Evaluating the research domain and achievement for a productive researcher who published 114 sole-author articles: A bibliometric analysis
- PMID: 32481321
- PMCID: PMC7249850
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000020334
Evaluating the research domain and achievement for a productive researcher who published 114 sole-author articles: A bibliometric analysis
Abstract
Background: Team science research includes authors from various fields collaborating to publish their work on certain topics. Despite the numerous papers that discussed the ordering of author names and the contributions of authors to an article, no paper evaluatedIn addition, few researchers publish academic articles without co-author collaboration. Whether the bibliometric indexes (eg, h-/x-index) of sole-author researchers are higher than those of other types of multiple authors is required for comparison. We aimed to evaluate a productive author who published 114 sole-author articles with exceptional RA and RD in academics.
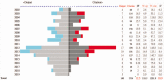
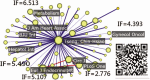
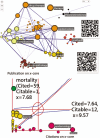
Methods: By searching the PubMed database (Pubmed.com), we used the keyword of (Taiwan[affiliation]) from 2016 to 2017 and downloaded 29,356 articles. One physician (Dr. Tseng from the field of Internal Medicine) who published 12 articles as a single author was selected. His articles and citations were searched in PubMed. A comparison of various types of author ordering placements was conducted using sensitivity analysis to inspect whether this sole author earns the highest metrics in RA. Social network analysis (SNA), Gini coefficient (GC), pyramid plot, and the Kano diagram were applied to gather the following data for visualization: RESULTS:: We observed that CONCLUSIONS:: The metrics on RA are high for the sole author studied. The author's RD can be denoted by the MeSH terms and measured by the GC. The author-weighted scheme is required for quantifying author credits in an article to evaluate the author's RA. Social network analysis incorporating the Kano diagrams provided insights into the relationships between actors (eg, coauthors, MeSH terms, or journals). The methods used in this study can be replicated to evaluate other productive studies on RA and RD in the future.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Defining the optimum strategy for identifying adults and children with coeliac disease: systematic review and economic modelling.Health Technol Assess. 2022 Oct;26(44):1-310. doi: 10.3310/ZUCE8371. Health Technol Assess. 2022. PMID: 36321689 Free PMC article.
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
The effectiveness of abstinence-based and harm reduction-based interventions in reducing problematic substance use in adults who are experiencing homelessness in high income countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2024 Apr 21;20(2):e1396. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1396. eCollection 2024 Jun. Campbell Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38645303 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ceftazidime with avibactam for treating severe aerobic Gram-negative bacterial infections: technology evaluation to inform a novel subscription-style payment model.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(73):1-230. doi: 10.3310/YAPL9347. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39487661 Free PMC article.
-
Falls prevention interventions for community-dwelling older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of benefits, harms, and patient values and preferences.Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 26;13(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02681-3. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39593159 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A leading bibliometric author does not have a dominant contribution to research based on the CJAL score: Bibliometric analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Jan 13;102(2):e32609. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032609. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 36637941 Free PMC article.
-
Authors who contributed most to the fields of hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis since 2011 using the hT-index: Bibliometric analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Sep 23;101(38):e30375. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000030375. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36197241 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccination associated with gross domestic product and fewer deaths in countries and regions: A verification study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Jan 28;101(4):e28619. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000028619. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 35089198 Free PMC article.
-
Using the Sankey diagram to visualize article features on the topics of whole-exome sequencing (WES) and whole-genome sequencing (WGS) since 2012: Bibliometric analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Sep 23;101(38):e30682. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000030682. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36197161 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of Canadian-produced research on the global orthopedic literature: a bibliometric analysis.Can J Surg. 2023 Dec 6;66(6):E583-E595. doi: 10.1503/cjs.007022. Print 2023 Nov-Dec. Can J Surg. 2023. PMID: 38056902 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Psychological Association. Playing for “Team Science”: Tips for students. 2019/11/21 Available at https://www.apa.org/science/about/psa/2013/04/team-science.
-
- Egghe L. Theory and practise of the g-index. Scientometrics 2006;69:131–52.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

