A quantitative-trait analysis of human plasma-dopamine beta-hydroxylase activity: evidence for a major functional polymorphism at the DBH locus
- PMID: 11170900
- PMCID: PMC1235285
- DOI: 10.1086/318198
A quantitative-trait analysis of human plasma-dopamine beta-hydroxylase activity: evidence for a major functional polymorphism at the DBH locus
Abstract
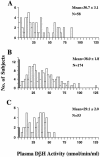
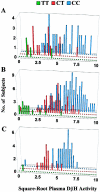
Dopamine-beta-hydroxylase (D beta H) catalyzes the conversion of dopamine to norepinephrine and is released from sympathetic neurons into the circulation. Plasma-D beta H activity varies widely between individuals, and a subgroup of the population has very low activity levels. Mounting evidence suggests that the DBH structural gene is itself the major quantitative-trait locus (QTL) for plasma-D beta H activity, and a single unidentified polymorphism may account for a majority of the variation in activity levels. Through use of both sequencing-based mutational analysis of extreme phenotypes and genotype/phenotype correlations in samples from African American, European American (EA), and Japanese populations, we have identified a novel polymorphism (--1021C-->T), in the 5' flanking region of the DBH gene, that accounts for 35%--52% of the variation in plasma-D beta H activity in these populations. In EAs, homozygosity at the T allele predicted the very low D beta H-activity trait, and activity values in heterozygotes formed an intermediate distribution, indicating codominant inheritance. Our findings demonstrate that --1021C-->T is a major genetic marker for plasma-D beta H activity and provide new tools for investigation of the role of both D beta H and the DBH gene in human disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The structure of linkage disequilibrium at the DBH locus strongly influences the magnitude of association between diallelic markers and plasma dopamine beta-hydroxylase activity.Am J Hum Genet. 2003 Jun;72(6):1389-400. doi: 10.1086/375499. Epub 2003 Apr 30. Am J Hum Genet. 2003. PMID: 12730829 Free PMC article.
-
Association of dopamine beta-hydroxylase polymorphism with hypertension through interaction with fasting plasma glucose in Japanese.Hypertens Res. 2005 Mar;28(3):215-21. doi: 10.1291/hypres.28.215. Hypertens Res. 2005. PMID: 16097364
-
Population genetics of a functional variant of the dopamine beta-hydroxylase gene (DBH).Am J Med Genet. 1997 Jul 25;74(4):374-9. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-8628(19970725)74:4<374::aid-ajmg7>3.0.co;2-p. Am J Med Genet. 1997. PMID: 9259372
-
Human genetics of plasma dopamine beta-hydroxylase activity: applications to research in psychiatry and neurology.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2004 Aug;174(4):463-76. doi: 10.1007/s00213-004-1840-8. Epub 2004 Apr 16. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2004. PMID: 15088079 Review.
-
Polymorphisms and low plasma activity of dopamine-beta-hydroxylase in ADHD children.Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2006 Dec;27(6):748-54. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2006. PMID: 17187001 Review.
Cited by
-
A Preliminary Study of DBH (Encoding Dopamine Beta-Hydroxylase) Genetic Variation and Neural Correlates of Emotional and Motivational Processing in Individuals With and Without Pathological Gambling.J Behav Addict. 2016 Jun;5(2):282-92. doi: 10.1556/2006.5.2016.026. Epub 2016 May 19. J Behav Addict. 2016. PMID: 27194378 Free PMC article.
-
mechanisms of disulfiram-induced cocaine abstinence: antabuse and cocaine relapse.Mol Interv. 2009 Aug;9(4):175-87. doi: 10.1124/mi.9.4.6. Mol Interv. 2009. PMID: 19720750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Candidate gene studies of ADHD: a meta-analytic review.Hum Genet. 2009 Jul;126(1):51-90. doi: 10.1007/s00439-009-0694-x. Epub 2009 Jun 9. Hum Genet. 2009. PMID: 19506906 Review.
-
Pharmacogenetic treatments for drug addiction: cocaine, amphetamine and methamphetamine.Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 2009;35(3):161-77. doi: 10.1080/00952990902825447. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 2009. PMID: 19462300 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An initial investigation of associations between dopamine-linked genetic variation and smoking motives in African Americans.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2015 Nov;138:104-10. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2015.09.018. Epub 2015 Sep 26. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2015. PMID: 26410615 Free PMC article.
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Database of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (dbSNP), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/SNP/ (for NCBI-assay ID numbers for 18 new SNPs detected in this study [accession numbers 2418871–2418888])
-
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/index.html (for DBH genomic sequences [accession numbers AC000404 and AC001227])
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for DβH [MIM 223360])
References
-
- Arató M, Bagdy G, Blümel F, Perényi A, Rihmer Z (1983) Reduced serum dopamine-beta-hydroxylase activity in paranoid schizophrenics. Pharmacopsychiatry 16:19–22 - PubMed
-
- Box GEP, Cox DR (1964) An analysis of transformations. J R Stat Soc B 26:211–252
-
- Craig SP, Buckle VJ, Lamouroux A, Mallet J, Craig IW (1988) Localization of the human dopamine beta hydroxylase (DBH) gene to chromosome 9q34. Cytogenet Cell Genet 48:48–50 - PubMed
-
- Cubells JF, Kobayashi K, Nagatsu T, Kidd KK, Kidd JR, Calafell F, Kranzler HR, Ichinose H, Gelernter J (1997) Population genetics of a functional variant of the dopamine beta-hydroxylase gene (DBH). Am J Med Genet 74:374–379 - PubMed
-
- Cubells JF, Kranzler HR, McCance-Katz E, Anderson GM, Malison RT, Price LH, Gelernter J (2000) A haplotype at the DBH locus, associated with low plasma dopamine beta-hydroxylase activity, also associates with cocaine-induced paranoia. Mol Psychiatry 5:56–63 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

