Marine-Derived Surface Active Agents: Health-Promoting Properties and Blue Biotechnology-Based Applications
- PMID: 32526944
- PMCID: PMC7355491
- DOI: 10.3390/biom10060885
Marine-Derived Surface Active Agents: Health-Promoting Properties and Blue Biotechnology-Based Applications
Abstract
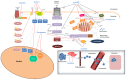
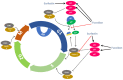
Surface active agents are characterized for their capacity to adsorb to fluid and solid-water interfaces. They can be classified as surfactants and emulsifiers based on their molecular weight (MW) and properties. Over the years, the chemical surfactant industry has been rapidly increasing to meet consumer demands. Consequently, such a boost has led to the search for more sustainable and biodegradable alternatives, as chemical surfactants are non-biodegradable, thus causing an adverse effect on the environment. To these ends, many microbial and/or marine-derived molecules have been shown to possess various biological properties that could allow manufacturers to make additional health-promoting claims for their products. Our aim, in this review article, is to provide up to date information of critical health-promoting properties of these molecules and their use in blue-based biotechnology (i.e., biotechnology using aquatic organisms) with a focus on food, cosmetic and pharmaceutical/biomedical applications.
Keywords: anti-aging; anti-cancer; anti-inflammatory; anti-microbial; anti-oxidant; anti-viral; biosurfactants; blue biotechnology; surface active agents.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Surface Active Agents and Their Health-Promoting Properties: Molecules of Multifunctional Significance.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Jul 21;12(7):688. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12070688. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 32708243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microbial Biosurfactant as an Alternate to Chemical Surfactants for Application in Cosmetics Industries in Personal and Skin Care Products: A Critical Review.Biomed Res Int. 2023 Apr 13;2023:2375223. doi: 10.1155/2023/2375223. eCollection 2023. Biomed Res Int. 2023. PMID: 37090190 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microbial biosurfactants production, applications and future potential.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010 Jun;87(2):427-44. doi: 10.1007/s00253-010-2589-0. Epub 2010 Apr 28. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20424836 Review.
-
Surfactants in microbiology and biotechnology: Part 2. Application aspects.Biotechnol Adv. 2007 Jan-Feb;25(1):99-121. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2006.10.004. Epub 2006 Oct 28. Biotechnol Adv. 2007. PMID: 17156965 Review.
-
An update on the use of unconventional substrates for biosurfactant production and their new applications.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2002 Mar;58(4):428-34. doi: 10.1007/s00253-001-0924-1. Epub 2002 Jan 26. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2002. PMID: 11954787 Review.
Cited by
-
Toxicity Profiling of Biosurfactants Produced by Novel Marine Bacterial Strains.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 27;22(5):2383. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052383. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33673549 Free PMC article.
-
Marine Microbial-Derived Antibiotics and Biosurfactants as Potential New Agents against Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infections.Mar Drugs. 2021 Apr 29;19(5):255. doi: 10.3390/md19050255. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 33946845 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive review on the potential of ultrasound for blue food protein extraction, modification and impact on bioactive properties.Ultrason Sonochem. 2024 Dec;111:107087. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2024.107087. Epub 2024 Sep 27. Ultrason Sonochem. 2024. PMID: 39362033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Potential of Using Marine-Derived Ingredients: From the Extraction to Cutting-Edge Cosmetics.Mar Drugs. 2023 Nov 29;21(12):620. doi: 10.3390/md21120620. Mar Drugs. 2023. PMID: 38132941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Surface-Active Compounds Produced by Microorganisms: Promising Molecules for the Development of Antimicrobial, Anti-Inflammatory, and Healing Agents.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Aug 16;11(8):1106. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11081106. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36009975 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amaral P.F., Coelho M.A.Z., Marrucho I.M., Coutinho J.A. Biosurfactants from yeasts: Characteristics, production and application. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2010;672:236–249. - PubMed
-
- De S., Malik S., Ghosh A., Saha R., Saha B. A review on natural surfactants. RSC Adv. 2015;5:65757–65767. doi: 10.1039/C5RA11101C. - DOI
-
- Sriram M.I., Gayathiri S., Gnanaselvi U., Jenifer P.S., Raj S.M., Gurunathan S. Novel lipopeptide biosurfactant produced by hydrocarbon degrading and heavy metal tolerant bacterium Escherichia fergusonii KLU01 as a potential tool for bioremediation. Bioresour. Technol. 2011;102:9291–9295. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2011.06.094. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

