Interventions for childhood apraxia of speech
- PMID: 29845607
- PMCID: PMC6494637
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006278.pub3
Interventions for childhood apraxia of speech
Abstract
Background: Childhood apraxia of speech (CAS) affects a child's ability to produce sounds and syllables precisely and consistently, and to produce words and sentences with accuracy and correct speech rhythm. It is a rare condition, affecting only 0.1% of the general population. Consensus has been reached that three core features have diagnostic validity: (1) inconsistent error production on both consonants and vowels across repeated productions of syllables or words; (2) lengthened and impaired coarticulatory transitions between sounds and syllables; and (3) inappropriate prosody (ASHA 2007). A deficit in motor programming or planning is thought to underlie the condition. This means that children know what they would like to say but there is a breakdown in the ability to programme or plan the fine and rapid movements required to accurately produce speech. Children with CAS may also have impairments in one or more of the following areas: non-speech oral motor function, dysarthria, language, phonological production impairment, phonemic awareness or metalinguistic skills and literacy, or combinations of these. High-quality evidence from randomised controlled trials (RCTs) is lacking on interventions for CAS.
Objectives: To assess the efficacy of interventions targeting speech and language in children and adolescents with CAS as delivered by speech and language pathologists/therapists.
Search methods: We searched CENTRAL, MEDLINE, Embase, eight other databases and seven trial registers up to April 2017. We searched the reference lists of included reports and requested information on unpublished trials from authors of published studies and other experts as well as information groups in the areas of speech and language therapy/pathology and linguistics.
Selection criteria: RCTs and quasi-RCTs of children aged 3 to 16 years with CAS diagnosed by a speech and language pathologist/therapist, grouped by treatment types.
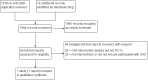
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors (FL, AM) independently assessed titles and abstracts identified from the searches and obtained full-text reports of all potentially relevant articles and assessed these for eligibility. The same two authors extracted data and conducted the 'Risk of bias' and GRADE assessments. One review author (EM) tabulated findings from excluded observational studies (Table 1).
Main results: This review includes only one RCT, funded by the Australian Research Council; the University of Sydney International Development Fund; Douglas and Lola Douglas Scholarship on Child and Adolescent Health; Nadia Verrall Memorial Scholarship; and a James Kentley Memorial Fellowship. This study recruited 26 children aged 4 to 12 years, with mild to moderate CAS of unknown cause, and compared two interventions: the Nuffield Dyspraxia Programme-3 (NDP-3); and the Rapid Syllable Transitions Treatment (ReST). Children were allocated randomly to one of the two treatments. Treatments were delivered intensively in one-hour sessions, four days a week for three weeks, in a university clinic in Australia. Speech pathology students delivered the treatments in the English language. Outcomes were assessed before therapy, immediately after therapy, at one month and four months post-therapy. Our review looked at one-month post-therapy outcomes only.We judged all core outcome domains to be low risk of bias. We downgraded the quality of the evidence by one level to moderate due to imprecision, given that only one RCT was identified. Both the NDP-3 and ReST therapies demonstrated improvement at one month post-treatment. A number of cases in each cohort had recommenced usual treatment by their speech and language pathologist between one month and four months post-treatment (NDP-3: 9/13 participants; ReST: 9/13 participants). Hence, maintenance of treatment effects to four months post-treatment could not be analysed without significant potential bias, and thus this time point was not included for further analysis in this review.There is limited evidence that, when delivered intensively, both the NDP-3 and ReST may effect improvement in word accuracy in 4- to 12-year-old children with CAS, measured by the accuracy of production on treated and non-treated words, speech production consistency and the accuracy of connected speech. The study did not measure functional communication.
Authors' conclusions: There is limited evidence that, when delivered intensively, both the NDP-3 and ReST may effect improvement in word accuracy in 4- to 12-year-old children with CAS, measured by the accuracy of production on treated and non-treated words, speech production consistency and the accuracy of connected speech. The study did not measure functional communication. No formal analyses were conducted to compare NDP-3 and ReST by the original study authors, hence one treatment cannot be reliably advocated over the other. We are also unable to say whether either treatment is better than no treatment or treatment as usual. No evidence currently exists to support the effectiveness of other treatments for children aged 4 to 12 years with idiopathic CAS without other comorbid neurodevelopmental disorders. Further RCTs replicating this study would strengthen the evidence base. Similarly, further RCTs are needed of other interventions, in other age ranges and populations with CAS and with co-occurring disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
Angela T Morgan (AM) — none known. Elizabeth Murray (EM) is an author of the included study, Murray 2015, and was not involved in selecting this study for inclusion, or extracting or reviewing data from this study. Study selection as well as data extraction and review was conducted by two independent authors — AM and FL. Frederique J Liégeois (FL) — none known.
