COVID-19 deep classification network based on convolution and deconvolution local enhancement
- PMID: 34182330
- PMCID: PMC8216864
- DOI: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104588
COVID-19 deep classification network based on convolution and deconvolution local enhancement
Abstract
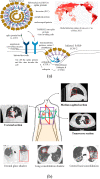
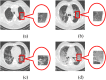
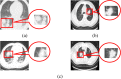
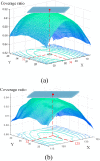
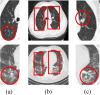
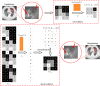
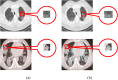
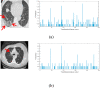
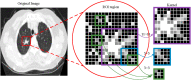
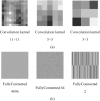
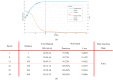
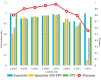
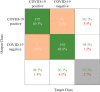
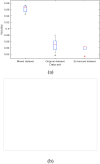
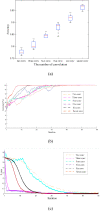
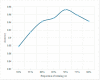
Computer Tomography (CT) detection can effectively overcome the problems of traditional detection of Corona Virus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), such as lagging detection results and wrong diagnosis results, which lead to the increase of disease infection rate and prevalence rate. The novel coronavirus pneumonia is a significant difference between the positive and negative patients with asymptomatic infections. To effectively improve the accuracy of doctors' manual judgment of positive and negative COVID-19, this paper proposes a deep classification network model of the novel coronavirus pneumonia based on convolution and deconvolution local enhancement. Through convolution and deconvolution operation, the contrast between the local lesion region and the abdominal cavity of COVID-19 is enhanced. Besides, the middle-level features that can effectively distinguish the image types are obtained. By transforming the novel coronavirus detection problem into the region of interest (ROI) feature classification problem, it can effectively determine whether the feature vector in each feature channel contains the image features of COVID-19. This paper uses an open-source COVID-CT dataset provided by Petuum researchers from the University of California, San Diego, which is collected from 143 novel coronavirus pneumonia patients and the corresponding features are preserved. The complete dataset (including original image and enhanced image) contains 1460 images. Among them, 1022 (70%) and 438 (30%) are used to train and test the performance of the proposed model, respectively. The proposed model verifies the classification precision in different convolution layers and learning rates. Besides, it is compared with most state-of-the-art models. It is found that the proposed algorithm has good classification performance. The corresponding sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), and precision are 0.98, 0.96, 0.98, and 0.97, respectively.
Keywords: COVID-19 classification network; Convolution; Deconvolution; Enhanced CT features; ROI extraction.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




Similar articles
-
NSCGCN: A novel deep GCN model to diagnosis COVID-19.Comput Biol Med. 2022 Nov;150:106151. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.106151. Epub 2022 Sep 30. Comput Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 36244303 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-RDNet: A novel coronavirus pneumonia classification model using the mixed dataset by CT and X-rays images.Biocybern Biomed Eng. 2022 Jul-Sep;42(3):977-994. doi: 10.1016/j.bbe.2022.07.009. Epub 2022 Aug 5. Biocybern Biomed Eng. 2022. PMID: 35945982 Free PMC article.
-
A Cascade-SEME network for COVID-19 detection in chest x-ray images.Med Phys. 2021 May;48(5):2337-2353. doi: 10.1002/mp.14711. Epub 2021 Mar 29. Med Phys. 2021. PMID: 33778966 Free PMC article.
-
UBNet: Deep learning-based approach for automatic X-ray image detection of pneumonia and COVID-19 patients.J Xray Sci Technol. 2022;30(1):57-71. doi: 10.3233/XST-211005. J Xray Sci Technol. 2022. PMID: 34864714
-
GACDN: generative adversarial feature completion and diagnosis network for COVID-19.BMC Med Imaging. 2021 Oct 21;21(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s12880-021-00681-6. BMC Med Imaging. 2021. PMID: 34674660 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Densely connected attention network for diagnosing COVID-19 based on chest CT.Comput Biol Med. 2021 Oct;137:104857. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104857. Epub 2021 Sep 9. Comput Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 34520988 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Machine Learning and Deep Learning Techniques for COVID-19 Screening Using Radiological Imaging: A Comprehensive Review.SN Comput Sci. 2023;4(1):65. doi: 10.1007/s42979-022-01464-8. Epub 2022 Nov 24. SN Comput Sci. 2023. PMID: 36467853 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kraemer Moritz U.G., Scarpino Samuel V., Vukosi Marivate, et al. Data curation during a pandemic and lessons learned from COVID-19. Nat. Comput. Sci. Jan. 2021;1(1):9–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

