The demographics and distribution of type B Niemann-Pick disease: novel mutations lead to new genotype/phenotype correlations
- PMID: 12369017
- PMCID: PMC378582
- DOI: 10.1086/345074
The demographics and distribution of type B Niemann-Pick disease: novel mutations lead to new genotype/phenotype correlations
Abstract
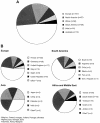
We have collected demographic and/or mutation information on a worldwide sample of 394 patients with type B Niemann-Pick disease (NPD). The disorder is panethnic, with the highest incidence occurring in individuals of Turkish, Arabic, and North African descent. Only five of the 394 patients were Ashkenazi Jewish, revealing that, unlike the type A form of NPD, type B NPD does not occur frequently within this population. Mutation analysis of the acid sphingomyelinase (ASM) gene (designated "SMPD1") was performed on 228 patients (324 unique alleles), and several novel, "common" mutations were found. Among these were the L137P, fsP189, and L549P mutations, which accounted for approximately 75% of the alleles in Turkish patients, the H421Y and K576N mutations, which accounted for approximately 85% of the alleles in Saudi Arabian patients, the S379P, R441X, R474W, and F480L mutations, which accounted for approximately 55% of the alleles in Portuguese/Brazilian patients, and the A196P mutation, which accounted for approximately 42% of the alleles in Scottish/English patients. The previously reported DeltaR608 mutation occurred on approximately 12% of the alleles studied. Overall, a total of 45 novel mutations were found, and several new genotype/phenotype correlations were identified. In particular, the L137P, A196P, and R474W mutations were consistent with a less severe form of type B NPD, whereas the H421Y and K576N mutations led to an early-onset, more severe form that was specific to Saudi Arabia. These data provide the first extensive demographic assessment of this disorder and describe several new mutations that can be used to predict phenotypic outcome and to gain new insights into the structure and function of ASM.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis of the sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase 1 gene (SMPD1) in Turkish Niemann-Pick disease patients: mutation profile and description of a novel mutation.Gene. 2013 Sep 10;526(2):484-6. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.03.116. Epub 2013 Apr 22. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23618813
-
Spectrum of SMPD1 mutations in Asian-Indian patients with acid sphingomyelinase (ASM)-deficient Niemann-Pick disease.Am J Med Genet A. 2016 Oct;170(10):2719-30. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.37817. Epub 2016 Jun 24. Am J Med Genet A. 2016. PMID: 27338287
-
Niemann-Pick disease: a frequent missense mutation in the acid sphingomyelinase gene of Ashkenazi Jewish type A and B patients.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3748-52. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3748. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991. PMID: 2023926 Free PMC article.
-
Niemann-Pick disease: mutation update, genotype/phenotype correlations, and prospects for genetic testing.Genet Test. 1997;1(1):13-9. doi: 10.1089/gte.1997.1.13. Genet Test. 1997. PMID: 10464620 Review.
-
The pathogenesis and treatment of acid sphingomyelinase-deficient Niemann-Pick disease.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2007 Oct;30(5):654-63. doi: 10.1007/s10545-007-0632-9. Epub 2007 Jul 12. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2007. PMID: 17632693 Review.
Cited by
-
Ethics of genetic counseling--basic concepts and relevance to Islamic communities.Ann Saudi Med. 2004 Mar-Apr;24(2):84-92. doi: 10.5144/0256-4947.2004.84. Ann Saudi Med. 2004. PMID: 15323267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of hyperlipidemia associated with Niemann-Pick disease type B by fenofibrate.Eur J Pediatr. 2006 Feb;165(2):138-9. doi: 10.1007/s00431-005-0009-8. Epub 2005 Oct 7. Eur J Pediatr. 2006. PMID: 16211396 No abstract available.
-
Plasma chitotriosidase and CCL18: early biochemical surrogate markers in type B Niemann-Pick disease.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2005;28(1):13-20. doi: 10.1007/s10545-005-4416-9. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2005. PMID: 15702402
-
Characterization of common SMPD1 mutations causing types A and B Niemann-Pick disease and generation of mutation-specific mouse models.Mol Genet Metab. 2008 Nov;95(3):152-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2008.08.004. Epub 2008 Sep 23. Mol Genet Metab. 2008. PMID: 18815062 Free PMC article.
-
Probability of high-risk genetic matching with oocyte and semen donors: complete gene analysis or genotyping test?J Assist Reprod Genet. 2022 Feb;39(2):341-355. doi: 10.1007/s10815-021-02381-0. Epub 2022 Jan 29. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2022. PMID: 35091964 Free PMC article.
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih/gov/Omim/ (for NPD [MIM 257200]) - PubMed
References
-
- Brooks DA, King BM, Crawley AC, Byers S, Hopwood JJ (1997) Enzyme replacement therapy in mucopolysaccharidosis VI: evidence for immune responses and altered efficacy of treatment in animal models. Biochim Biophys Acta 1361:203–216 - PubMed
-
- Elleder M, Cihula J (1983) Niemann-Pick disease (variation in the sphingomyelinase deficient group): neurovisceral phenotype (A) with an abnormally protracted clinical course and variable expression of neurological symptomatology in three siblings. Eur J Pediatr 140:323–328 - PubMed
-
- Elleder M, Nevoral J, Spicakova V, Hyniova H, Kraus J, Krasny J, Vanier MT (1986) A new variant of sphingomyelinase deficiency (Niemann-Pick): visceromegaly, minimal neurological lesions and low in vivo degradation rate of sphingomyelin. J Inherit Metab Dis 9:357–366 - PubMed
-
- Ferlinz K, Hurwitz R, Sandhoff K (1991) Molecular basis of acid sphingomyelinase deficiency in a patient with Niemann-Pick disease type A. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 179:1187–1191 - PubMed
-
- Francis SH, Colbran JL, McAllister-Lucas LM, Corbin JD (1994) Zinc interactions and conserved motifs of the cGMP-binding CGMP-specific phosphodiesterase suggest that it is a zinc hydrolase. J Biol Chem 269:22477–22480 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