Figures
Update of
-
Intervention for childhood apraxia of speech.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Jul 16;(3):CD006278. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006278.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 May 30;5:CD006278. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006278.pub3. PMID: 18646142 Updated. Review.
Similar articles
-
Intervention for childhood apraxia of speech.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Jul 16;(3):CD006278. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006278.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 May 30;5:CD006278. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006278.pub3. PMID: 18646142 Updated. Review.
-
A Cochrane review of treatment for childhood apraxia of speech.Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2009 Mar;45(1):103-10. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2009. PMID: 19156019 Review.
-
Non-speech oral motor treatment for children with developmental speech sound disorders.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Mar 25;2015(3):CD009383. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009383.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25805060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A comparison of two treatments for childhood apraxia of speech: methods and treatment protocol for a parallel group randomised control trial.BMC Pediatr. 2012 Aug 3;12:112. doi: 10.1186/1471-2431-12-112. BMC Pediatr. 2012. PMID: 22863021 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A Randomized Controlled Trial for Children With Childhood Apraxia of Speech Comparing Rapid Syllable Transition Treatment and the Nuffield Dyspraxia Programme-Third Edition.J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2015 Jun;58(3):669-86. doi: 10.1044/2015_JSLHR-S-13-0179. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2015. PMID: 25807891 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
GATAD2B-associated neurodevelopmental disorder (GAND): clinical and molecular insights into a NuRD-related disorder.Genet Med. 2020 May;22(5):878-888. doi: 10.1038/s41436-019-0747-z. Epub 2020 Jan 17. Genet Med. 2020. PMID: 31949314 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic aetiologies for childhood speech disorder: novel pathways co-expressed during brain development.Mol Psychiatry. 2023 Apr;28(4):1647-1663. doi: 10.1038/s41380-022-01764-8. Mol Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 36117209 Free PMC article.
-
Speech and language deficits are central to SETBP1 haploinsufficiency disorder.Eur J Hum Genet. 2021 Aug;29(8):1216-1225. doi: 10.1038/s41431-021-00894-x. Epub 2021 Apr 27. Eur J Hum Genet. 2021. PMID: 33907317 Free PMC article.
-
Level of Vocabulary Development and Selected Elements Regarding Sensory Integration and Balance in 5-Year-Old Girls and Boys.Children (Basel). 2021 Mar 7;8(3):200. doi: 10.3390/children8030200. Children (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33800019 Free PMC article.
-
Guiding Mothers About Early Detection and Addressing Speech Delay and Disorders Among Children in a Rural Setup.Cureus. 2023 Nov 15;15(11):e48822. doi: 10.7759/cureus.48822. eCollection 2023 Nov. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38106793 Free PMC article.
References
References to studies included in this review
Murray 2015 {published data only}
-
- Murray E, McCabe P, Ballard KJ. A randomized controlled trial for children with childhood apraxia of speech comparing rapid syllable transition treatment and the Nuffield Dyspraxia Programme ‐Third Edition. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research 2015;58(3):669‐86. [DOI: 10.1044/2015_JSLHR-S-13-0179; PUBMED: 25807891] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Murray E. (Faculty of Health Sciences, The University of Sydney, Lidcombe, Australia). [personal communication]. Conversation with: A Morgan (Murdoch Children's Research Institute, Melbourne, Australia) 13 August 2015.
References to studies excluded from this review
Baas 2008 {published data only}
-
- Baas BS, Strand EA, LM Elmer, Barbaresi WJ. Treatment of severe childhood apraxia of speech in a 12‐year‐old male with CHARGE association. Journal of Medical Speech‐language Pathology 2008;16(4):181‐90.
