The Most-Cited Authors Who Published Papers in JMIR mHealth and uHealth Using the Authorship-Weighted Scheme: Bibliometric Analysis
- PMID: 32379053
- PMCID: PMC7319608
- DOI: 10.2196/11567
The Most-Cited Authors Who Published Papers in JMIR mHealth and uHealth Using the Authorship-Weighted Scheme: Bibliometric Analysis
Abstract
Background: Many previous papers have investigated most-cited articles or most productive authors in academics, but few have studied most-cited authors. Two challenges are faced in doing so, one of which is that some different authors will have the same name in the bibliometric data, and the second is that coauthors' contributions are different in the article byline. No study has dealt with the matter of duplicate names in bibliometric data. Although betweenness centrality (BC) is one of the most popular degrees of density in social network analysis (SNA), few have applied the BC algorithm to interpret a network's characteristics. A quantitative scheme must be used for calculating weighted author credits and then applying the metrics in comparison.
Objective: This study aimed to apply the BC algorithm to examine possible identical names in a network and report the most-cited authors for a journal related to international mobile health (mHealth) research.
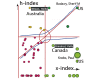
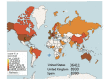
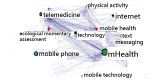
Methods: We obtained 676 abstracts from Medline based on the keywords "JMIR mHealth and uHealth" (Journal) on June 30, 2018. The author names, countries/areas, and author-defined keywords were recorded. The BCs were then calculated for the following: (1) the most-cited authors displayed on Google Maps; (2) the geographical distribution of countries/areas for the first author; and (3) the keywords dispersed by BC and related to article topics in comparison on citation indices. Pajek software was used to yield the BC for each entity (or node). Bibliometric indices, including h-, g-, and x-indexes, the mean of core articles on g(Ag)=sum (citations on g-core/publications on g-core), and author impact factor (AIF), were applied.
Results: We found that the most-cited author was Sherif M Badawy (from the United States), who had published six articles on JMIR mHealth and uHealth with high bibliometric indices (h=3; AIF=8.47; x=4.68; Ag=5.26). We also found that the two countries with the highest BC were the United States and the United Kingdom and that the two keyword clusters of mHealth and telemedicine earned the highest indices in comparison to other counterparts. All visual representations were successfully displayed on Google Maps.
Conclusions: The most cited authors were selected using the authorship-weighted scheme (AWS), and the keywords of mHealth and telemedicine were more highly cited than other counterparts. The results on Google Maps are novel and unique as knowledge concept maps for understanding the feature of a journal. The research approaches used in this study (ie, BC and AWS) can be applied to other bibliometric analyses in the future.
Keywords: Google Maps; authorship collaboration; betweenness centrality; knowledge concept map; social network analysis; the author-weighted scheme.
©Wei-Chih Kan, Willy Chou, Tsair-Wei Chien, Yu-Tsen Yeh, Po-Hsin Chou. Originally published in JMIR mHealth and uHealth (http://mhealth.jmir.org), 07.05.2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The 10 top-cited authors who published papers in journal medicine since 2000 using the betweenness centrality to identify unique names: Bibliometric analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Jun 23;102(25):e34050. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000034050. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37352024 Free PMC article.
-
Whether article types of a scholarly journal are different in cited metrics using cluster analysis of MeSH terms to display: A bibliometric analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Oct;98(43):e17631. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000017631. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31651878 Free PMC article.
-
Using the Kano model to display the most cited authors and affiliated countries in schizophrenia research.Schizophr Res. 2020 Feb;216:422-428. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2019.10.058. Epub 2019 Dec 18. Schizophr Res. 2020. PMID: 31862218
-
Physical Activity, Sedentary Behavior, and Diet-Related eHealth and mHealth Research: Bibliometric Analysis.J Med Internet Res. 2018 Apr 18;20(4):e122. doi: 10.2196/jmir.8954. J Med Internet Res. 2018. PMID: 29669703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Top 100 Most-Cited Papers in Erosive Tooth Wear: A Bibliometric Analysis.Caries Res. 2022;56(1):29-35. doi: 10.1159/000521877. Epub 2022 Jan 27. Caries Res. 2022. PMID: 35086091 Review.
Cited by
-
Research trends and hotspots of exercise for people with sarcopenic: A bibliometric analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Dec 15;102(50):e35148. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035148. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 38115285 Free PMC article.
-
Visualizing burst spots on research for four authors in MDPI journals named to be Citation Laureates 2021 using temporal bar graph.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Aug 11;102(32):e34578. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000034578. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37565889 Free PMC article.
-
Research trends and hotspots of breast cancer management during the COVID-19 pandemic: A bibliometric analysis.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 3;12:918349. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.918349. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35992886 Free PMC article.
-
The evolution and mapping trends of mobile health (m-Health): a bibliometric analysis (1997-2023).Mhealth. 2024 Jul 23;10:23. doi: 10.21037/mhealth-23-20. eCollection 2024. Mhealth. 2024. PMID: 39114458 Free PMC article.
-
A Study of eHealth from the Perspective of Social Sciences.Healthcare (Basel). 2021 Jan 21;9(2):108. doi: 10.3390/healthcare9020108. Healthcare (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33494182 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Avula J, Avula H. Authors, authorship order, the moving finger writes. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2015;19(3):258–62. doi: 10.4103/0972-124X.145782. http://www.jisponline.com/article.asp?issn=0972-124X;year=2015;volume=19... - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baber Z, Gibbons M, Limoges C, Nowotny H, Schwartzman S, Scott P, Trow M. The New Production of Knowledge: The Dynamics of Science and Research in Contemporary Societies. Contemporary Sociology. 1995 Nov;24(6):751. doi: 10.2307/2076669. https://www.books.com.tw/products/F010045750 - DOI
-
- Wu JC, Chiang T. Comparing child mortality in Taiwan and selected industrialized countries. J Formos Med Assoc. 2007 Mar;106(2):177–80. doi: 10.1016/S0929-6646(09)60237-0. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0929-6646(09)60237-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sadoughi F, Valinejadi A, Shirazi M, Khademi R. Social Network Analysis of Iranian Researchers on Medical Parasitology: A 41 Year Co-Authorship Survey. Iran J Parasitol. 2016;11(2):204–212. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/28096854 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Osareh F, Khademi R, Rostami MK, Shirazi MS. Co-authorship Network Structure Analysis of Iranian Researchers’ scientific outputs from 1991 to 2013 based on the Social Science Citation Index (SSCI) Collnet Journal of Scientometrics and Information Management. 2015 Feb 10;8(2):263–271. doi: 10.1080/09737766.2014.1015301. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/09737766.2014.1015301 - DOI - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

