Safety and efficacy of tafasitamab with or without lenalidomide added to first-line R-CHOP for DLBCL: the phase 1b First-MIND study
- PMID: 37369099
- PMCID: PMC10651865
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2023020637
Safety and efficacy of tafasitamab with or without lenalidomide added to first-line R-CHOP for DLBCL: the phase 1b First-MIND study
Abstract
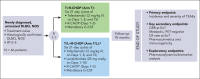
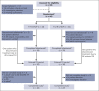
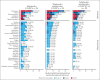
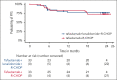
Anti-CD19 immunotherapy tafasitamab is used in combination with lenalidomide in patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) who are ineligible for autologous stem cell transplant. Open-label, phase 1b, First-MIND study assessed safety and preliminary efficacy of tafasitamab + R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) ± lenalidomide as first-line therapy in patients with DLBCL. From December 2019 to August 2020, 83 adults with untreated DLBCL (International Prognostic Index 2-5) were screened and 66 were randomly assigned (33 per arm) to R-CHOP-tafasitamab (arm T) or R-CHOP-tafasitamab-lenalidomide (arm T/L) for 6 cycles. Primary end point was safety; secondary end points included end-of-treatment (EoT) overall response rate (ORR) and complete response (CR) rate. All patients had ≥1 treatment-emergent adverse event, mostly grade 1 or 2. Grade ≥3 neutropenia and thrombocytopenia occurred, respectively, in 57.6% and 12.1% (arm T) and 84.8% and 36.4% (arm T/L) of patients. Nonhematologic toxicities occurred at similar rates among arms. R-CHOP mean relative dose intensity was ≥89% in both arms. EoT ORR was 75.8% (CR 72.7%) in arm T and 81.8% (CR 66.7%) in arm T/L; best ORR across visits was 90.0% and 93.9%. Eighteen-month duration of response and of CR rates were 72.7% and 74.5% (arm T) and 78.7% and 86.5% (arm T/L); 24-month progression-free and overall survival rates were 72.7% and 90.3% (arm T) and 76.8% and 93.8% (arm T/L). Manageable safety and promising signals of efficacy were observed in both arms. Potential benefit of adding tafasitamab + lenalidomide to R-CHOP is being investigated in phase 3 frontMIND (NCT04824092). This study is registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT04134936.
© 2023 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: D.B. received consultancy fees from Roche, Gilead Sciences, Janssen-Cilag, Takeda, MorphoSys AG, and Debiopharm Group; travel, accommodations, and expenses from Roche, Gilead Sciences, and Takeda; and research funding from Roche, Gilead Sciences, Janssen-Cilag, Takeda, MorphoSys AG, Pharmacyclics, Archigen Biotech, and Dr Reddy’s Laboratories. M.A. received consultancy from Incyte, Gilead, Karyopharm, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Takeda; travel, accommodations, and expenses from Roche, Gilead, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, and AbbVie; and research funding from Johnson & Johnson, Roche, and Takeda. E.P.P. received consultancy fees from Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene, Sanofi, GlaxoSmithKline, and Incyte; travel, accommodations, and expenses from Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene, and AbbVie; and speaker's bureau fees from Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene, AbbVie, Takeda, Sanofi, and AstraZeneca. P.B.S. received consultancy fees from Roche, AbbVie, Gilead, Janssen, AstraZeneca, Takeda, MSD, Bristol Myers Squibb, Incyte, and BeiGene; research funding from Roche, Takeda, and Incyte; and honoraria from Roche, AbbVie, Gilead, Janssen, AstraZeneca, MSD, Bristol Myers Squibb, Incyte, and BeiGene. M.T. received consultancy fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Gilead, Incyte, Janssen, MorphoSys AG, Roche, Takeda, Celgene, and Novartis and travel, accommodations, and expenses from AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb, Gilead, Janssen, Roche, and Takeda; received honoraria from AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Incyte, Janssen, MorphoSys AG, Roche, Takeda, Novartis, Portola, and AstraZeneca; is a member in an entity’s board of directors or advisory committees from AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb, Incyte, Janssen, MorphoSys AG, Roche, Takeda, Novartis, and Portola; and is employed by the 1st Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, General Hospital in Prague. J.D. received research funding from MorphoSys AG and Regeneron. M.W.-L. is employed at MorphoSys AG. S.W. is employed at MorphoSys AG. A.M. is employed at MorphoSys AG. M.D.-H. was employed at MorphoSys AG (until 31 December 2021). J.M.B. received consultancy fees from MorphoSys AG, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Verastem Oncology, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Kymera Therapeutics, X4 Pharmaceuticals, AbbVie, SeaGen, Kura Oncology, Roche/Genentech, Epizyme, and BeiGene and received speaker's bureau fees from SeaGen and BeiGene. G.S.N. received consultancy fees from Celgene, MorphoSys AG, Genentech, Selvita, Debiopharm Group, and Kite/Gilead; received research funding from Celgene, NanoString Technologies, and MorphoSys AG; and is a member on an entity’s board of directors or advisory committees at Celgene, MorphoSys AG, Genentech, Selvita, Debiopharm Group, and Kite/Gilead. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
The current affiliation for M.D.-H is Daiichi-Sankyo Europe GmbH, Munich, Germany.
