A Genomic Survey of Signalling in the Myxococcaceae
- PMID: 33171896
- PMCID: PMC7694542
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms8111739
A Genomic Survey of Signalling in the Myxococcaceae
Abstract
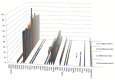
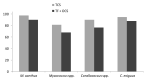
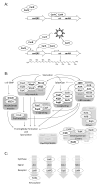
As prokaryotes diverge by evolution, essential 'core' genes required for conserved phenotypes are preferentially retained, while inessential 'accessory' genes are lost or diversify. We used the recently expanded number of myxobacterial genome sequences to investigate the conservation of their signalling proteins, focusing on two sister genera (Myxococcus and Corallococcus), and on a species within each genus (Myxococcus xanthus and Corallococcus exiguus). Four new C. exiguus genome sequences are also described here. Despite accessory genes accounting for substantial proportions of each myxobacterial genome, signalling proteins were found to be enriched in the core genome, with two-component system genes almost exclusively so. We also investigated the conservation of signalling proteins in three myxobacterial behaviours. The linear carotenogenesis pathway was entirely conserved, with no gene gain/loss observed. However, the modular fruiting body formation network was found to be evolutionarily plastic, with dispensable components in all modules (including components required for fruiting in the model myxobacterium M. xanthus DK1622). Quorum signalling (QS) is thought to be absent from most myxobacteria, however, they generally appear to be able to produce CAI-I (cholerae autoinducer-1), to sense other QS molecules, and to disrupt the QS of other organisms, potentially important abilities during predation of other prokaryotes.
Keywords: Myxococcales; carotenoids; comparative genomics; development; fruiting body formation; myxobacteria; one-component systems; quorum signalling; two-component systems.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Myxobacterial Genomics and Post-Genomics: A Review of Genome Biology, Genome Sequences and Related 'Omics Studies.Microorganisms. 2021 Oct 13;9(10):2143. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9102143. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34683464 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Genomics and Pan-Genomics of the Myxococcaceae, including a Description of Five Novel Species: Myxococcus eversor sp. nov., Myxococcus llanfairpwllgwyngyllgogerychwyrndrobwllllantysiliogogogochensis sp. nov., Myxococcus vastator sp. nov., Pyxidicoccus caerfyrddinensis sp. nov., and Pyxidicoccus trucidator sp. nov.Genome Biol Evol. 2020 Dec 6;12(12):2289-2302. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evaa212. Genome Biol Evol. 2020. PMID: 33022031 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Evolutionary Relationships for Prioritization of Myxobacteria for Natural Product Discovery.Microorganisms. 2021 Jun 24;9(7):1376. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9071376. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34202719 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Genomics of Myxobacterial Chemosensory Systems.J Bacteriol. 2018 Jan 10;200(3):e00620-17. doi: 10.1128/JB.00620-17. Print 2018 Feb 1. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 29158239 Free PMC article.
-
Myxobacterial vesicles death at a distance?Adv Appl Microbiol. 2011;75:1-31. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-387046-9.00001-3. Adv Appl Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21807244 Review.
Cited by
-
Phylogenomic Analysis Substantiates the gyrB Gene as a Powerful Molecular Marker to Efficiently Differentiate the Most Closely Related Genera Myxococcus, Corallococcus, and Pyxidicoccus.Front Microbiol. 2021 Oct 11;12:763359. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.763359. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34707598 Free PMC article.
-
Myxobacterial Genomics and Post-Genomics: A Review of Genome Biology, Genome Sequences and Related 'Omics Studies.Microorganisms. 2021 Oct 13;9(10):2143. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9102143. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34683464 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lysis profile and preference of Myxococcus sp. PT13 for typical soil bacteria.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jun 12;14:1211756. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1211756. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37378286 Free PMC article.
-
MyxoPortal: a database of myxobacterial genomic features.Database (Oxford). 2024 Jul 2;2024:baae056. doi: 10.1093/database/baae056. Database (Oxford). 2024. PMID: 38958433 Free PMC article.
-
Genomes of Novel Myxococcota Reveal Severely Curtailed Machineries for Predation and Cellular Differentiation.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2021 Nov 10;87(23):e0170621. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01706-21. Epub 2021 Sep 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34524899 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

