How do patients and other members of the public engage with the orphan drug development? A narrative qualitative synthesis
- PMID: 37069597
- PMCID: PMC10108537
- DOI: 10.1186/s13023-023-02682-w
How do patients and other members of the public engage with the orphan drug development? A narrative qualitative synthesis
Abstract
Background: The diversity of patient experiences of orphan drug development has until recently been overlooked, with the existing literature reporting the experience of some patients and not others. The current evidence base (the best available current research) is dominated by quantitative surveys and patient reported outcome measures defined by researchers. Where research that uses qualitative methods of data collection and analysis has been conducted, patient experiences have been studied using content analysis and automatic textual analysis, rather than in-depth qualitative analytical methods. Systematic reviews of patient engagement in orphan drug development have also excluded qualitative studies. The aim of this paper is to review qualitative literature about how patients and other members of the public engage with orphan drug development.
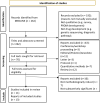
Methods: We conducted a systematic search of qualitative papers describing a range of patient engagement practices and experiences were identified and screened. Included papers were appraised using a validated tool (CASP), supplemented by reporting guidance (COREQ), by two independent researchers.
Results: 262 papers were identified. Thirteen papers reported a range of methods of qualitative data collection. Many conflated patient and public involvement and engagement (PPIE) with qualitative research. Patients were typically recruited via their physician or patient organisations. We identified an absence of overarching philosophical or methodological frameworks, limited details of informed consent processes, and an absence of recognisable methods of data analysis. Our narrative synthesis suggests that patients and caregivers need to be involved in all aspects of trial design, including the selection of clinical endpoints that capture a wider range of outcomes, the identification of means to widen access to trial participation, the development of patient facing materials to optimise their decision making, and patients included in the dissemination of trial results.
Conclusions: This narrative qualitative synthesis identified the explicit need for methodological rigour in research with patients with rare diseases (e.g. appropriate and innovative use of qualitative methods or PPIE, rather than their conflation); strenuous efforts to capture the perspectives of under-served, under-researched or seldom listened to communities with experience of rare diseases (e.g. creative recruitment and wider adoption of post-colonial practices); and a re-alignment of the research agenda (e.g. the use of co-design to enable patients to set the agenda, rather than respond to what they are being offered).
Keywords: Orphan drugs; Patient engagement; Patient involvement; Qualitative research; Rare diseases; Systematic review.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
The Effectiveness of Integrated Care Pathways for Adults and Children in Health Care Settings: A Systematic Review.JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2009;7(3):80-129. doi: 10.11124/01938924-200907030-00001. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2009. PMID: 27820426
-
Health professionals' experience of teamwork education in acute hospital settings: a systematic review of qualitative literature.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016 Apr;14(4):96-137. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-1843. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016. PMID: 27532314 Review.
-
The experience of patient partners in research: a qualitative systematic review and thematic synthesis.Res Involv Engagem. 2022 Oct 3;8(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s40900-022-00388-0. Res Involv Engagem. 2022. PMID: 36192817 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Directive 2001/20/EC of the European Parliament and the Council of 4 Apr 2001 on the approximation of laws, regulations and administrative provisions of the Member States relating to the implementation of good clinical practice in the conduct of clinical trials on medicinal products for human use. Off J Eur Commun. 2001, L121. - PubMed
-
- Regulation (EU) No 536/2014 of the European Parliament and the Council of 16 April 2014 on clinical trials on medicinal products for human use, and repealing Directive 2001/20/EC (Text with EEA relevance). Off J Eur Commun. 2014. L 158/1.
-
- Department of Health & Social Care. The UK Rare Diseases Framework. 2021. https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploa...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

