Gene expression reprogramming of Pseudomonas alloputida in response to arginine through the transcriptional regulator ArgR
- PMID: 38511653
- PMCID: PMC10963909
- DOI: 10.1099/mic.0.001449
Gene expression reprogramming of Pseudomonas alloputida in response to arginine through the transcriptional regulator ArgR
Abstract
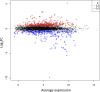
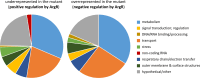
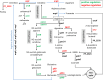
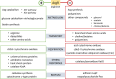
Different bacteria change their life styles in response to specific amino acids. In Pseudomonas putida (now alloputida) KT2440, arginine acts both as an environmental and a metabolic indicator that modulates the turnover of the intracellular second messenger c-di-GMP, and expression of biofilm-related genes. The transcriptional regulator ArgR, belonging to the AraC/XylS family, is key for the physiological reprogramming in response to arginine, as it controls transport and metabolism of the amino acid. To further expand our knowledge on the roles of ArgR, a global transcriptomic analysis of KT2440 and a null argR mutant growing in the presence of arginine was carried out. Results indicate that this transcriptional regulator influences a variety of cellular functions beyond arginine metabolism and transport, thus widening its regulatory role. ArgR acts as positive or negative modulator of the expression of several metabolic routes and transport systems, respiratory chain and stress response elements, as well as biofilm-related functions. The partial overlap between the ArgR regulon and those corresponding to the global regulators RoxR and ANR is also discussed.
Keywords: arginine; gene expression; metabolism; redox; regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of the Transcriptional Regulator ArgR in the Connection between Arginine Metabolism and c-di-GMP Signaling in Pseudomonas putida.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022 Apr 12;88(7):e0006422. doi: 10.1128/aem.00064-22. Epub 2022 Mar 7. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35254100 Free PMC article.
-
ArgR directly inhibits lipA transcription in Pseudomonas protegens Pf-5.Biochimie. 2019 Dec;167:34-41. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2019.08.018. Epub 2019 Sep 3. Biochimie. 2019. PMID: 31491441
-
The phosphodiesterase RmcA contributes to the adaptation of Pseudomonas putida to l-arginine.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2023 Jan 17;370:fnad077. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnad077. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2023. PMID: 37550221 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Metabolic Response of Pseudomonas putida to L-arginine.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024 Mar 2. doi: 10.1007/5584_2024_797. Online ahead of print. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 38429473
-
Nutrient Sensing and Biofilm Modulation: The Example of L-arginine in Pseudomonas.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 15;23(8):4386. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084386. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35457206 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

