The spectrum of SLC17A5-gene mutations resulting in free sialic acid-storage diseases indicates some genotype-phenotype correlation
- PMID: 10947946
- PMCID: PMC1287888
- DOI: 10.1086/303077
The spectrum of SLC17A5-gene mutations resulting in free sialic acid-storage diseases indicates some genotype-phenotype correlation
Abstract
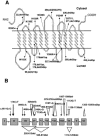
Lysosomal free sialic acid-storage diseases include the allelic disorders Salla disease (SD) and infantile sialic acid-storage disease (ISSD). The defective gene, SLC17A5, coding for the lysosomal free sialic acid transporter was recently isolated by positional cloning. In the present study, we have identified a large number of mutations in SLC17A5 in patients presenting with either Salla disease or the ISSD phenotype. We also report for the first time the exon-intron boundaries of SLC17A5. All Finnish patients with SD (n=80) had a missense mutation changing a highly conserved arginine to cysteine (R39C); 91% of them were homozygotes for this old founder mutation. The compound-heterozygote patients, with the founder mutation in only one allele, presented with a more severe phenotype than did the homozygote patients. The same R39C mutation was also found both in most of the Swedish patients with SD and in a heterozygous form in five patients from central Europe who presented with an unusually severe (intermediate) SD phenotype. Ten different mutations, including deletions, insertions, and missense and nonsense mutations, were identified in patients with the most severe ISSD phenotype, most of whom were compound heterozygotes. Our results indicate some genotype-phenotype correlation in free sialic acid-storage diseases, suggesting that the phenotype associated with the homozygote R39C mutation is milder than that associated with other mutations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Biochemical and molecular analyses of infantile free sialic acid storage disease in North American children.Am J Med Genet A. 2003 Jul 1;120A(1):28-33. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.20024. Am J Med Genet A. 2003. PMID: 12794688
-
Homozygosity for the p.K136E mutation in the SLC17A5 gene as cause of an Italian severe Salla disease.Neurogenetics. 2005 Dec;6(4):195-9. doi: 10.1007/s10048-005-0011-3. Epub 2005 Sep 17. Neurogenetics. 2005. PMID: 16170568
-
Identification of a large intronic transposal insertion in SLC17A5 causing sialic acid storage disease.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2017 Feb 10;12(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s13023-017-0584-6. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2017. PMID: 28187749 Free PMC article.
-
Sialic acid storage disorders: observations on clinical and biochemical variation.Dev Neurosci. 1991;13(4-5):327-30. doi: 10.1159/000112181. Dev Neurosci. 1991. PMID: 1817039 Review.
-
Free sialic acid storage disorder: Progress and promise.Neurosci Lett. 2021 Jun 11;755:135896. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2021.135896. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Neurosci Lett. 2021. PMID: 33862140 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Infantile Sialic Acid Storage Disease: Two Unrelated Inuit Cases Homozygous for a Common Novel SLC17A5 Mutation.JIMD Rep. 2014;12:79-84. doi: 10.1007/8904_2013_247. Epub 2013 Jul 31. JIMD Rep. 2014. PMID: 23900835 Free PMC article.
-
An Unusual Developmental Profile of Salla Disease in a Patient with the SallaFIN Mutation.Case Rep Neurol Med. 2012;2012:615721. doi: 10.1155/2012/615721. Epub 2012 Nov 22. Case Rep Neurol Med. 2012. PMID: 23227378 Free PMC article.
-
Functional characterization of wild-type and mutant human sialin.EMBO J. 2004 Nov 24;23(23):4560-70. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600464. Epub 2004 Oct 28. EMBO J. 2004. PMID: 15510212 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal screening of sialic acid storage disease and confirmation in cultured fibroblasts by LC-MS/MS.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2011 Oct;34(5):1069-73. doi: 10.1007/s10545-011-9351-3. Epub 2011 May 27. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2011. PMID: 21617927 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal hydrops fetalis associated with infantile free sialic acid storage disease due to a novel homozygous deletion in the SLC17A5 gene.Cold Spring Harb Mol Case Stud. 2021 Oct 19;7(5):a006106. doi: 10.1101/mcs.a006106. Print 2021 Oct. Cold Spring Harb Mol Case Stud. 2021. PMID: 34667062 Free PMC article.
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim (for SASD [MIM 269920]) - PubMed
References
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410 - PubMed
-
- Aula P, Autio S, Raivio KO, Rapola J, Thoden CJ, Koskela SL, Yamashina I (1979) “Salla disease”: a new lysosomal storage disorder. Arch Neurol 36:88–94 - PubMed
-
- Aula P, Gahl W. Disorders of free sialic acid storage. In: Scriver CR BA, Sly WS, Valle D (eds) The metabolic and molecular basis of inherited disease. McGraw-Hill, New York (in press)
-
- Aula P, Renlund M, Raivio KO, Koskela SL (1986) Screening of inherited oligosaccharidurias among mentally retarded patients in northern Finland. J Ment Defic Res 30:365–368 - PubMed
-
- Fois A, Balestri P, Farnetani MA, Mancini GM, Borgogni P, Margollicci MA, Molinelli M, Alessandrini C, Gerli R (1987) Free sialic acid storage disease: a new Italian case. Eur J Pediatr 146:195–198 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

