Tisotumab Vedotin in Combination With Carboplatin, Pembrolizumab, or Bevacizumab in Recurrent or Metastatic Cervical Cancer: Results From the innovaTV 205/GOG-3024/ENGOT-cx8 Study
- PMID: 37651655
- PMCID: PMC10730069
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.23.00720
Tisotumab Vedotin in Combination With Carboplatin, Pembrolizumab, or Bevacizumab in Recurrent or Metastatic Cervical Cancer: Results From the innovaTV 205/GOG-3024/ENGOT-cx8 Study
Abstract
Purpose: Tissue factor is highly expressed in cervical carcinoma and can be targeted by tisotumab vedotin (TV), an antibody-drug conjugate. This phase Ib/II study evaluated TV in combination with bevacizumab, pembrolizumab, or carboplatin for recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer (r/mCC).
Methods: This open-label, multicenter study (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03786081) included dose-escalation arms that assessed dose-limiting toxicities (DLTs) and identified the recommended phase II dose (RP2D) of TV in combination with bevacizumab (arm A), pembrolizumab (arm B), or carboplatin (arm C). The dose-expansion arms evaluated TV antitumor activity and safety at RP2D in combination with carboplatin as first-line (1L) treatment (arm D) or with pembrolizumab as 1L (arm E) or second-/third-line (2L/3L) treatment (arm F). The primary end point of dose expansion was objective response rate (ORR).
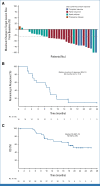
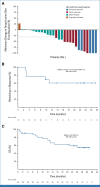
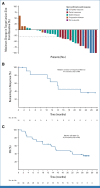
Results: A total of 142 patients were enrolled. In dose escalation (n = 41), no DLTs were observed; the RP2D was TV 2 mg/kg plus bevacizumab 15 mg/kg on day 1 once every 3 weeks, pembrolizumab 200 mg on day 1 once every 3 weeks, or carboplatin AUC 5 on day 1 once every 3 weeks. In dose expansion (n = 101), the ORR was 54.5% (n/N, 18/33; 95% CI, 36.4 to 71.9) with 1L TV + carboplatin (arm D), 40.6% (n/N, 13/32; 95% CI, 23.7 to 59.4) with 1L TV + pembrolizumab (arm E), and 35.3% (12/34; 19.7 to 53.5) with 2L/3L TV + pembrolizumab (arm F). The median duration of response was 8.6 months, not reached, and 14.1 months, in arms D, E, and F, respectively. Grade ≥3 adverse events (≥15%) were anemia, diarrhea, nausea, and thrombocytopenia in arm D and anemia in arm F (none ≥15%, arm E).
Conclusion: TV in combination with bevacizumab, carboplatin, or pembrolizumab demonstrated manageable safety and encouraging antitumor activity in treatment-naive and previously treated r/mCC.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tisotumab vedotin in recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer.Curr Probl Cancer. 2023 Jun;47(3):100952. doi: 10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2023.100952. Epub 2023 Feb 10. Curr Probl Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36842202 Review.
-
Tisotumab vedotin in Japanese patients with recurrent/metastatic cervical cancer: Results from the innovaTV 206 study.Cancer Sci. 2022 Aug;113(8):2788-2797. doi: 10.1111/cas.15443. Epub 2022 Jun 15. Cancer Sci. 2022. PMID: 35633184 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of tisotumab vedotin in previously treated recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer (innovaTV 204/GOG-3023/ENGOT-cx6): a multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 2 study.Lancet Oncol. 2021 May;22(5):609-619. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00056-5. Epub 2021 Apr 9. Lancet Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33845034 Clinical Trial.
-
Phase 1b study of anti-NaPi2b antibody-drug conjugate lifastuzumab vedotin (DNIB0600A) in patients with platinum-sensitive recurrent ovarian cancer.Gynecol Oncol. 2020 Sep;158(3):631-639. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2020.05.039. Epub 2020 Jun 11. Gynecol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32534811 Clinical Trial.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Tisotumab Vedotin in the Treatment of Recurrent or Metastatic Cervical Cancer: A Short Report on the Emerging Data.Cancer Manag Res. 2023 Sep 27;15:1063-1072. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S294080. eCollection 2023. Cancer Manag Res. 2023. PMID: 37790898 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advanced, recurrent, and persistent cervical cancer management: in the era of immunotherapy.Front Oncol. 2024 Aug 5;14:1392639. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1392639. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39161386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibody drug conjugates in recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer: a focus on tisotumab vedotin state of art.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2024 Sep 22;16:17588359241277647. doi: 10.1177/17588359241277647. eCollection 2024. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39323928 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immuno-Molecular Targeted Therapy Use and Survival Benefit in Patients with Stage IVB Cervical Carcinoma in Commission on Cancer®-Accredited Facilities in the United States.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Mar 6;16(5):1071. doi: 10.3390/cancers16051071. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38473428 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody-drug conjugates and immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer treatment: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 27;14(1):22357. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-68311-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39333227 Free PMC article.
-
Recent breakthroughs in the management of locally advanced and recurrent/metastatic cervical cancer.J Gynecol Oncol. 2024 Jan;35(1):e30. doi: 10.3802/jgo.2024.35.e30. Epub 2023 Nov 30. J Gynecol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38072400 Free PMC article. Review.

