Disorders Related to PI3Kδ Hyperactivation: Characterizing the Clinical and Immunological Features of Activated PI3-Kinase Delta Syndromes
- PMID: 34422726
- PMCID: PMC8374435
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2021.702872
Disorders Related to PI3Kδ Hyperactivation: Characterizing the Clinical and Immunological Features of Activated PI3-Kinase Delta Syndromes
Abstract
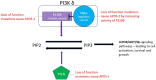
Phosphoinositide-3-kinase δ (PI3Kδ) is found in immune cells and is part of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR/S6K signalling pathway essential to cell survival, growth and differentiation. Hyperactivation of PI3Kδ enzyme results in Activated PI3-kinase delta syndrome (APDS). This childhood onset, autosomal dominant, combined immunodeficiency, is caused by heterozygous gain of function (GOF) mutations in PIK3CD (encodes PI3Kδ catalytic subunit p110δ), mutations in PIK3R1 (encodes PI3Kδ regulatory subunit p85α) or LOF mutations in PTEN (terminates PI3Kδ signalling) leading to APDS1, APDS2 and APDS-Like (APDS-L), respectively. APDS was initially described in 2013 and over 285 cases have now been reported. Prompt diagnosis of APDS is beneficial as targeted pharmacological therapies such as sirolimus and potentially PI3Kδ inhibitors can be administered. In this review, we provide an update on the clinical and laboratory features of this primary immunodeficiency. We discuss the common manifestations such as sinopulmonary infections, bronchiectasis, lymphoproliferation, susceptibility to herpesvirus, malignancy, as well as more rare non-immune features such as short stature and neurodevelopmental abnormalities. Laboratory characteristics, such as antibody deficiency and B cell and T cell, phenotypes are also summarised.
Keywords: PI3 K; PIK3CD; PIK3R1; activated PI3K delta syndrome; phosphatase and tensin homolog.
Copyright © 2021 Redenbaugh and Coulter.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activated PI3 Kinase Delta Syndrome: From Genetics to Therapy.Front Immunol. 2018 Feb 27;9:369. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00369. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29535736 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical, Immunological, and Genetic Features in Patients with Activated PI3Kδ Syndrome (APDS): a Systematic Review.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2020 Dec;59(3):323-333. doi: 10.1007/s12016-019-08738-9. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31111319
-
Conformational disruption of PI3Kδ regulation by immunodeficiency mutations in PIK3CD and PIK3R1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Feb 21;114(8):1982-1987. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1617244114. Epub 2017 Feb 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28167755 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced AKT Phosphorylation of Circulating B Cells in Patients With Activated PI3Kδ Syndrome.Front Immunol. 2018 Apr 5;9:568. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00568. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29675019 Free PMC article.
-
Activated PI3Kinase Delta Syndrome-A Multifaceted Disease.Front Pediatr. 2021 Jun 25;9:652405. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.652405. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34249806 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Initial sirolimus dosage recommendations for pediatric patients with PIK3CD mutation-related immunodeficiency disease.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 14;13:919487. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.919487. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36188573 Free PMC article.
-
Activated phosphoinositde 3-kinase (PI3Kδ) syndrome: an Italian point of view on diagnosis and new advances in treatment.Ital J Pediatr. 2024 May 20;50(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s13052-024-01662-5. Ital J Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 38769568 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Aspects of B Cell Immunodeficiencies: The Past, the Present and the Future.Cells. 2022 Oct 24;11(21):3353. doi: 10.3390/cells11213353. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36359748 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetics of Immune Dysregulation and Cancer Predisposition: Two Sides of the Same Coin.Clin Exp Immunol. 2022 Dec 15;210(2):114-127. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxac089. Clin Exp Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36165533 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Activated phosphoinositide 3-kinase delta syndrome: report of seven cases].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2024 May 15;26(5):499-505. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2312065. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38802911 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous