Gut Bacteria of Rattus rattus (Rat) Produce Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial Lipopeptides
- PMID: 34056379
- PMCID: PMC8154139
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.1c01137
Gut Bacteria of Rattus rattus (Rat) Produce Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial Lipopeptides
Abstract
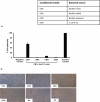
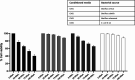
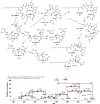
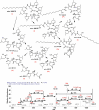
Among several animals, Rattus rattus (rat) lives in polluted environments and feeds on organic waste/small invertebrates, suggesting the presence of inherent mechanisms to thwart infections. In this study, we isolated gut bacteria of rats for their antibacterial activities. Using antibacterial assays, the findings showed that the conditioned media from selected bacteria exhibited bactericidal activities against Gram-negative (Escherichia coli K1, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Serratia marcescens, and Salmonella enterica) and Gram-positive (Bacillus cereus, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, and Streptococcus pyogenes) pathogenic bacteria. The conditioned media retained their antibacterial properties upon heat treatment at boiling temperature for 10 min. Using MTT assays, the conditioned media showed minimal cytotoxic effects against human keratinocyte cells. Active conditioned media were subjected to tandem mass spectrometry, and the results showed that conditioned media from Bacillus subtilis produced a large repertoire of surfactin and iturin A (lipopeptides) molecules. To our knowledge, this is the first report of isolation of lipopeptides from bacteria isolated from the rat gut. In short, these findings are important and provide a platform to develop effective antibacterial drugs.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Gut bacteria of Cuora amboinensis (turtle) produce broad-spectrum antibacterial molecules.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 18;9(1):17012. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-52738-w. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31740685 Free PMC article.
-
Gut bacteria of cockroaches are a potential source of antibacterial compound(s).Lett Appl Microbiol. 2018 May;66(5):416-426. doi: 10.1111/lam.12867. Epub 2018 Mar 25. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29457249
-
Gut Bacteria of Water Monitor Lizard (Varanus salvator) Are a Potential Source of Antibacterial Compound(s).Antibiotics (Basel). 2019 Sep 24;8(4):164. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics8040164. Antibiotics (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31554316 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Antibacterial Molecule(s) from Animals Living in Polluted Environments.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2020;21(5):425-437. doi: 10.2174/1389201020666191002153435. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 31577204
-
Tobramycin: a review of its antibacterial and pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic use.Drugs. 1976;12(3):166-200. doi: 10.2165/00003495-197612030-00002. Drugs. 1976. PMID: 789045 Review.
Cited by
-
Azole-based compounds as potential anti-Acanthamoeba agents.RSC Med Chem. 2024 Apr 3;15(5):1578-1588. doi: 10.1039/d4md00029c. eCollection 2024 May 22. RSC Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38784450
-
Antibacterial Properties of Ethacridine Lactate and Sulfmethoxazole Loaded Functionalized Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Apr 14;12(4):755. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12040755. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37107117 Free PMC article.
-
Moxifloxacin and Sulfamethoxazole-Based Nanocarriers Exhibit Potent Antibacterial Activities.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Aug 11;10(8):964. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10080964. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34439014 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Antiamoebic Tyrocidine-Derived Peptide against Brain-Eating Amoebae.ACS Omega. 2022 Aug 10;7(33):28797-28805. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c01614. eCollection 2022 Aug 23. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 36033708 Free PMC article.
-
Antiamoebic Activity of Imidazothiazole Derivatives against Opportunistic Pathogen Acanthamoeba castellanii.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Aug 31;11(9):1183. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11091183. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36139962 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Laxminarayan R.; Duse A.; Wattal C.; Zaidi A. K. M.; Wertheim H. F. L.; Sumpradit N.; Vlieghe E.; Hara G. L.; Gould I. M.; Goossens H.; Greko C.; So A. D.; Bigdeli M.; Tomson G.; Woodhouse W.; Ombaka E.; Peralta A. Q.; Qamar F. N.; Mir F.; Kariuki S.; Bhutta Z. A.; Coates A.; Bergstrom R.; Wright G. D.; BrowN E. D.; Cars O. Antibiotic resistance-the need for global solutions. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 1057–1098. 10.1016/S1473-3099(13)70318-9. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

