Antimicrobial Nanogels with Nanoinjection Capabilities for Delivery of the Hydrophobic Antibacterial Agent Triclosan
- PMID: 33345194
- PMCID: PMC7737311
- DOI: 10.1021/acsapm.0c01031
Antimicrobial Nanogels with Nanoinjection Capabilities for Delivery of the Hydrophobic Antibacterial Agent Triclosan
Abstract
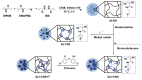
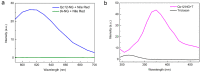
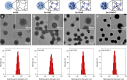
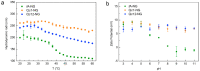
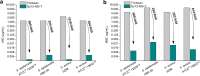
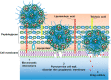
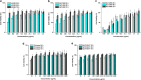
With the ever-growing problem of antibiotic resistance, developing antimicrobial strategies is urgently needed. Herein, a hydrophobic drug delivery nanocarrier is developed for combating planktonic bacteria that enhances the efficiency of the hydrophobic antimicrobial agent, Triclosan, up to a 1000 times. The poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]methacrylamide), p(NIPAM-co-DMAPMA), based nanogel is prepared via a one-pot precipitation polymerization, followed by quaternization with 1-bromododecane to form hydrophobic domains inside the nanogel network through intraparticle self-assembly of the aliphatic chains (C12). Triclosan, as the model hydrophobic antimicrobial drug, is loaded within the hydrophobic domains inside the nanogel. The nanogel can adhere to the bacterial cell wall via electrostatic interactions and induce membrane destruction via the insertion of the aliphatic chains into the cell membrane. The hydrophobic antimicrobial Triclosan can be actively injected into the cell through the destroyed membrane. This approach dramatically increases the effective concentration of Triclosan at the bacterial site. Both the minimal inhibitory concentration and minimal bactericidal concentration against the Gram-positive bacteria S. aureus and S. epidermidis decreased 3 orders of magnitude, compared to free Triclosan. The synergy of physical destruction and active nanoinjection significantly enhances the antimicrobial efficacy, and the designed nanoinjection delivery system holds great promise for combating antimicrobial resistance as well as the applications of hydrophobic drugs delivery for many other possible applications.
© 2020 American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): P.v.R also is co-founder, scientific advisor, and share-holder of BiomACS BV, a biomedical oriented screening company.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Highly Efficient Antimicrobial and Antifouling Surface Coatings with Triclosan-Loaded Nanogels.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020 Dec 30;12(52):57721-57731. doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c18172. Epub 2020 Dec 15. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020. PMID: 33320528 Free PMC article.
-
Triclosan-loaded pH-responsive copolymer to target bacteria and to have long bacteriostatic efficacy.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2020 May 30;148:105320. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2020.105320. Epub 2020 Mar 31. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2020. PMID: 32240797
-
Optimization of Cationic Nanogel PEGylation to Achieve Mammalian Cytocompatibility with Limited Loss of Gram-Negative Bactericidal Activity.Biomacromolecules. 2020 Apr 13;21(4):1528-1538. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.0c00081. Epub 2020 Apr 2. Biomacromolecules. 2020. PMID: 32207917
-
Strategies for new antimicrobial proteins and peptides: lysozyme and aprotinin as model molecules.Curr Pharm Des. 2002;8(9):671-93. doi: 10.2174/1381612023395349. Curr Pharm Des. 2002. PMID: 11945164 Review.
-
Triclosan and antimicrobial resistance in bacteria: an overview.Microb Drug Resist. 2006 Summer;12(2):83-90. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2006.12.83. Microb Drug Resist. 2006. PMID: 16922622 Review.
Cited by
-
β-Cyclodextrin/Triclosan Complex-Grafted Methacrylated Glycol Chitosan Hydorgel by Photocrosslinking via Visible Light Irradiation for a Tissue Bio-Adhesive.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 12;22(2):700. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020700. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33445775 Free PMC article.
-
A novel chitosan-based doxepin nano-formulation for chemotherapy-induced oral mucositis: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trial.Inflammopharmacology. 2023 Oct;31(5):2411-2420. doi: 10.1007/s10787-023-01325-7. Epub 2023 Sep 5. Inflammopharmacology. 2023. PMID: 37668810 Clinical Trial.
-
Antimicrobial and Antiviral Properties of Triclosan-Containing Polymer Composite: Aging Effects of pH, UV, and Sunlight Exposure.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Feb 28;15(5):1236. doi: 10.3390/polym15051236. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36904477 Free PMC article.
-
UV-Triggered Drug Release from Mesoporous Titanium Nanoparticles Loaded with Berberine Hydrochloride: Enhanced Antibacterial Activity.Molecules. 2024 Apr 3;29(7):1607. doi: 10.3390/molecules29071607. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38611885 Free PMC article.
-
Highly Efficient Antimicrobial and Antifouling Surface Coatings with Triclosan-Loaded Nanogels.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020 Dec 30;12(52):57721-57731. doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c18172. Epub 2020 Dec 15. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020. PMID: 33320528 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

