Does sex affect the efficacy of systemic pharmacological treatments of pain in knee osteoarthritis? A systematic review
- PMID: 38375468
- PMCID: PMC10875265
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ocarto.2024.100438
Does sex affect the efficacy of systemic pharmacological treatments of pain in knee osteoarthritis? A systematic review
Abstract
Objective: To determine whether sex influences the analgesic efficacy of systemic pharmacological treatment in patients with knee osteoarthritis.
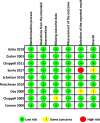
Design: A systematic review, guided by Cochrane methods, sourced studies from Medline, Cochrane Library, Embase, and CINAHL Plus with Full Text as of October 10, 2022. Eligible studies were double-blind RCTs evaluating systemic pharmacological treatments for knee osteoarthritis in adults, with minimum 30-day treatment duration, reporting sex-specific results or mentioning sex subgroup analysis for analgesic efficacy. The risk of bias was assessed using the Cochrane Risk of Bias tool version 2 (RoB 2).
Results: 9 studies (5201 participants) met inclusion criteria, analyzing drugs including duloxetine, etoricoxib, tapentadol, naproxcinod, lutikizumab, and rofecoxib. Only one study reported sex-specific results. Review findings suggested no significant sex-based differences in treatment efficacy, however, data were limited due to a lack of sex-specific reporting or inclusion of sex in subgroup analyses.
Conclusions: Current evidence does not support the existence of sex differences in the analgesic efficacy of systemic knee osteoarthritis treatments. However, this conclusion is substantially limited by the paucity of sex-specific reporting of results or subgroup analyses in most primary studies, emphasizing the need for future research to report on sex-stratified data to allow for comprehensive, personalized treatment strategies.
Keywords: Knee osteoarthritis; Osteoarthritis pain; Sex differences; Systematic review; Treatment efficacy.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Intra-articular viscosupplementation with hylan g-f 20 to treat osteoarthritis of the knee: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2005;5(10):1-66. Epub 2005 Jun 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2005. PMID: 23074461 Free PMC article.
-
Palliative Treatment of Cancer-Related Pain [Internet].Oslo, Norway: Knowledge Centre for the Health Services at The Norwegian Institute of Public Health (NIPH); 2005 Dec. Report from Norwegian Knowledge Centre for the Health Services (NOKC) No. 09-2005. Oslo, Norway: Knowledge Centre for the Health Services at The Norwegian Institute of Public Health (NIPH); 2005 Dec. Report from Norwegian Knowledge Centre for the Health Services (NOKC) No. 09-2005. PMID: 29320015 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
WITHDRAWN: Non-aspirin, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for treating osteoarthritis of the knee.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jul 18;2006(1):CD000142. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000142.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. PMID: 17636601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Paracetamol versus placebo for knee and hip osteoarthritis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Feb 25;2(2):CD013273. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013273. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 30801133 Free PMC article.
References
-
- CDC. Osteoarthritis (OA) cdc.gov. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/arthritis/basics/osteoarthritis.htm Available from:
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous