A Highly Sensitive Cell-Based TLR Reporter Platform for the Specific Detection of Bacterial TLR Ligands
- PMID: 35087538
- PMCID: PMC8786796
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.817604
A Highly Sensitive Cell-Based TLR Reporter Platform for the Specific Detection of Bacterial TLR Ligands
Abstract
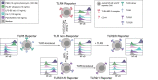
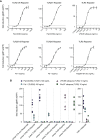
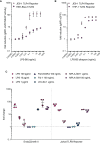
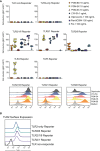
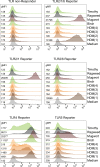
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are primary pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), which recognize conserved microbial components. They play important roles in innate immunity but also in the initiation of adaptive immune responses. Impurities containing TLR ligands are a frequent problem in research but also for the production of therapeutics since TLR ligands can exert strong immunomodulatory properties even in minute amounts. Consequently, there is a need for sensitive tools to detect TLR ligands with high sensitivity and specificity. Here we describe the development of a platform based on a highly sensitive NF-κB::eGFP reporter Jurkat JE6-1 T cell line for the detection of TLR ligands. Ectopic expression of TLRs and their coreceptors and CRISPR/Cas9-mediated deletion of endogenously expressed TLRs was deployed to generate reporter cell lines selectively expressing functional human TLR2/1, TLR2/6, TLR4 or TLR5 complexes. Using well-defined agonists for the respective TLR complexes we could demonstrate high specificity and sensitivity of the individual reporter lines. The limit of detection for LPS was below 1 pg/mL and ligands for TLR2/1 (Pam3CSK4), TLR2/6 (Fsl-1) and TLR5 (flagellin) were detected at concentrations as low as 1.0 ng/mL, 0.2 ng/mL and 10 pg/mL, respectively. We showed that the JE6-1 TLR reporter cells have the utility to characterize different commercially available TLR ligands as well as more complex samples like bacterially expressed proteins or allergen extracts. Impurities in preparations of microbial compounds as well as the lack of specificity of detection systems can lead to erroneous results and currently there is no consensus regarding the involvement of TLRs in the recognition of several molecules with proposed immunostimulatory functions. This reporter system represents a highly suitable tool for the definition of structural requirements for agonists of distinct TLR complexes.
Keywords: TLR; bacterial contamination; biosensor; reporter cell; toll-like receptor.
Copyright © 2022 Radakovics, Battin, Leitner, Geiselhart, Paster, Stöckl, Hoffmann-Sommergruber and Steinberger.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A human monocytic NF-κB fluorescent reporter cell line for detection of microbial contaminants in biological samples.PLoS One. 2017 May 24;12(5):e0178220. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0178220. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28542462 Free PMC article.
-
A new cell-based innate immune receptor assay for the examination of receptor activity, ligand specificity, signalling pathways and the detection of pyrogens.J Immunol Methods. 2010 Jun 30;358(1-2):93-103. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2010.03.020. Epub 2010 Apr 10. J Immunol Methods. 2010. PMID: 20385141
-
Ligand-induced differential cross-regulation of Toll-like receptors 2, 4 and 5 in intestinal epithelial cells.Mol Immunol. 2007 Jul;44(15):3702-14. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2007.04.001. Epub 2007 May 9. Mol Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17493681
-
Toll-like receptors in bony fish: from genomics to function.Dev Comp Immunol. 2011 Dec;35(12):1263-72. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2011.03.006. Epub 2011 Mar 15. Dev Comp Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21414346 Review.
-
Expression and function of Toll-like receptors in T lymphocytes.Curr Opin Immunol. 2007 Feb;19(1):39-45. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2006.11.007. Epub 2006 Nov 28. Curr Opin Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17129718 Review.
Cited by
-
Toll-like receptors 7 and 9 regulate the proliferation and differentiation of B cells in systemic lupus erythematosus.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 15;14:1093208. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1093208. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36875095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Study of the Synergistic Immunomodulatory and Antifibrotic Effects of Dual-Loaded Budesonide and Serpine1 siRNA Lipid-Polymer Nanoparticles Targeting Macrophage Dysregulation in Tendinopathy.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024 Apr 17;16(15):18643-18657. doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c02363. Epub 2024 Apr 2. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 38564504 Free PMC article.
-
Interrogating ligand-receptor interactions using highly sensitive cellular biosensors.Nat Commun. 2023 Nov 28;14(1):7804. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-43589-1. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 38016944 Free PMC article.
-
An Update on Toll-like Receptor 2, Its Function and Dimerization in Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Processes.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 5;24(15):12464. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512464. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Saturated very long-chain fatty acids regulate macrophage plasticity and invasiveness.J Neuroinflammation. 2022 Dec 17;19(1):305. doi: 10.1186/s12974-022-02664-y. J Neuroinflammation. 2022. PMID: 36528616 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pasare C, Medzhitov R. Toll-Like Receptors: Linking Innate and Adaptive Immunity. In: Gupta S, Paul WE, Steinman R, editors. Mechanisms of Lymphocyte Activation and Immune Regulation X Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. Boston, MA: Springer US. (2005). p. 11–8. doi: 10.1007/0-387-24180-9_2 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