Figures

Comment in
-
A new frontier for R-CHOP: is two better than one?Blood. 2023 Oct 19;142(16):1331-1332. doi: 10.1182/blood.2023021521. Blood. 2023. PMID: 37856095 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Addition of Lenalidomide to R-CHOP Improves Outcomes in Newly Diagnosed Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma in a Randomized Phase II US Intergroup Study ECOG-ACRIN E1412.J Clin Oncol. 2021 Apr 20;39(12):1329-1338. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.01375. Epub 2021 Feb 8. J Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33555941 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
ROBUST: A Phase III Study of Lenalidomide Plus R-CHOP Versus Placebo Plus R-CHOP in Previously Untreated Patients With ABC-Type Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma.J Clin Oncol. 2021 Apr 20;39(12):1317-1328. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.01366. Epub 2021 Feb 23. J Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33621109 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Combination of ibrutinib with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) for treatment-naive patients with CD20-positive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma: a non-randomised, phase 1b study.Lancet Oncol. 2014 Aug;15(9):1019-26. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70311-0. Epub 2014 Jul 17. Lancet Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25042202 Clinical Trial.
-
Ideal dose intensity of R-CHOP in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2022 Jun;22(6):583-595. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2022.2071262. Epub 2022 May 5. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2022. PMID: 35472312 Review.
-
Rituximab: a review of its use in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukaemia.Drugs. 2003;63(8):803-43. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200363080-00005. Drugs. 2003. PMID: 12662126 Review.
Cited by
-
Tafasitamab for the treatment of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024 Dec 31;20(1):2309701. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2024.2309701. Epub 2024 Feb 1. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024. PMID: 38299612 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Targets and Advanced Therapies in Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphomas.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jun 17;16(12):2243. doi: 10.3390/cancers16122243. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38927948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The future of immunotherapy for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Int J Cancer. 2025 Jan 15;156(2):251-261. doi: 10.1002/ijc.35156. Epub 2024 Sep 25. Int J Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39319495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A real-world pharmacovigilance study of polatuzumab vedotin based on the FDA adverse event reporting system (FAERS).Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jun 25;15:1405023. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1405023. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38983914 Free PMC article.
-
New Insights into First-Line Therapy in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Are We Improving Outcomes?J Clin Med. 2024 Mar 27;13(7):1929. doi: 10.3390/jcm13071929. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38610693 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wild CP, Weiderpass E, Stewart BW, editors. World Cancer Report: Cancer Research for Cancer Prevention. International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2020. http://publications.iarc.fr/586
-
- Coiffier B, Thieblemont C, Van Den Neste E, et al. Long-term outcome of patients in the LNH-98.5 trial, the first randomized study comparing rituximab-CHOP to standard CHOP chemotherapy in DLBCL patients: a study by the Groupe d’Etudes des Lymphomes de l’Adulte. Blood. 2010;116(12):2040–2045. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sehn LH, Berry B, Chhanabhai M, et al. The revised International Prognostic Index (R-IPI) is a better predictor of outcome than the standard IPI for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP. Blood. 2007;109(5):1857–1861. - PubMed
-
- Gleeson M, Counsell N, Cunningham D, et al. A comparison of prognostic indices in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma within the UK NCRI R-CHOP 14 versus 21 phase III trial [abstract] Blood. 2018;132(suppl 1):2956.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