Ballard 2010 {published data only}
Beathard 2008 {published data only}
-
- Beathard B, Krout RE. A music therapy clinical case study of a girl with childhood apraxia of speech: finding Lily's voice. Arts in Psychotherapy 2008;35(2):107‐16. [DOI: 10.1016/j.aip.2008.01.004] - DOI
Binger 2007 {published data only}
Binger 2008 {published data only}
Binger 2011 {published data only}
Bornman 2001 {published data only}
-
- Bornman J, Alant E, Meiring E. The use of a digital voice output device to facilitate language development in a child with developmental apraxia of speech: a case study. Disability and Rehabilitation 2001;23(14):623‐34. [PUBMED: 11697460] - PubMed
Bose 2001 {published data only}
-
- Bose A, Square PA, Schlosser R, Lieshout P. Effects of PROMPT therapy on speech motor function in a person with aphasia and apraxia of speech. Aphasiology 2001;15(8):767‐85. [DOI: 10.1080/02687040143000186] - DOI
Carter 2004 {published data only}
-
- Carter P, Edwards S. EPG therapy for children with long‐standing speech disorders: predictions and outcomes. Clinical Linguistics and Phonetics 2004;18(6‐8):359‐72. [PUBMED: 15573477] - PubMed
Chappell 1973 {published data only}
-
- Chappell GE. Childhood verbal apraxia and its treatment. Journal of Speech and Hearing Disorders 1973;38(3):362‐8. [PUBMED: 4721796] - PubMed
Culp 1989 {published data only}
-
- Culp DM. Developmental apraxia and augmentative or alternative communication ‐ a case example. Augmentative and Alternative Communication 1989;5(1):27‐34. [DOI: 10.1080/07434618912331274936] - DOI
Cumley 1999 {published data only}
-
- Cumley GD, Swanson S. Augmentative and alternative communication options for children with developmental apraxia of speech: three case studies. Augmentative and Alternative Communication 1999;15(2):110‐25. [DOI: 10.1080/07434619912331278615] - DOI
Dale 2013 {published data only}
Daly 1972 {published data only}
Dworkin 1988 {published data only}
-
- Dworkin JP, Abkarian GG, John DF. Apraxia of speech: the effectiveness of a treatment regimen. Journal of Speech and Hearing Disorders 1988;53(3):280‐94. [PUBMED: 3398481] - PubMed
Edeal 2011 {published data only}
Forrest 2001 {published data only}
Groenen 1996 {published data only}
-
- Groenen P, Maassen B, Crul T, Thoonen G. The specific relation between perception and production errors for place of articulation in developmental apraxia of speech. Journal of Speech and Hearing Research 1996;39(3):468‐82. [PUBMED: 8783127] - PubMed
Hadar 1984 {published data only}
-
- Hadar U, Twiston‐Davies R, Steiner TJ, Rose FC. A psychomotor approach to improving speech by modulating suprasegmental control in motor dysphasia and articulatory apraxia. Advances in Neurology 1984;42:337‐51. [PUBMED: 6507181] - PubMed
Hall 1989 {published data only}
-
- Hall PK. The occurrence of developmental apraxia of speech in a mild articulation disorder: a case study. Journal of Communication Disorders 1989;22(4):265‐76. [PUBMED: 2794108] - PubMed
Hall 1990 {published data only}
-
- Hall PK, Hardy JC, LaVelle WE. A child with signs of developmental apraxia of speech with whom a palatal lift prosthesis was used to manage palatal dysfunction. Journal of Speech and Hearing Disorders 1990;55(3):454‐60. [PUBMED: 2381187] - PubMed
Harris 1996 {published data only}
-
- Harris L, Doyle ES, Haaf R. Language treatment approach for users of AAC: experimental single‐subject investigation. Augmentative and Alternative Communication (Baltimore, Md. : 1985) 1996;12(4):230‐43. [DOI: 10.1080/07434619612331277698] - DOI
Hayden 2006 {published data only}
-
- Hayden D. The PROMPT model: use and application for children with mixed phonological‐motor impairment. Advances in Speech Language Pathology 2006;8(3):265‐81. [DOI: 10.1080/14417040600861094] - DOI
Head 1975 {published data only}
Helfrich‐Miller 1994 {published data only}
-
- Helfrich‐Miller KR. A clinical perspective: melodic intonation therapy for developmental apraxia. Clinics in Communication Disorders 1994;4(3):175‐82. [PUBMED: 7994292] - PubMed
Iuzzini 2010 {published data only}
Jaroma 1984 {published data only}
Kadis 2014 {published data only}
Katz 2006 {published data only}
-
- Katz WF, Bharadwaj SV, Stettler MP. Influences of electromagnetic articulography sensors on speech produced by healthy adults and individuals with aphasia and apraxia. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research 2006;49(3):645‐59. [DOI: 10.1044/1092-4388(2006/047); PUBMED: 16787902] - DOI - PubMed
King 2013 {published data only}
Kingston 1987 {published data only}
-
- Kingston LM, Rosenthal JB. Oral stereognosis in children with disordered articulation: measurement issues, and a treatment study. Australian Journal of Human Communication Disorders 1987;15(1):1‐14. [DOI: 10.3109/asl2.1987.15.issue-1.01] - DOI
Klick 1985 {published data only}
-
- Klick SL. Adapted cuing technique for use in treatment of dyspraxia. Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools 1985;16:256‐9. [DOI: 10.1044/0161-1461.1604.256] - DOI
Krauss 1982 {published data only}
-
- Krauss T, Galloway H. Melodic intonation therapy with language delayed apraxic children. Journal of Music Therapy 1982;19(2):102‐13. [DOI: 10.1093/jmt/19.2.102] - DOI
Lagasse 2012 {published data only}
-
- Lagasse B. Evaluation of melodic intonation therapy for developmental apraxia of speech. Music Therapy Perspectives 2012;30(1):49‐55. [DOI: 10.1093/mtp/30.1.49] - DOI
Lozano 1978 {published data only}
-
- Lozano RA, Dreyer DE. Some effects of delayed auditory feedback on dyspraxia of speech. Journal of Communication Disorders 1978;11(5):407‐15. [PUBMED: 730833] - PubMed
Lüke 2016 {published data only}
Lundeborg 2007 {published data only}
Maas 2012a {published data only}
Maas 2012b {published data only}
Martikainen 2011 {published data only}
-
- Martikainen A‐L, Korpilahti P. Intervention for childhood apraxia of speech: a single‐case study. Child Language Teaching and Therapy 2011;27(1):9‐20. [DOI: 10.1177/0265659010369985] - DOI
Martin 2016 {published data only}
-
- Martin MK, Wright LE, Perry S, Cornett D, Schraeder M, Johnson JT. Children with developmental verbal dyspraxia: changes in articulation and perceived resilience with intensive multimodal intervention. Child Language Teaching and Therapy 2016;32(3):261‐75. [DOI: 10.1177/0265659015615924] - DOI
McCabe 2014 {published data only}
-
- McCabe P, Macdonald‐D'Silva AG, Rees LJ, Ballard KJ, Arciuli J. Orthographically sensitive treatment for dysprosody in children with childhood apraxia of speech using ReST intervention. Developmental Neurorehabilitation 2014;17(2):137‐46. [DOI: 10.3109/17518423.2014.906002; PUBMED: 24694312] - DOI - PubMed
McNeill 2009a {published data only}
-
- McNeill BC, Gillon GT, Dodd B. Phonological awareness and early reading development in childhood apraxia of speech (CAS). International Journal of Language & Communication Disorders / Royal College of Speech & Language Therapists 2009;44(2):175‐92. [DOI: 10.1080/13682820801997353; PUBMED: 19234970] - DOI - PubMed
McNeill 2009b {published data only}
-
- McNeill BC, Gillon GT, Dodd B. A longitudinal case study of the effects of an integrated phonological awareness program for identical twin boys with childhood apraxia of speech (CAS). International Journal of Speech‐language Pathology 2009;11(6):482‐95. [DOI: 10.3109/17549500902842583; PUBMED: 21271925 ] - DOI - PubMed
McNeill 2010 {published data only}
-
- McNeill BC, Gillon GT, Dodd B. The longer term effects of an integrated phonological awareness intervention for children with childhood apraxia of speech. Asia Pacific Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing 2010;13(3):145‐61. [DOI: 10.1179/136132810805335074] - DOI
Morgan Barry 1995 {published data only}
-
- Morgan Barry R. The relationship between dysarthria and verbal dyspraxia in children: a comparative study using profiling and instrumental analyses. Clinical Linguistics & Phonetics 1995;9(4):277‐309. [DOI: 10.3109/02699209508985338] - DOI
Moriarty 2006 {published data only}
Namasivayam 2013 {published data only}
-
- Namasivayam AK, Pukonen M, Goshulak D, Yu VY, Kadis DS, Kroll R, et al. Relationship between speech motor control and speech intelligibility in children with speech sound disorders. Journal of Communication Disorders 2013;46(3):264‐80. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jcomdis.2013.02.003; PUBMED: 23628222] - DOI - PubMed
Namasivayam 2015 {published data only}
Preston 2013 {published data only}
Preston 2016 {published data only}
Preston 2017 {published data only}
