Mapping breast cancer journal publications in conflict settings in the MENA region: a scoping review
- PMID: 33209120
- PMCID: PMC7652545
- DOI: 10.3332/ecancer.2020.1129
Mapping breast cancer journal publications in conflict settings in the MENA region: a scoping review
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer is a major cause of cancer-related morbidity and mortality among women in the the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region. Conflict and political instability in the region may affect medical research output, including that on breast cancer. This scoping review aims to systematically identify and map breast cancer publications across different stages of the cancer care pathway and across conflict-affected countries within the MENA region. The findings of this work will highlight the impact of conflict on cancer research that could be mitigated with the proper contextualised capacity strengthening intervention.
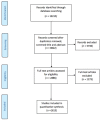
Methods: We followed the PRISMA-Scr methodology. We searched for peer-reviewed publications on topics related to breast cancer in 11 databases: Medline, PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science, PROQUEST, CINAHL, Global Index Medicus, Arab World Searches Complete, Popline, Scopus and Google Scholar using both controlled vocabulary and keywords. Publication abstracts and full-text versions were screened for duplicates and included in our study based on pre-specified eligibility criteria: focused on breast cancer, related to the specific country of analysis and human or health system studies. We used a structured data extraction form to extract information related to the article, its methodology and the cancer care pathway being studied.
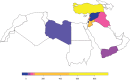
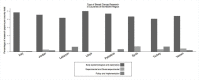
Results: A total of 19,215 citations were retrieved from our search. After removing duplicates, a total of 8,622 articles remained. Title and abstract screening retained 1,613 articles. Publications with first author affiliations to Turkey were consistently the highest across all categories of the cancer care pathway. Trends show an increase in articles from Lebanon, Jordan and Palestine after 2015. Early exploratory and epidemiological studies represented the majority of breast cancer research, followed by policy and implementation research and lastly experimental research. Most research conducted followed an observational study design. Important gaps were identified in the research output related to advanced breast cancer and palliative care (Libya, Syria and Yemen), mental health (Libya), and knowledge and education of breast cancer (Libya and Syria).
Conclusion: This scoping review has identified key areas in breast cancer research that lack significant research activity in conflict MENA settings. These areas, including but are not limited to palliative care, mental health, and education, can be prioritised and developed through regional collaboration and contextualised capacity strengthening initiatives.
Keywords: breast cancer; conflict; research capacity.
© the authors; licensee ecancermedicalscience.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ethics of Procuring and Using Organs or Tissue from Infants and Newborns for Transplantation, Research, or Commercial Purposes: Protocol for a Bioethics Scoping Review.Wellcome Open Res. 2024 Dec 5;9:717. doi: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.23235.1. eCollection 2024. Wellcome Open Res. 2024. PMID: 39839977 Free PMC article.
-
A model to enhance breast cancer screening among rural women aged 40-75 years in Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA): A scoping review.J Med Imaging Radiat Sci. 2024 Mar;55(1):109-124. doi: 10.1016/j.jmir.2023.12.003. Epub 2023 Dec 30. J Med Imaging Radiat Sci. 2024. PMID: 38161135
-
Defining the optimum strategy for identifying adults and children with coeliac disease: systematic review and economic modelling.Health Technol Assess. 2022 Oct;26(44):1-310. doi: 10.3310/ZUCE8371. Health Technol Assess. 2022. PMID: 36321689 Free PMC article.
-
Falls prevention interventions for community-dwelling older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of benefits, harms, and patient values and preferences.Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 26;13(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02681-3. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39593159 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions to increase COVID-19 vaccine uptake: a scoping review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Aug 3;8(8):CD015270. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015270. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35920693 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prostate cancer in the Arab world: Bibliometric review and research priority recommendations.Arab J Urol. 2022 Jan 23;20(2):81-87. doi: 10.1080/2090598X.2021.2024984. eCollection 2022. Arab J Urol. 2022. PMID: 35530565 Free PMC article.
-
The challenges of international collaboration in conflict and health research: experience from the Research for Health in Conflict-Middle East and North Africa (R4HC-MENA) partnership.Confl Health. 2023 Jun 14;17(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s13031-023-00527-8. Confl Health. 2023. PMID: 37316903 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreatic cancer in the MENA region, a bibliometric review.Ecancermedicalscience. 2022 Apr 29;16:1380. doi: 10.3332/ecancer.2022.1380. eCollection 2022. Ecancermedicalscience. 2022. PMID: 35702406 Free PMC article.
References
-
- States LoA. Member States. [ https://arab.org/directory/league-of-arab-states/]
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
