A Cyclic-di-GMP signalling network regulates biofilm formation and surface associated motility of Acinetobacter baumannii 17978
- PMID: 32029764
- PMCID: PMC7005169
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-58522-5
A Cyclic-di-GMP signalling network regulates biofilm formation and surface associated motility of Acinetobacter baumannii 17978
Abstract
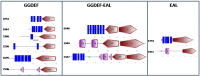
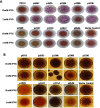
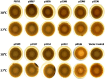
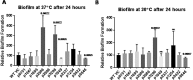
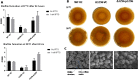
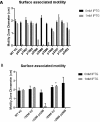
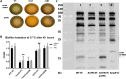
Acinetobacter baumannii has emerged as an increasing multidrug-resistant threat in hospitals and a common opportunistic nosocomial pathogen worldwide. However, molecular details of the pathogenesis and physiology of this bacterium largely remain to be elucidated. Here we identify and characterize the c-di-GMP signalling network and assess its role in biofilm formation and surface associated motility. Bioinformatic analysis revealed eleven candidate genes for c-di-GMP metabolizing proteins (GGDEF/EAL domain proteins) in the genome of A. baumannii strain 17978. Enzymatic activity of the encoded proteins was assessed by molecular cloning and expression in the model organisms Salmonella typhimurium and Vibrio cholerae. Ten of the eleven GGDEF/EAL proteins altered the rdar morphotype of S. typhimurium and the rugose morphotype of V. cholerae. The over expression of three GGDEF proteins exerted a pronounced effect on colony formation of A. baumannii on Congo Red agar plates. Distinct panels of GGDEF/EAL proteins were found to alter biofilm formation and surface associated motility of A. baumannii upon over expression. The GGDEF protein A1S_3296 appeared as a major diguanylate cyclase regulating macro-colony formation, biofilm formation and the surface associated motility. AIS_3296 promotes Csu pili mediated biofilm formation. We conclude that a functional c-di-GMP signalling network in A. baumannii regulates biofilm formation and surface associated motility of this increasingly important opportunistic bacterial pathogen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Detailed analysis of c-di-GMP mediated regulation of csgD expression in Salmonella typhimurium.BMC Microbiol. 2017 Feb 2;17(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12866-017-0934-5. BMC Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28148244 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of biofilm-formation in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium by the periplasmic DsbA/DsbB oxidoreductase system requires the GGDEF-EAL domain protein STM3615.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 25;9(8):e106095. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0106095. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25153529 Free PMC article.
-
Hierarchical involvement of various GGDEF domain proteins in rdar morphotype development of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Mol Microbiol. 2006 May;60(3):602-16. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05123.x. Mol Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16629664
-
Diguanylate Cyclases in Vibrio cholerae: Essential Regulators of Lifestyle Switching.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Oct 22;10:582947. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.582947. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33194821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting cyclic di-GMP signalling: a strategy to control biofilm formation?Curr Pharm Des. 2015;21(1):12-24. doi: 10.2174/1381612820666140905124701. Curr Pharm Des. 2015. PMID: 25189859 Review.
Cited by
-
What makes another life possible in bacteria? Global regulators as architects of bacterial biofilms.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Oct 14;38(12):236. doi: 10.1007/s11274-022-03376-4. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36229744 Review.
-
Mechanisms Protecting Acinetobacter baumannii against Multiple Stresses Triggered by the Host Immune Response, Antibiotics and Outside-Host Environment.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 31;21(15):5498. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155498. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32752093 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of Quorum Sensing and Biofilms in Less Investigated Gram-Negative ESKAPE Pathogens.Front Microbiol. 2021 Jul 29;12:676510. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.676510. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34394026 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Temporal Transcriptomics of Gut Escherichia coli in Caenorhabditis elegans Models of Aging.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Oct 31;9(2):e0049821. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00498-21. Epub 2021 Sep 15. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34523995 Free PMC article.
-
Design of novel hybrid secondary metabolite targets to diguanylate cyclase of Acinetobacter baumannii.FEMS Microbes. 2021 Nov 22;2:xtab017. doi: 10.1093/femsmc/xtab017. eCollection 2021. FEMS Microbes. 2021. PMID: 37334229 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

