Safety of Fezolinetant for Vasomotor Symptoms Associated With Menopause: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 36897180
- PMCID: PMC10026946
- DOI: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000005114
Safety of Fezolinetant for Vasomotor Symptoms Associated With Menopause: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the safety, tolerability, and effect of fezolinetant on endometrial health over 52 weeks.
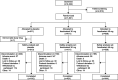
Methods: We conducted a phase 3, randomized, double-blind, 52-week safety study (SKYLIGHT 4 [Study to Find Out How Safe Long-term Treatment With Fezolinetant is in Women With Hot Flashes Going Through Menopause]) of placebo, fezolinetant 30 mg, and fezolinetant 45 mg once daily (1:1:1). Participants were postmenopausal and seeking treatment for vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause. Primary endpoints were treatment-emergent adverse events, percentage of participants with endometrial hyperplasia, and percentage with endometrial malignancy. Endometrial hyperplasia or malignancy was evaluated according to U.S. Food and Drug Administration guidance (point estimate of 1% or less with an upper bound of one-sided 95% CI of 4% or less). Secondary endpoints included change in bone mineral density (BMD) and trabecular bone score. A sample size of 1,740 was calculated to enable observation of one or more events (≈80% probability for events with background rate of less than 1%).
Results: A total of 1,830 participants were randomized and took one or more medication dose (July 2019-January 2022). Treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in 64.1% (391/610) of the placebo group, 67.9% (415/611) of the fezolinetant 30-mg group, and 63.9% (389/609) of the fezolinetant 45-mg group. Treatment-emergent adverse events leading to discontinuation were similar across groups (placebo, 26/610 [4.3%]; fezolinetant 30 mg, 34/611 [5.6%]; fezolinetant 45 mg, 28/609 [4.6%]). Endometrial safety was assessed in 599 participants. In the fezolinetant 45-mg group, 1 of 203 participants had endometrial hyperplasia (0.5%; upper limit of one-sided 95% CI 2.3%); there were no cases in the placebo (0/186) or fezolinetant 30 mg (0/210) group. Endometrial malignancy occurred in 1 of 210 in the fezolinetant 30-mg group (0.5%; 95% CI 2.2%) with no cases in the other groups. Liver enzyme elevations more than three times the upper limit of normal occurred in 6 of 583 placebo, 8 of 590 fezolinetant 30 mg, and 12 of 589 fezolinetant 45 mg participants; no Hy's law cases were reported (ie, no severe drug-induced liver injury with alanine aminotransferase or aspartate aminotransferase more than three times the upper limit of normal and total bilirubin more than two times the upper limit of normal, with no elevation of alkaline phosphatase and no other reason to explain the combination). Changes in BMD and trabecular bone score were similar across groups.
Conclusion: Results from SKYLIGHT 4 confirm the 52-week safety and tolerability of fezolinetant and support its continued development.
Funding source: Astellas Pharma Inc.
Clinical trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov , NCT04003389.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Fezolinetant for treatment of moderate-to-severe vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause (SKYLIGHT 1): a phase 3 randomised controlled study.Lancet. 2023 Apr 1;401(10382):1091-1102. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00085-5. Epub 2023 Mar 13. Lancet. 2023. PMID: 36924778 Clinical Trial.
-
Long-term safety of fezolinetant in Chinese women with vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause: the phase 3 open-label MOONLIGHT 3 clinical trial.J Int Med Res. 2024 May;52(5):3000605241246624. doi: 10.1177/03000605241246624. J Int Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38818887 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Fezolinetant treatment of moderate-to-severe vasomotor symptoms due to menopause: effect of intrinsic and extrinsic factors in two phase 3 studies (SKYLIGHT 1 and 2).Menopause. 2024 Apr 1;31(4):247-257. doi: 10.1097/GME.0000000000002340. Menopause. 2024. PMID: 38517210 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Fezolinetant: A New Nonhormonal Treatment for Vasomotor Symptoms.J Pharm Technol. 2023 Dec;39(6):291-297. doi: 10.1177/87551225231198700. Epub 2023 Sep 16. J Pharm Technol. 2023. PMID: 37974591 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fezolinetant for the treatment of vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause: a meta-analysis.Climacteric. 2024 Jun;27(3):245-254. doi: 10.1080/13697137.2024.2334083. Epub 2024 Apr 15. Climacteric. 2024. PMID: 38619017 Review.
Cited by
-
Primary ovarian insufficiency: update on clinical and genetic findings.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Sep 26;15:1464803. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1464803. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39391877 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of fezolinetant, a neurokinin-3 antagonist, in treating vasomotor symptoms in postmenopausal women: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Dec 15;102(50):e36592. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036592. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 38115258 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of fezolinetant for moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause among women in East Asia: a phase 3 randomized study (MOONLIGHT I).J Int Med Res. 2024 May;52(5):3000605241247684. doi: 10.1177/03000605241247684. J Int Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38818888 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Fezolinetant for moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause.Aust Prescr. 2024 Oct;47(5):162-163. doi: 10.18773/austprescr.2024.042. Aust Prescr. 2024. PMID: 39526081 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Fezolinetant: First Approval.Drugs. 2023 Aug;83(12):1137-1141. doi: 10.1007/s40265-023-01917-1. Drugs. 2023. PMID: 37462862 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

