Production of Mannosylerythritol Lipids (MELs) to be Used as Antimicrobial Agents Against S. aureus ATCC 6538
- PMID: 32123984
- PMCID: PMC7334285
- DOI: 10.1007/s00284-020-01927-2
Production of Mannosylerythritol Lipids (MELs) to be Used as Antimicrobial Agents Against S. aureus ATCC 6538
Abstract
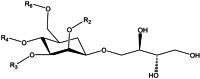
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a current major health issue, both for the high rates of resistance observed in bacteria that cause common infections and for the complexity of the consequences of AMR. Pathogens like Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Mycobacterium tuberculosis among others are clear examples of antibiotic-resistant threats. Biosurfactants have recently emerged as a potential new generation of anti-adhesive and anti-biofilm agents; mannosylerythritol lipids (MELs) are biosurfactants produced by a range of fungi. A range of structural variants of MELs can be formed and the proportion of each isomer in the fermentation depends on the yeast used, the carbon substrate used for growth and the duration of the fermentation. In order to allow assessment of the possible functions of MELs as antimicrobial molecules, small quantities of MEL were produced by controlled fermentation. Fermentations of the yeast Pseudozyma aphidis using rapeseed oil as a carbon source yielded up to 165 gMELs/kgSubstrate. The MELs formed by this strain was a mixture of MEL-A, MEL-B, MEL-C and MEL-D. The MELs produced were tested against S. aureus ATCC 6538 on pre-formed biofilm and on co-incubation biofilm experiments on silicone discs; showing a disruption of biomass, reduction of the biofilm metabolic activity and a bacteriostatic/bactericidal effect confirmed by a release of oxygen uptake [Formula: see text], the reduction of citrate synthase activity and scanning electron microscopy. The results show that MELs are promising antimicrobial molecules for biomedical technological applications that could be studied in detail in large-scale systems and in conjunction with animal tissue models.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mannosylerythritol lipids: dual inhibitory modes against Staphylococcus aureus through membrane-mediated apoptosis and biofilm disruption.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Jun;104(11):5053-5064. doi: 10.1007/s00253-020-10561-8. Epub 2020 Apr 4. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32248439
-
Enhanced separation and analysis procedure reveals production of tri-acylated mannosylerythritol lipids by Pseudozyma aphidis.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016 Nov;43(11):1537-1550. doi: 10.1007/s10295-016-1838-3. Epub 2016 Sep 22. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27659961
-
Structural characterization and surface-active properties of a new glycolipid biosurfactant, mono-acylated mannosylerythritol lipid, produced from glucose by Pseudozyma antarctica.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007 Sep;76(4):801-10. doi: 10.1007/s00253-007-1051-4. Epub 2007 Jul 3. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007. PMID: 17607573
-
Mannosylerythritol lipids: production and applications.J Oleo Sci. 2015;64(2):133-41. doi: 10.5650/jos.ess14185. Epub 2015 Jan 20. J Oleo Sci. 2015. PMID: 25748373 Review.
-
Tailor-made mannosylerythritol lipids: current state and perspectives.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 Aug;102(16):6877-6884. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-9160-9. Epub 2018 Jun 20. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29926140 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances in Biomedical, Therapeutic and Pharmaceutical Applications of Microbial Surfactants.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Mar 30;13(4):466. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13040466. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 33808361 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Surface-Active Compounds Produced by Microorganisms: Promising Molecules for the Development of Antimicrobial, Anti-Inflammatory, and Healing Agents.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Aug 16;11(8):1106. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11081106. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36009975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipase-Catalyzed Production of Sorbitol Laurate in a "2-in-1" Deep Eutectic System: Factors Affecting the Synthesis and Scalability.Molecules. 2021 May 7;26(9):2759. doi: 10.3390/molecules26092759. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34067126 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial Biosurfactants: Antimicrobial Activity and Potential Biomedical and Therapeutic Exploits.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jan 22;17(1):138. doi: 10.3390/ph17010138. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38276011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Promising Application, Efficient Production, and Genetic Basis of Mannosylerythritol Lipids.Biomolecules. 2024 May 5;14(5):557. doi: 10.3390/biom14050557. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38785964 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

