In vitro identification of antimicrobial hemolytic lipopeptide from halotolerant Bacillus by Zymogram, FTIR, and GC mass analysis
- PMID: 34249269
- PMCID: PMC8244604
- DOI: 10.22038/IJBMS.2021.53419.12022
In vitro identification of antimicrobial hemolytic lipopeptide from halotolerant Bacillus by Zymogram, FTIR, and GC mass analysis
Abstract
Objectives: The multi-drug resistant bacteria and clinical infections are some of the biggest global concerns, so new drugs are needed. Antimicrobial peptides and lipopeptides are new bioactive agents with great potential that can become a new strategy for clinical applications.
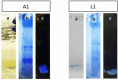
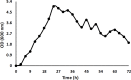
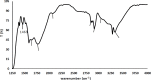
Materials and methods: Some Bacillus strains were isolated based on hemolytic antimicrobial production from the soil. The extracellular proteins were extracted by acidic precipitation and chloroform/methanol method and analyzed by SDS-PAGE electrophoresis and stained with Sudan black. The black fragment was purified and characterized by FTIR, GC/MS, and HPLC analysis to demonstrate the presence of lipids and proteins. The anti-microbial ability and stability of the purified lipopeptide were assayed by the Kirby-Bauer method. Also, it was examined for metal removal.
Results: A new Bacillus halotolerans strain SCM 034 with hemolytic antimicrobial production was isolated. According to GC/MS (detecting C16, C17) and HPLC (detecting leucine, glutamic acid, valine, arginine, glycine, and aspartic acid) data, the black fragment was lipopeptide. Polyacrylamide hydrogel containing lipopeptide and gel purified lipopeptide showed anti-microbial activities against S. aureus and S. cerevisiae that were stable for a few months. Also, the lipopeptide was useful for cation removal and decreased cobalt, nickel, and calcium by 10.81 %, 24.39 %, and 34 %, respectively.
Conclusion: Production of antibacterial lipopeptide hemolysin from this strain is reported for the first time and according to the results, lipopeptides have unique properties with biomedical and pharmaceutical applications. Also, polyacrylamide hydrogel lipopeptide is a promising candidate for wound healing.
Keywords: Antimicrobial; Bacillus halotolerans; Hemolysin; Hydrogel; Lipopeptide; Polyacrylamide gel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Production of biosurfactant by salt-resistant Bacillus in lead-supplemented media: application and toxicity.Int Microbiol. 2023 Nov;26(4):869-880. doi: 10.1007/s10123-023-00334-4. Epub 2023 Feb 22. Int Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36810942
-
Simultaneous Production of Antibacterial Protein and Lipopeptides in Bacillus tequilensis, Detected by MALDI-TOF and GC Mass Analyses.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2023 Jun;15(3):749-760. doi: 10.1007/s12602-021-09883-4. Epub 2022 Jan 16. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2023. PMID: 35034324
-
Antimicrobial potential of a lipopeptide biosurfactant derived from a marine Bacillus circulans.J Appl Microbiol. 2008 Jun;104(6):1675-84. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2007.03701.x. Epub 2008 Jan 9. J Appl Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18194244
-
Lipopeptides from Bacillus and Paenibacillus spp.: A Gold Mine of Antibiotic Candidates.Med Res Rev. 2016 Jan;36(1):4-31. doi: 10.1002/med.21321. Epub 2014 May 28. Med Res Rev. 2016. PMID: 24866700 Review.
-
Structural diversity and applications of lipopeptide biosurfactants as biocontrol agents against phytopathogens: A review.Microbiol Res. 2024 Jan;278:127518. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2023.127518. Epub 2023 Oct 14. Microbiol Res. 2024. PMID: 37897841 Review.
Cited by
-
Production of Lipopeptide Biosurfactant Using Wastewater from Parboiled Paddy Rice and Evaluation of Antifungal Property of the Biosurfactant Against Two Dermatophyte Fungi.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2024 Dec;196(12):9010-9026. doi: 10.1007/s12010-024-05000-7. Epub 2024 Aug 1. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39088023
-
Unveiling Antibacterial Potential and Physiological Characteristics of Thermophilic Bacteria Isolated from a Hot Spring in Iran.Microorganisms. 2024 Apr 20;12(4):834. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12040834. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38674778 Free PMC article.
-
Production of biosurfactant by salt-resistant Bacillus in lead-supplemented media: application and toxicity.Int Microbiol. 2023 Nov;26(4):869-880. doi: 10.1007/s10123-023-00334-4. Epub 2023 Feb 22. Int Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36810942
References
-
- Meena KR, Tandon T, Sharma A, Kanwar SS. Lipopeptide antibiotic production by Bacillusvelezensis KLP2016. J Appl Pharm Sci. 2018;8:91–98.
-
- Padmavathi AR, Abinaya B, Pandian SK. Phenol, 2, 4-bis (1, 1-dimethylethyl) of marine bacterial origin inhibits quorum sensing mediated biofilm formation in the uropathogen Serratiamarcescens. Biofouling. 2014;30:1111–1122. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
