CASRN: 738-70-5
Drug Levels and Effects
Summary of Use during Lactation
Because of the low levels of trimethoprim in breastmilk, amounts ingested by the infant are small and would not be expected to cause any adverse effects in breastfed infants.
Drug Levels
Maternal Levels. In 20 mothers in the immediate postpartum period given oral trimethoprim, peak milk levels occurred 3 hours after the dose. In 14 of these women who received a daily dosage of 320 mg, the peak milk level averaged 2.4 mg/L and the trough averaged 1 mg/L. In 6 other women who received a daily dosage of 480 mg, the peak milk level averaged 4 mg/L and the trough averaged 1.5 mg/L. The authors calculated that a breastfed infant would receive a daily dosage of 0.75 mg with a maternal dosage of 320 mg daily and 1.7 mg with a maternal dosage of 480 mg.[1,2]
Forty women in the early postpartum period received oral co-trimoxazole and had milk levels measured several times daily for 5 days. After trimethoprim doses of 320 mg daily, average milk levels were about 2 mg/L. Milk levels increased to about 3 mg/L by day 5 of therapy. In 10 other women who received trimethoprim 480 mg daily, average milk levels were only slightly higher.[3] With the usual dose of trimethoprim 320 mg daily, an exclusively breastfed infant would be expected to receive 0.45 mg/kg daily of trimethoprim. This is very low in comparison to the established treatment dosages of 8 mg/kg daily for infants over 2 months of age.
Infant Levels. Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Effects in Breastfed Infants
In one study, no adverse effects were noted in infants during 4 days of maternal therapy with co-trimoxazole.[1]
In a telephone follow-up study, 12 nursing mothers reported taking co-trimoxazole (dosage unspecified). Two mothers reported poor feeding in their infants. Diarrhea was not reported among the exposed infants.[4]
Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk
Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Alternate Drugs to Consider
References
- 1.
- Arnauld R, Soutoul JH, Gallier J, et al. Study on the passage of trimethoprim into mother's milk. Ouest Med 1972;25:959-64.
- 2.
- Borderon E, Soutoul JH, Borderon JC, et al. Excretion of antibiotics in human milk. Med Mal Infect 1975;5:373-6.
- 3.
- Miller RD, Salter AJ. The passage of trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole into breast milk and its significance. In, Daikos CK, ed. Progress in Chemotherapy. Antibacterial chemotherapy 1974;1:687-91.
- 4.
- Ito S, Blajchman A, Stephenson M, et al. Prospective follow-up of adverse reactions in breast-fed infants exposed to maternal medication. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1993;168:1393-9. [PubMed: 8498418]
Substance Identification
Substance Name
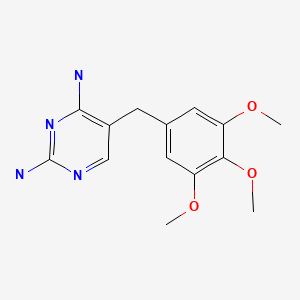
Trimethoprim
CAS Registry Number
738-70-5
Drug Class
Breast Feeding
Lactation
Milk, Human
Anti-Infective Agents, Urinary
Antibacterial Agents
Folic Acid Antagonists
Disclaimer: Information presented in this database is not meant as a substitute for professional judgment. You should consult your healthcare provider for breastfeeding advice related to your particular situation. The U.S. government does not warrant or assume any liability or responsibility for the accuracy or completeness of the information on this Site.
Publication Details
Publication History
Last Revision: November 15, 2024.
Copyright
Attribution Statement: LactMed is a registered trademark of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
Publisher
National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, Bethesda (MD)
NLM Citation
Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Child Health and Human Development; 2006-. Trimethoprim. [Updated 2024 Nov 15].