A locus for autosomal dominant hereditary spastic ataxia, SAX1, maps to chromosome 12p13
- PMID: 11774073
- PMCID: PMC384953
- DOI: 10.1086/338933
A locus for autosomal dominant hereditary spastic ataxia, SAX1, maps to chromosome 12p13
Abstract
The hereditary spastic ataxias (HSA) are a group of clinically heterogeneous neurodegenerative disorders characterized by lower-limb spasticity and generalized ataxia. HSA was diagnosed in three unrelated autosomal dominant families from Newfoundland, who presented mainly with severe leg spasticity, dysarthria, dysphagia, and ocular-movement abnormalities. A genomewide scan was performed on one family, and linkage to a novel locus for HSA on chromosome 12p13, which contains the as-yet-unidentified gene locus SAX1, was identified. Fine mapping confirmed linkage in the two large families, and the third, smaller family showed LOD scores suggestive of linkage. Haplotype construction by use of 13 polymorphic markers revealed that all three families share a disease haplotype, which key recombinants and overlapping haplotypes refine to about 5 cM, flanked by markers D12S93 and GATA151H05. SAX1 is the first locus mapped for autosomal dominant HSA.
Figures
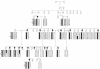

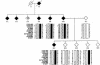
Similar articles
-
A new locus for autosomal dominant "pure" hereditary spastic paraplegia mapping to chromosome 12q13, and evidence for further genetic heterogeneity.Am J Hum Genet. 1999 Sep;65(3):757-63. doi: 10.1086/302555. Am J Hum Genet. 1999. PMID: 10441583 Free PMC article.
-
A new locus for autosomal dominant pure spastic paraplegia, on chromosome 2q24-q34.Am J Hum Genet. 2000 Feb;66(2):702-7. doi: 10.1086/302776. Am J Hum Genet. 2000. PMID: 10677329 Free PMC article.
-
A founder effect in three large Newfoundland families with a novel clinically variable spastic ataxia and supranuclear gaze palsy.Am J Med Genet A. 2004 Dec 15;131(3):249-54. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.30397. Am J Med Genet A. 2004. PMID: 15523628
-
A new locus on chromosome 12p13.3 for pseudohypoaldosteronism type II, an autosomal dominant form of hypertension.Am J Hum Genet. 2000 Aug;67(2):302-10. doi: 10.1086/303020. Epub 2000 Jun 22. Am J Hum Genet. 2000. PMID: 10869238 Free PMC article.
-
A locus for autosomal dominant "pure" hereditary spastic paraplegia maps to chromosome 19q13.Am J Hum Genet. 2000 Feb;66(2):728-32. doi: 10.1086/302783. Am J Hum Genet. 2000. PMID: 10677333 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
VAMP1 mutation causes dominant hereditary spastic ataxia in Newfoundland families.Am J Hum Genet. 2012 Sep 7;91(3):548-52. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.07.018. Am J Hum Genet. 2012. PMID: 22958904 Free PMC article.
-
Linkage disequilibrium mapping in the Newfoundland population: a re-evaluation of the refinement of the Bardet-Biedl syndrome 1 critical interval.Hum Genet. 2005 Jan;116(1-2):62-71. doi: 10.1007/s00439-004-1184-9. Epub 2004 Oct 23. Hum Genet. 2005. PMID: 15517396
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Center for Medical Genetics, Marshfield Medical Research Foundation, http://research.marshfieldclinic.org/genetics/
-
- Cooperative Human Linkage Center, The, http://lpg.nci.nih.gov/CHLC/
-
- Fondation Jean Dausset–CEPH, http://www.cephb.fr/
-
- Genome Database, The, http://www.gdb.org/
-
- HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee, http://www.gene.ucl.ac.uk/nomenclature/
References
-
- Archer BTI, Ozcelik T, Jahn R, Francke U, Sudhof TC (1990) Structures and chromosomal localizations of two human genes encoding synaptobrevins 1 and 2. J Biol Chem 265:17267–17273 - PubMed
-
- Bouchard JP, Richter A, Melancon SB, Mathieu J, Michaud J (2000) Autosomal recessive spastic ataxia (Charlevoix-Saguenay). In: Klockgether T (ed) Handbook of ataxia disorders. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 312–323
-
- Casari G, Rugarli E (2001) Molecular basis of inherited spastic paraplegias. Curr Opin Genet Dev 11:336–342 - PubMed
-
- Craig SP, Day INM, Thompson RJ, Craig IW (1990) Localisation of neurone-specific enolase (ENO2) to 12p13. Cytogenet Cell Genet 54:71–73 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