Ray 2003 {published data only}
-
- Ray J. Effects of orofacial myofunctional therapy on speech intelligibility in individuals with persistent articulatory impairments. International Journal of Orofacial Myology 2003;29:5‐14. [PUBMED: 14689652] - PubMed
Richardson 2004 {published data only}
Rosenbek 1974 {published data only}
-
- Rosenbek J, Hansen R, Baughman CH, Lemme M. Treatment of developmental apraxia of speech: a case study. Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools 1974;5:13‐22. [DOI: 10.1044/0161-1461.0501.13] - DOI
Rosenthal 1994 {published data only}
-
- Rosenthal JB. Rate control therapy for developmental apraxia of speech. Clinics in Communication Disorders 1994;4(3):190‐200. [PUBMED: 7994294] - PubMed
Skelton 2014 {published data only}
Square 1994 {published data only}
-
- Square PA. Treatment approaches for developmental apraxia of speech. Clinics in Communication Disorders 1994;4(3):151‐61. [PUBMED: 7994290] - PubMed
Stokes 2010 {published data only}
-
- Stokes SF, Griffiths R. The use of facilitative vowel contexts in the treatment of post‐alveolar fronting: a case study. International Journal of Language & Communication Disorders / Royal College of Speech & Language Therapists 2010;45(3):368‐80. [DOI: 10.3109/13682820903094737; PUBMED: 20144008] - DOI - PubMed
Strand 2000 {published data only}
-
- Strand EA, Debertine P. The efficacy of integral stimulation intervention with developmental apraxia of speech. Journal of Medical Speech‐language Pathology 2000;8(4):295‐300. [www.researchgate.net/publication/286964810_The_efficacy_of_integral_stim...]
Strand 2006 {published data only}
-
- Strand EA, Stoeckel R, Baas B. Treatment of severe childhood apraxia of speech: a treatment efficacy study. Journal of Medical Speech‐language Pathology 2006;14(4):297‐307. [psycnet.apa.org/record/2006‐22884‐013]
Thomas 2014 {published data only}
Thomas 2016 {published data only}
Tierney 2016 {published data only}
Vashdi 2013 {published data only}
-
- Vashdi E. Using VML (verbal motor learning) method techniques in treatment of prosody disorder due to childhood apraxia of speech: a case study. International Journal of Child Health and Human Development 2013;6(2):255‐60. [www.novapublishers.com/catalog/product_info.php?products_id=52658]
Vashdi 2014 {published data only}
-
- Vashdi E. The influence of initial phoneme cue technique on word formation: a case study of a child with apraxia of speech and autism. International Journal of Child Health and Human Development 2014;7(2):197‐203. [www.novapublishers.com/catalog/product_info.php?products_id=53974]
Velleman 1994 {published data only}
-
- Velleman SL, Strand K. Developmental verbal dyspraxia. In: Bernthal JE, Bankson NW editor(s). Child Phonology: Characteristics, Assessment, and Intervention with Special Populations. New York (NY): Thieme, 1994:110‐39. [ISBN 0‐86577‐502‐8]
Yoss 1974 {published data only}
-
- Yoss KA, Darley FL. Developmental apraxia of speech in children with defective articulation. Journal of Speech and Hearing Research 1974;17(3):399‐416. [PUBMED: 4421901] - PubMed
Zaretsky 2010 {published data only}
-
- Zaretsky E, Velleman SL, Curro K. Through the magnifying glass: underlying literacy deficits and remediation potential in childhood apraxia of speech. International Journal of Speech‐language Pathology 2010;12(1):58‐68. [PUBMED: 20380250] - PubMed
Additional references
ASHA 2007
-
- American Speech‐Language‐Hearing Association (ASHA). Technical Report. Childhood Apraxia of Speech: Ad Hoc Committee on Apraxia of Speech in Children. www.asha.org/policy/TR2007‐00278/ (accessed 20 April 2018).
Chumpelik 1984
-
- Chumpelik D. The PROMPT system of therapy: theoretical framework and applications for developmental apraxia of speech. Seminars in Speech and Language 1984;5(2):139‐56. [DOI: 10.1055/s-0028-1085172] - DOI
Crosbie 2005
Davis 2005
Delaney 2004
-
- Delaney AL, Kent RD. Developmental profiles of children diagnosed with apraxia of speech. Annual Convention of the American Speech‐Language‐Hearing Association; 2004 Nov 18‐20; Philadelphia (PA). 2004.
Dodd 2006
-
- Dodd B, Hua Z, Crosbie S, Holm A, Ozanne A. DEAP: Diagnostic Evaluation of Articulation and Phonology. San Antonio (TX): PsychCorp of Harcourt Assessment, 2006.
