hum Genet. 2019. PMID: 31235867 Free PMC article.
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/ (for PWS-SRO [accession number AC009696] and AS-SRO [accession number AF148319])
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for AS [MIM 105830] and PWS [MIM 176270])
References
-
- Buiting K, Färber C, Kroisel P, Wagner K, Brueton L, Robertson ME, Lich C, Horsthemke B (2000) Imprinting centre deletions in two PWS families: implications for diagnostic testing and genetic counseling. Clin Genet 58:284–290 - PubMed
-
- Buiting K, Lich C, Cottrell S, Barnicoat A, Horsthemke B (1999) A 5-kb imprinting center deletion in a family with Angelman syndrome reduces the shortest region of deletion overlap to 880 bp. Hum Genet 105:665–666 - PubMed
-
- Buiting K, Saitoh S, Groß S, Dittrich B, Schwartz S, Nicholls R, Horsthemke B (1995) Inherited microdeletions in the Angelman and Prader-Willi syndromes define an imprinting center on human chromosome 15. Nat Genet 9:395–400 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

