A Review on Microbial Products and Their Perspective Application as Antimicrobial Agents
- PMID: 34944505
- PMCID: PMC8699383
- DOI: 10.3390/biom11121860
A Review on Microbial Products and Their Perspective Application as Antimicrobial Agents
Abstract
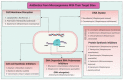
Microorganisms including actinomycetes, archaea, bacteria, fungi, yeast, and microalgae are an auspicious source of vital bioactive compounds. In this review, the existing research regarding antimicrobial molecules from microorganisms is summarized. The potential antimicrobial compounds from actinomycetes, particularly Streptomyces spp.; archaea; fungi including endophytic, filamentous, and marine-derived fungi, mushroom; and microalgae are briefly described. Furthermore, this review briefly summarizes bacteriocins, halocins, sulfolobicin, etc., that target multiple-drug resistant pathogens and considers next-generation antibiotics. This review highlights the possibility of using microorganisms as an antimicrobial resource for biotechnological, nutraceutical, and pharmaceutical applications. However, more investigations are required to isolate, separate, purify, and characterize these bioactive compounds and transfer these primary drugs into clinically approved antibiotics.
Keywords: bacteriocins; chlorellin; filamentous fungi; halocin; lipopeptides; microalgae.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Bacillus genus bacteria are producers of biologically active compounds with antimicrobial effect].Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 2010 May-Jun;(3):85-9. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 2010. PMID: 20737685 Review. Russian.
-
Microalgae: therapeutic potentials and applications.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 May;48(5):4757-4765. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06422-w. Epub 2021 May 24. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34028654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The current status of natural products from marine fungi and their potential as anti-infective agents.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2006 May;33(5):325-37. doi: 10.1007/s10295-005-0070-3. Epub 2006 Jan 21. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2006. PMID: 16429315 Review.
-
Antimicrobial metabolites from marine microorganisms.Chin J Nat Med. 2016 Feb;14(2):101-116. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(16)60003-1. Chin J Nat Med. 2016. PMID: 26968676 Review.
-
Antimicrobial peptides and proteins in the face of extremes: Lessons from archaeocins.Biochimie. 2015 Nov;118:344-55. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2015.06.004. Epub 2015 Jun 17. Biochimie. 2015. PMID: 26092421 Review.
Cited by
-
Chemogenetic activation or inhibition of histaminergic neurons bidirectionally modulates recognition memory formation and retrieval in male and female mice.Sci Rep. 2024 May 17;14(1):11283. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-61998-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38760416 Free PMC article.
-
Reduction of Mycotoxigenic Fungi Growth and Their Mycotoxin Production by Bacillus subtilis QST 713.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Nov 17;14(11):797. doi: 10.3390/toxins14110797. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36422971 Free PMC article.
-
Current Insights in Fungal Importance-A Comprehensive Review.Microorganisms. 2023 May 24;11(6):1384. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11061384. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37374886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymer Conjugates of Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs) with d-Amino Acids (d-aa): State of the Art and Future Opportunities.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Feb 19;14(2):446. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14020446. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35214178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential Chemical Profile of Metabolite Extracts Produced by the Diaporthe citri (G-01) Endophyte Mediated by Varying the Fermented Broth pH.Metabolites. 2022 Jul 26;12(8):692. doi: 10.3390/metabo12080692. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 35893260 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Prevention C.f.D.C.a. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States. [(accessed on 29 January 2021)]; Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/pdf/threats-report/2019-ar-threats-re....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

