Exploratory Analysis Comparing Fosnetupitant Versus Fosaprepitant for Prevention of Highly Emetogenic Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting (CINV): A Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase 3 Study (CONSOLE)
- PMID: 35246827
- PMCID: PMC9098704
- DOI: 10.1007/s40487-022-00188-2
Exploratory Analysis Comparing Fosnetupitant Versus Fosaprepitant for Prevention of Highly Emetogenic Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting (CINV): A Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase 3 Study (CONSOLE)
Abstract
Introduction: We describe the results of an exploratory analysis performed on the first head-to-head study (JapicCTI-194611) comparing two different intravenous (IV) neurokinin 1 (NK1) receptor antagonists, fosnetupitant and fosaprepitant, in combination with palonosetron (PALO) and dexamethasone (DEX) for the prevention of highly emetogenic chemotherapy (HEC)-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV). This analysis was performed to validate the findings of the primary analysis (previously published) utilizing a last observation carried forward (LOCF) approach for missing values for the efficacy endpoint of complete response (no emetic event and no rescue medication), while also evaluating the time periods encompassing the 0-168-hour (h) "extended overall phase" interval.
Methods: Patients scheduled to receive cisplatin-based chemotherapy were randomized 1:1 to fosnetupitant 235 mg or fosaprepitant 150 mg in combination with PALO 0.75 mg and DEX. Complete response rates were calculated and compared (stratified by age category and sex with a Mantel-Haenszel test) during the study's primary overall phase (0-120 h) and during additional time intervals of interest [acute (0-24 h), delayed (24-120 h), extended delayed (> 24-168 h), beyond delayed (120-168 h), and extended overall (0-168 h)].
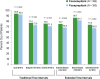
Results: A total of 785 patients were included (fosnetupitant N = 392, fosaprepitant N = 393). Complete response rates were numerically higher for fosnetupitant versus fosaprepitant for all time intervals and statistically significant for the extended overall phase. Complete response rates for fosnetupitant versus fosaprepitant during the overall, acute, delayed, extended delayed, beyond delayed, and extended overall phases were 75.5% vs. 71.0% (p = 0.1530), 93.9% vs. 92.6% (p = 0.4832), 77.0% vs. 72.8% (p = 0.1682), 74.7% vs. 68.4% (p = 0.0506), 86.7% vs. 81.7% (p = 0.0523), and 73.5% vs. 66.9% (p = 0.0450), respectively.
Conclusion: In this exploratory analysis, fosnetupitant appeared to be more effective than fosaprepitant in preventing CINV associated with cisplatin-based HEC during the extended 7-day period following chemotherapy. INFOGRAPHIC.
Keywords: Antiemetic; Aprepitant; CINV; Fosaprepitant; Fosnetupitant; NEPA; Palonosetron.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pooled Analysis of Studies Evaluating Fosnetupitant and Risk Factors for Cisplatin-Induced Nausea and Vomiting During the Extended Overall Phase.Adv Ther. 2023 Nov;40(11):4928-4944. doi: 10.1007/s12325-023-02648-1. Epub 2023 Sep 16. Adv Ther. 2023. PMID: 37715851 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase III Study of Fosnetupitant Versus Fosaprepitant for Prevention of Highly Emetogenic Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting: CONSOLE.J Clin Oncol. 2022 Jan 10;40(2):180-188. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.01315. Epub 2021 Nov 18. J Clin Oncol. 2022. PMID: 34793245 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A randomized phase III study evaluating the efficacy of single-dose NEPA, a fixed antiemetic combination of netupitant and palonosetron, versus an aprepitant regimen for prevention of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV) in patients receiving highly emetogenic chemotherapy (HEC).Ann Oncol. 2018 Feb 1;29(2):452-458. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx698. Ann Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29092012 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Netupitant/Palonosetron: A Review in Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting.Drugs. 2021 Jul;81(11):1331-1342. doi: 10.1007/s40265-021-01558-2. Epub 2021 Jul 22. Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34292534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of the combination neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist, palonosetron, and dexamethasone compared to others for the prophylaxis of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Ann Palliat Med. 2018 Apr;7(2):221-233. doi: 10.21037/apm.2018.03.09. Ann Palliat Med. 2018. PMID: 29764184 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy and safety of 5HT3RA, DEX, and NK1RA for the prevention of FOLFIRINOX-induced nausea and vomiting in patients with pancreatic cancer: a retrospective cohort study.Support Care Cancer. 2023 Oct 26;31(12):657. doi: 10.1007/s00520-023-08136-0. Support Care Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37884842
-
Single-dose NEPA versus an aprepitant regimen for prevention of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting in patients receiving moderately emetogenic chemotherapy.Cancer Med. 2023 Aug;12(15):15769-15776. doi: 10.1002/cam4.6121. Epub 2023 Aug 3. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 37537943 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Real-World Treatment Outcomes, Healthcare Resource Use, and Costs Associated with Antiemetics Among Cancer Patients on Cisplatin-Based Chemotherapy.Adv Ther. 2023 Jul;40(7):3217-3226. doi: 10.1007/s12325-023-02537-7. Epub 2023 May 28. Adv Ther. 2023. PMID: 37245189 Free PMC article.
-
Pooled Analysis of Studies Evaluating Fosnetupitant and Risk Factors for Cisplatin-Induced Nausea and Vomiting During the Extended Overall Phase.Adv Ther. 2023 Nov;40(11):4928-4944. doi: 10.1007/s12325-023-02648-1. Epub 2023 Sep 16. Adv Ther. 2023. PMID: 37715851 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Fosnetupitant for the Prevention of Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting: A Short Review and Clinical Perspective.Adv Ther. 2023 May;40(5):1913-1925. doi: 10.1007/s12325-023-02474-5. Epub 2023 Mar 8. Adv Ther. 2023. PMID: 36884027 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources