Disruption of the bipartite imprinting center in a family with Angelman syndrome
- PMID: 11283796
- PMCID: PMC1226110
- DOI: 10.1086/320120
Disruption of the bipartite imprinting center in a family with Angelman syndrome
Abstract
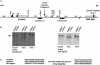
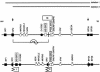
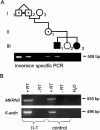
Imprinting in 15q11-q13 is controlled by a bipartite imprinting center (IC), which maps to the SNURF-SNRPN locus. Deletions of the exon 1 region impair the establishment or maintenance of the paternal imprint and can cause Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS). Deletions of a region 35 kb upstream of exon 1 impair maternal imprinting and can cause Angelman syndrome (AS). So far, in all affected sibs with an imprinting defect, an inherited IC deletion was identified. We report on two sibs with AS who do not have an IC deletion but instead have a 1-1.5 Mb inversion separating the two IC elements. The inversion is transmitted silently through the male germline but impairs maternal imprinting after transmission through the female germline. Our findings suggest that the close proximity and/or the correct orientation of the two IC elements are/is necessary for the establishment of a maternal imprint.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sporadic imprinting defects in Prader-Willi syndrome and Angelman syndrome: implications for imprint-switch models, genetic counseling, and prenatal diagnosis.Am J Hum Genet. 1998 Jul;63(1):170-80. doi: 10.1086/301935. Am J Hum Genet. 1998. PMID: 9634532 Free PMC article.
-
Minimal definition of the imprinting center and fixation of chromosome 15q11-q13 epigenotype by imprinting mutations.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Jul 23;93(15):7811-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.15.7811. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996. PMID: 8755558 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic imprinting: potential function and mechanisms revealed by the Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes.Mol Hum Reprod. 1997 Apr;3(4):321-32. doi: 10.1093/molehr/3.4.321. Mol Hum Reprod. 1997. PMID: 9237260 Review.
-
A 5-kb imprinting center deletion in a family with Angelman syndrome reduces the shortest region of deletion overlap to 880 bp.Hum Genet. 1999 Dec;105(6):665-6. doi: 10.1007/s004399900196. Hum Genet. 1999. PMID: 10647904
-
Mechanisms of imprinting of the Prader-Willi/Angelman region.Am J Med Genet A. 2008 Aug 15;146A(16):2041-52. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.32364. Am J Med Genet A. 2008. PMID: 18627066 Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetics of human diseases and scope in future therapeutics.J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2017 May 22;12(3):205-211. doi: 10.1016/j.jtumed.2017.04.003. eCollection 2017 Jun. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 31435241 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular and Clinical Aspects of Angelman Syndrome.Mol Syndromol. 2012 Apr;2(3-5):100-112. doi: 10.1159/000328837. Epub 2011 Jul 28. Mol Syndromol. 2012. PMID: 22670133 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of candidate imprinted genes in PWS subjects with atypical genetics: a possible inactivating mutation in the SNURF/SNRPN minimal promoter.J Hum Genet. 2007;52(4):297-307. doi: 10.1007/s10038-007-0109-6. Epub 2007 Jan 30. J Hum Genet. 2007. PMID: 17262171
-
Microarray based comparative genomic hybridization testing in deletion bearing patients with Angelman syndrome: genotype-phenotype correlations.J Med Genet. 2006 Jun;43(6):512-6. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2005.036913. Epub 2005 Sep 23. J Med Genet. 2006. PMID: 16183798 Free PMC article.
-
The comorbidity of autism with the genomic disorders of chromosome 15q11.2-q13.Neurobiol Dis. 2010 May;38(2):181-91. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2008.08.011. Epub 2008 Sep 18. Neurobiol Dis. 2010. PMID: 18840528 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim (for PWS [MIM 176270] and AS [MIM 105830])
References
-
- Buiting K, Saitoh S, Groß S, Dittrich B, Schwartz S, Nicholls R, Horsthemke B (1995) Inherited microdeletions in the Angelman and Prader-Willi syndromes define an imprinting center on human chromosome 15. Nat Genet 9:395–400 - PubMed
-
- Buiting K, Lich C, Cottrell S, Barnicoat A, Horsthemke B (1999a) A 5-kb imprinting center deletion in a family with Angelman syndrome reduces the shortest region of deletion overlap to 880 bp. Hum Genet 105:665–666 - PubMed
-
- Buiting K, Groß S, Ji Y, Senger G, Nicholls RD, Horsthemke B (1999b) Expressed copies of the MN7 (D15F37) gene family map close to the common deletion breakpoints in the Prader-Willi/Angelman syndromes. Cytogenet Cell Genet 81:247–253 - PubMed
-
- Buiting K, Färber C, Kroisel P, Wagner K, Brueton L, Robertson ME, Lich C, Horsthemke B (2000) Imprinting centre (IC) deletions in two PWS families: implications and strategies for diagnostic testing and genetic counselling. Clin Genet 58:284–290 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