Dodd 2008
Eadie 2015
Egger 1997
Eising 2018
-
- Eising E, Carrion‐Castillo A, Vino A, Strand EA, Jakielski KJ, Scerri TS, et al. A set of regulatory genes co‐expressed in embryonic human brain is implicated in disrupted speech development. Molecular Psychiatry 2018 Feb 20 [Epub ahead of print]. [DOI: 10.1038/s41380-018-0020-x; PUBMED: 29463886] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Fedorenko 2016
Gillon 2000
Goldman 2000
-
- Goldman R, Fristoe M. Goldman‐Fristoe Test of Articulation‒2. 2nd Edition. Minneapolis (MN): Pearson Assessments, 2000.
Gozzard 2004
-
- Gozzard H, Baker E, McCabe P. Single Word Test of Polysyllables. Unpublished manuscript 2004.
GRADEpro GDT 2015 [Computer program]
-
- McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime). GRADEpro GDT. Version accessed prior to 30 April 2018. Hamilton (ON): McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime), 2015.
Higgins 2011a
Higgins 2011b
-
- Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Altman DG, editor(s). Chapter 16: Special topics in statistics. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Jacks 2006
Lai 2001
Liégeois 2012
Liégeois 2014
Liégeois 2016
Maas 2008
Maas 2014
McNeill 2009
-
- McNeill BC, Gillon GT, Dodd B. Effectiveness of an integrated phonological awareness approach for children with childhood apraxia of speech (CAS). Child Language Teaching and Therapy 2009;25(3):341‐66. [DOI: 10.1177/0265659009339823] - DOI
Mei 2017
Moher 2009
Morgan 2017
-
- Morgan A, Fisher SE, Scheffer IE, Hildebrand M. FOXP2‐related speech and language disorders. 2016 Jun 23 [updated 2017 Feb 2]. In: Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Bean LJH, Stephens K, et al. editor(s). GeneReviews®. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, 1993‐2018. [www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK368474/?report=reader#_NBK368474_pubdet_] - PubMed
Morgan 2018
Morley 1954
Morley 1972
-
- Morley ME. The Development and Disorders of Speech in Childhood. Baltimore (MD): Williams & Wilkins Co., 1972. [ISBN 0443008957]
Murray 2012
-
- Murray E, McCabe P, Ballard KJ. A comparison of two treatments for childhood apraxia of speech: methods and treatment protocol for a parallel group randomised control trial. BMC Pediatrics 2012;12:112. [DOI: 10.1186/1471-2431-12-112; ACTRN12612000744853; PMC3441276; PUBMED: 22863021] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Peter 2017
RCSLT 2011
-
- Royal College of Speech and Language Therapists (RCSLT). Developmental verbal dyspraxia policy statement. www.rcslt.org/speech_and_language_therapy/rcslt_position_papers (accessed prior to 21 March 2018).
Review Manager 2014 [Computer program]
-
- Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager 5 (RevMan 5). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Schünemann 2017
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Higgins JPT, Vist GE, Glasziou P, Akl E, et al. Chapter 11: Completing ‘Summary of findings’ tables and grading the confidence in or quality of the evidence. In: Higgins JPT, Churchill R, Chandler J, Cumpston MS, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 5.2.0 (updated June 2017). Cochrane, 2017. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Shriberg 2010
Shriberg 2011
Turner 2015
Vargha‐Khadem 2005
Velleman 2011
-
- Velleman SL, Mervis CB. Children with 7q11.23 Duplication Syndrome: speech, language, cognitive, and behavioral characteristics and their implications for intervention. Perspectives on Language Learning and Education 2011;18(3):108‐16. [DOI: 10.1044/lle18.3.108; PMC3383616; PUBMED: 22754604] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
White 2010
Williams 2004
-
- Williams P, Stephens H, editor(s). The Nuffield Centre Dyspraxia Programme. 3rd Edition. London (UK): The Nuffield Centre Dyspraxia Programme Ltd., 2004. [www.ndp3.org]
Williams 2010
-
- Williams P, Stephens H. The Nuffield Centre Dyspraxia Programme. In: Williams AL, McLeod S, McAuley RJ editor(s). Interventions for Speech Sound Disorders in Children. Baltimore (MD): Brookes Publishing Company, 2010:159‐77.
Yoss 1975
-
- Yoss KA. Developmental apraxia of speech in children: familial patterns and behavioral characteristics. American Speech and Hearing Association North Central Regional Conference, 1975 May 9; Minneapolis (MN). 1975.
References to other published versions of this review
Morgan 2006
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous